Regiocentric management focuses on aligning business strategies with the cultural and economic characteristics of a specific region, enhancing local responsiveness and competitive advantage. This approach enables companies to leverage regional market knowledge while maintaining a coherent strategy across neighboring countries. Explore the rest of the article to understand how regiocentric strategies can drive your business growth in diverse markets.
Table of Comparison
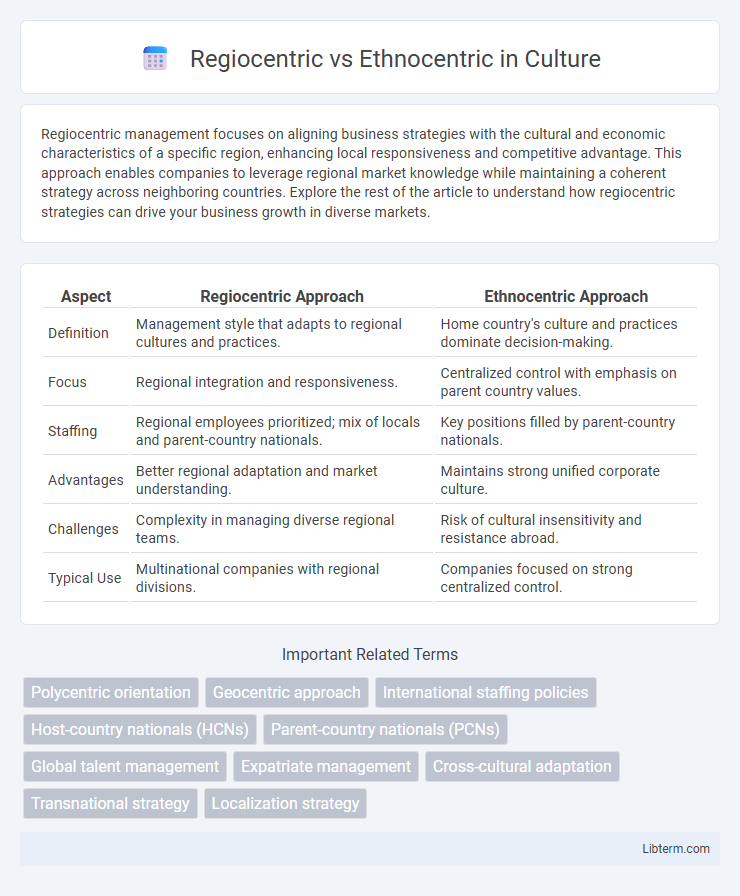
| Aspect | Regiocentric Approach | Ethnocentric Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management style that adapts to regional cultures and practices. | Home country's culture and practices dominate decision-making. |
| Focus | Regional integration and responsiveness. | Centralized control with emphasis on parent country values. |
| Staffing | Regional employees prioritized; mix of locals and parent-country nationals. | Key positions filled by parent-country nationals. |
| Advantages | Better regional adaptation and market understanding. | Maintains strong unified corporate culture. |
| Challenges | Complexity in managing diverse regional teams. | Risk of cultural insensitivity and resistance abroad. |
| Typical Use | Multinational companies with regional divisions. | Companies focused on strong centralized control. |
Understanding Regiocentric and Ethnocentric Approaches
The ethnocentric approach in international business emphasizes the home country's culture and management style, often leading firms to replicate domestic strategies abroad. In contrast, the regiocentric approach focuses on regional similarities, integrating management and marketing practices tailored to specific geographic areas. Understanding these approaches is crucial for multinational companies aiming to balance global integration with local responsiveness and regional adaptation.
Key Definitions: Regiocentric vs Ethnocentric
Regiocentric orientation emphasizes managing business operations within a specific geographic region, adapting strategies to regional market needs and cultural nuances. Ethnocentric orientation centers on a home-country approach, where business practices, policies, and management styles are standardized based on the parent company's culture and norms. Understanding these key definitions is essential for multinational companies to navigate global markets effectively and align organizational strategies with regional or home-country priorities.
Core Principles of the Ethnocentric Strategy
The core principles of the ethnocentric strategy center on prioritizing the home country's culture, values, and business practices in international operations, often leading to key managerial positions being filled by nationals from the parent country. This approach assumes that what works well domestically will be effective globally, emphasizing standardized policies and centralized decision-making. Ethnocentric firms typically maintain tight control over subsidiaries to ensure consistency with headquarters' objectives and organizational culture.
Regiocentric Approach: Main Features
The regiocentric approach emphasizes management and marketing strategies tailored to regional similarities rather than individual countries or a global scale, enabling companies to leverage regional expertise and cultural affinity. It integrates regional priorities, allowing firms to adapt products and business practices to fit the distinct needs and consumer behaviors found within specific geographic areas like Asia-Pacific or Europe. This approach balances global efficiency with local responsiveness by deploying regional decision-making centers that coordinate operations across multiple countries within the same region.
Advantages of an Ethnocentric Approach
An ethnocentric approach centralizes decision-making within the home country, ensuring consistent corporate culture and standardized practices, which can enhance brand identity and streamline operations across global subsidiaries. This strategy allows companies to leverage proven expertise and control key functions, facilitating efficient communication and unified policies. It also helps maintain quality standards by deploying experienced home-country managers familiar with the company's values and objectives.
Benefits of Regiocentric Practices
Regiocentric practices enhance cultural integration by aligning management strategies with regional cultural norms, improving communication and workforce cohesion across borders. These practices support better regional market adaptation and customer understanding, leading to increased competitiveness and market share within specific areas. Employing regiocentric approaches also promotes efficient resource allocation and talent mobility within regions, boosting operational efficiency and regional innovation.
Challenges in Implementing Ethnocentric Strategies
Ethnocentric strategies often face challenges like cultural insensitivity, which can result in poor local employee morale and reduced market effectiveness. The centralization of decision-making in the home country may slow responsiveness to local market demands and hinder operational flexibility. Furthermore, the lack of local managerial input frequently causes misalignment with regional customer preferences and regulatory environments.
Limitations of the Regiocentric Model
The regiocentric model faces limitations such as difficulties in maintaining consistent corporate culture across diverse regions and challenges in balancing regional responsiveness with global integration. This model can lead to complexity in decision-making processes and slower adaptation to local market nuances compared to purely ethnocentric or polycentric approaches. Companies may also encounter increased costs due to managing multiple regional headquarters and coordinating varied operational strategies.
Ethnocentric vs Regiocentric: Comparative Analysis
Ethnocentric management prioritizes home-country practices, assuming they are superior, which can limit global adaptability and local responsiveness. Regiocentric approaches emphasize regional similarities and tailor strategies to regional markets, enhancing cultural alignment and operational flexibility within specific geographic clusters. Comparing the two, ethnocentric models often lead to standardized control but risk alienating local markets, while regiocentric models balance centralized coordination with regional customization for improved market penetration and competitive advantage.
Choosing the Right Approach for Global Expansion
Selecting the right approach between regiocentric and ethnocentric strategies depends on a company's global expansion objectives and cultural adaptability. Regiocentric approaches prioritize regional market needs by customizing marketing and management practices to fit cultural and economic differences within specific geographic areas. Ethnocentric strategies centralize decision-making in the home country, maintaining uniformity but potentially limiting responsiveness to local market nuances.
Regiocentric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com