Rituality enhances daily life by infusing ordinary actions with meaning and intention, creating a sense of connection and purpose. Engaging in rituals can reduce stress, improve focus, and foster a deeper awareness of the present moment. Discover how embracing rituality can transform your routines and enrich your well-being by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
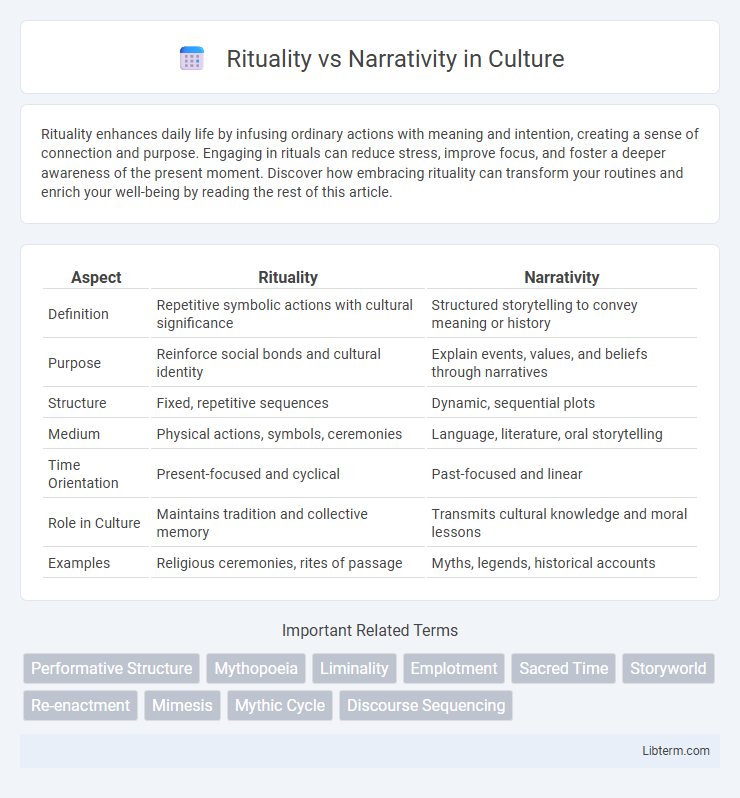
| Aspect | Rituality | Narrativity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetitive symbolic actions with cultural significance | Structured storytelling to convey meaning or history |
| Purpose | Reinforce social bonds and cultural identity | Explain events, values, and beliefs through narratives |
| Structure | Fixed, repetitive sequences | Dynamic, sequential plots |
| Medium | Physical actions, symbols, ceremonies | Language, literature, oral storytelling |
| Time Orientation | Present-focused and cyclical | Past-focused and linear |
| Role in Culture | Maintains tradition and collective memory | Transmits cultural knowledge and moral lessons |
| Examples | Religious ceremonies, rites of passage | Myths, legends, historical accounts |
Understanding Rituality: Definitions and Origins
Rituality refers to the structured and repetitive actions performed in specific cultural or religious contexts, embodying collective beliefs and social cohesion. Rooted in anthropological studies, its origins trace back to early human societies where rituals functioned to reinforce group identity and convey symbolic meanings. Understanding rituality involves examining these patterned behaviors as integral to social rituals that transcend mere habit, reflecting deep-rooted cultural narratives and shared values.
The Core Elements of Narrativity
Narrativity centers on core elements such as characters, events, and a structured storyline that conveys meaning through temporal and causal relationships, distinguishing it from rituality's repetitive and symbolic actions. Essential components include a clearly developed plot, conflict, and resolution, which enable the audience to engage in interpretation and emotional connection. This narrative framework allows stories to communicate complex human experiences, shaping cultural identity and individual understanding.
Rituality and Narrativity: Key Differences
Rituality emphasizes repetitive, symbolic actions that reinforce cultural or social values, often performed collectively with a focus on tradition and cohesion. Narrativity centers on storytelling, structuring information or experiences into a coherent sequence with characters, events, and causality to convey meaning or lessons. The key difference lies in rituality's embodiment through practice and communal participation, while narrativity is expressed through narrative frameworks that organize experiences temporally and thematically.
The Interplay Between Ritual and Narrative Structures
Rituality and narrativity intertwine through the structured repetition and symbolic actions of rituals that convey cultural narratives, embedding collective memories into performative acts. Narrative structures provide a coherent framework for interpreting these rituals, transforming symbolic gestures into meaningful stories that reinforce identity and shared values. This dynamic interplay allows rituals to function as living narratives, continuously shaping and reshaping communal understanding.
Historical Evolution of Ritual and Narrative Forms
Rituality and narrativity represent distinct yet intertwined modes of human expression, with rituality rooted in repetitive, symbolic actions that reinforce social cohesion and collective identity, while narrativity centers on structured storytelling that conveys meaning and preserves cultural memory. Historical evolution reveals that early human societies relied heavily on ritual practices for religious ceremonies and communal rites, which gradually incorporated narrative elements to explain origins, moral codes, and cosmologies. Over time, narrative forms expanded from oral epics and mythologies to written texts and digital media, reflecting complex cultural transformations, while rituals persisted as embodied traditions, adapting to modern contexts but maintaining their foundational role in social rituals and cultural continuity.
Rituality in Modern Societies
Rituality in modern societies manifests through repeated symbolic actions that reinforce social bonds and cultural identity, often observed in ceremonies, festivals, and daily routines. These rituals serve to create a sense of continuity and collective memory, contrasting the linear, cause-and-effect structure found in narrativity. The persistence of ritual practices in urbanized and technologically advanced contexts highlights their role in maintaining community cohesion amid rapid social changes.
Narrativity’s Role in Contemporary Culture
Narrativity shapes contemporary culture by constructing meaningful stories that influence identity, memory, and social cohesion through shared narratives in media, literature, and digital platforms. It enables societies to interpret complex realities, fostering empathy and understanding across diverse experiences and historical contexts. The pervasive role of narrativity supports cultural continuity and transformation by integrating individual and collective experiences into coherent discourses.
Cognitive Impacts: Rituality vs Narrativity
Rituality engages the brain through repetitive, symbolic actions that enhance memory consolidation and emotional regulation by activating procedural memory networks. Narrativity stimulates cognitive functions related to language processing, imagination, and episodic memory by constructing coherent storylines that facilitate understanding and empathy. Both approaches uniquely influence cognition, with rituality fostering embodied cognition and narrativity promoting narrative comprehension and meaning-making.
Case Studies: Ritual-Centered vs Narrative-Centered Practices
Rituality emphasizes repetitive, symbolic actions that reinforce communal identity, exemplified by indigenous ceremonies where consistent enactment fosters social cohesion. Narrativity centers on storytelling structures that create meaning through plot development, as seen in therapeutic practices using personal narratives to reconstruct individual experience. Case studies contrasting ritual-centered practices in religious festivals with narrative-centered methods in psychological counseling reveal distinct mechanisms in meaning-making and memory formation.
Future Perspectives: Blending Rituality and Narrativity
Future perspectives in cultural theory emphasize the convergence of rituality and narrativity to foster deeper communal engagement and meaning-making. Integrating ritual practices with narrative structures enhances collective identity formation and emotional resonance, leveraging symbolic actions and storytelling's cognitive appeal. Emerging interdisciplinary studies suggest this blend can drive innovative approaches in education, therapy, and digital media, enriching participatory experiences through interactive and embodied narratives.
Rituality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com