Embracing gender diversity leads to richer perspectives and more innovative solutions in organizations. Fostering an inclusive environment where all genders are valued enhances collaboration and drives better business outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for promoting gender diversity in your workplace.
Table of Comparison
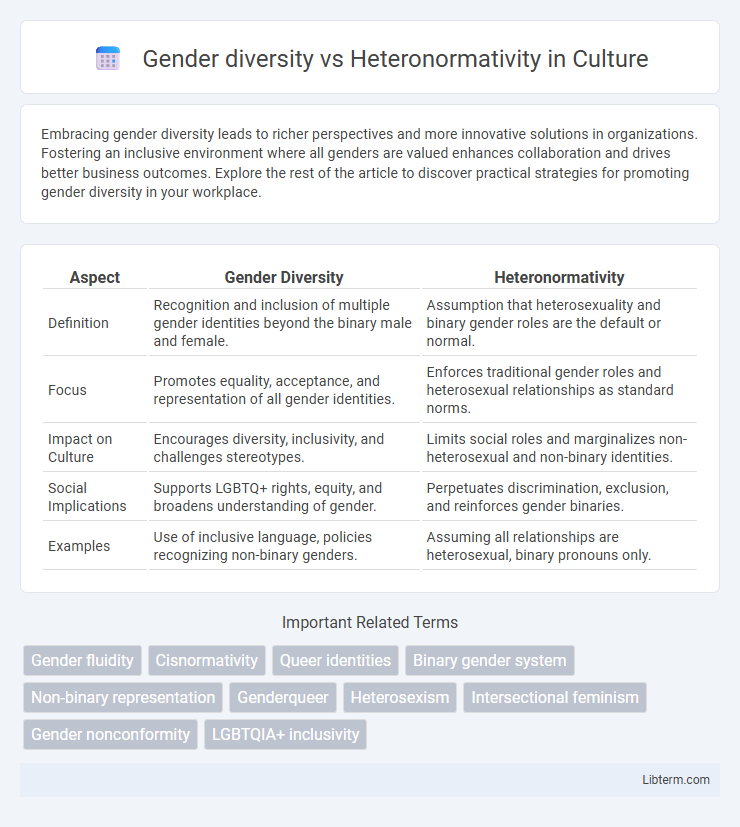
| Aspect | Gender Diversity | Heteronormativity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognition and inclusion of multiple gender identities beyond the binary male and female. | Assumption that heterosexuality and binary gender roles are the default or normal. |
| Focus | Promotes equality, acceptance, and representation of all gender identities. | Enforces traditional gender roles and heterosexual relationships as standard norms. |
| Impact on Culture | Encourages diversity, inclusivity, and challenges stereotypes. | Limits social roles and marginalizes non-heterosexual and non-binary identities. |
| Social Implications | Supports LGBTQ+ rights, equity, and broadens understanding of gender. | Perpetuates discrimination, exclusion, and reinforces gender binaries. |
| Examples | Use of inclusive language, policies recognizing non-binary genders. | Assuming all relationships are heterosexual, binary pronouns only. |
Understanding Gender Diversity: Beyond Binary Definitions
Gender diversity encompasses a spectrum of identities beyond the traditional binary of male and female, recognizing non-binary, genderqueer, and transgender experiences. Heteronormativity, which assumes heterosexual orientation and binary gender roles as the norm, often marginalizes these identities, limiting social inclusion and understanding. Embracing gender diversity challenges cultural norms and promotes a more inclusive and accurate recognition of human experience.
Heteronormativity Explained: Origins and Impact
Heteronormativity, rooted in traditional social norms, assumes heterosexuality as the default sexual orientation and enforces binary gender roles. This framework marginalizes gender diversity by invalidating non-heterosexual identities and reinforcing systemic inequalities in social, legal, and cultural institutions. Understanding heteronormativity's origins in historical power structures highlights its ongoing impact on limiting inclusivity and visibility for LGBTQ+ individuals.
The Spectrum of Gender Identities
The spectrum of gender identities challenges the traditional heteronormativity framework by recognizing a wide range of expressions beyond the binary male-female division. Gender diversity includes identities such as non-binary, genderqueer, genderfluid, agender, and Two-Spirit, reflecting complex cultural and individual experiences. Embracing this diversity promotes inclusivity and better understanding within social, legal, and workplace environments.
Social Constructs: How Heteronormativity Shapes Society
Heteronormativity shapes society by establishing rigid binaries that prioritize heterosexual relationships and traditional gender roles, marginalizing diverse gender identities and sexual orientations. This social construct influences institutions, media representations, and everyday interactions, reinforcing norms that exclude non-conforming individuals. Challenging heteronormativity requires recognizing and validating gender diversity as essential to fostering inclusive and equitable social environments.
Challenges Faced by Gender Diverse Individuals
Gender diverse individuals frequently encounter systemic barriers rooted in heteronormativity, including limited legal protections and social stigmatization. These challenges manifest in healthcare disparities, workplace discrimination, and increased vulnerability to mental health issues due to lack of acceptance and understanding. Overcoming these obstacles requires inclusive policies and education that affirm diverse gender identities beyond traditional heteronormative frameworks.
The Role of Media in Reinforcing Heteronormativity
Media outlets often perpetuate heteronormativity by predominantly portraying heterosexual relationships as the societal norm, overshadowing diverse gender identities and expressions. Television shows, films, and advertisements frequently reinforce binary gender roles and exclude non-cisgender narratives, limiting public awareness and acceptance. This consistent representation marginalizes gender diversity and sustains societal expectations aligned with heteronormative ideals.
Education and Awareness: Breaking Gender Stereotypes
Education and awareness programs play a crucial role in breaking gender stereotypes by challenging heteronormative assumptions embedded in traditional curricula. Incorporating diverse gender identities and expressions into educational content fosters inclusivity, promotes empathy, and empowers students to embrace gender diversity. Research shows that schools implementing comprehensive gender diversity education report reduced bullying and increased acceptance among students.
Legal Rights and Protections for Gender Diversity
Legal rights and protections for gender diversity challenge heteronormative frameworks by recognizing non-binary and transgender identities in policies such as anti-discrimination laws and gender marker changes on official documents. Countries advancing gender diversity legally provide protections against workplace discrimination, healthcare access rights, and recognition of diverse family structures. Strengthening these legal frameworks promotes equal treatment, reduces social stigma, and fosters inclusive environments for gender-diverse individuals globally.
Toward Inclusive Communities: Fostering Gender Acceptance
Fostering gender acceptance requires actively challenging heteronormativity, which assumes heterosexuality as the default and marginalizes diverse gender identities. Inclusive communities implement policies and practices that recognize and respect a spectrum of gender expressions, promoting equality and reducing discrimination. Emphasizing education, representation, and safe spaces contributes to creating environments where all individuals feel valued and supported.
Embracing Diversity: Strategies to Counter Heteronormativity
Embracing gender diversity requires implementing inclusive policies that recognize and validate non-binary, transgender, and gender-nonconforming identities to counter heteronormativity's limitations. Educational programs promoting awareness and sensitivity around diverse gender expressions foster an environment that challenges traditional gender binaries and heteronormative assumptions. Creating safe spaces and support networks within organizations further enhances acceptance and equal representation, empowering individuals to express their authentic identities freely.
Gender diversity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com