Bureaucratic authority is a management system based on clearly defined rules, hierarchy, and roles, ensuring efficient and predictable decision-making within organizations. This form of authority relies on formal procedures and impersonal relationships to maintain order and consistency. Explore the rest of the article to understand how bureaucratic authority impacts organizational success and your role within it.
Table of Comparison
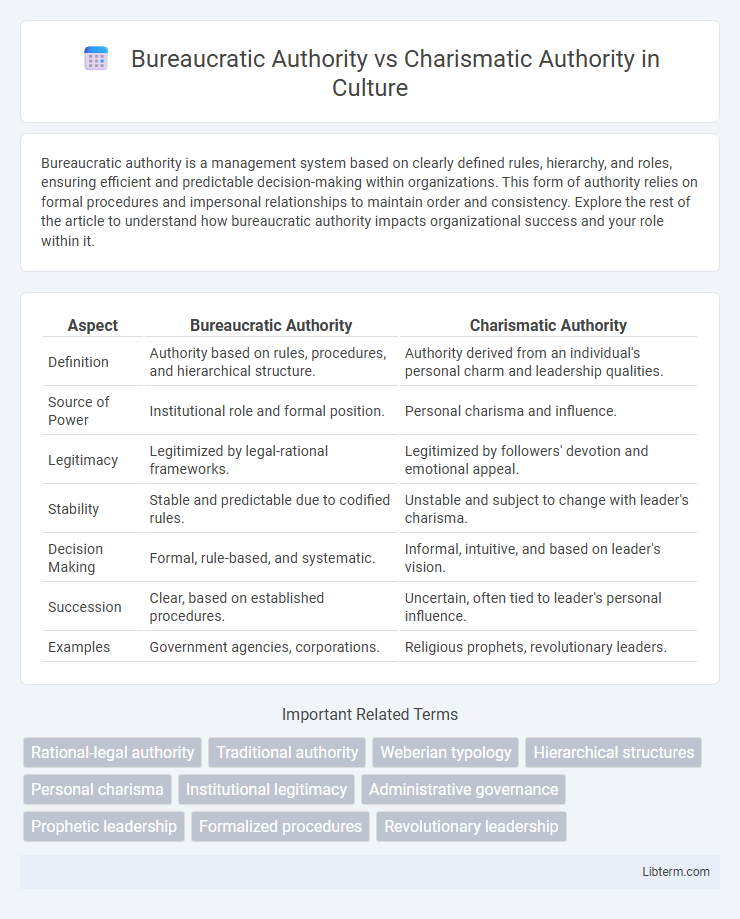
| Aspect | Bureaucratic Authority | Charismatic Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority based on rules, procedures, and hierarchical structure. | Authority derived from an individual's personal charm and leadership qualities. |
| Source of Power | Institutional role and formal position. | Personal charisma and influence. |
| Legitimacy | Legitimized by legal-rational frameworks. | Legitimized by followers' devotion and emotional appeal. |
| Stability | Stable and predictable due to codified rules. | Unstable and subject to change with leader's charisma. |
| Decision Making | Formal, rule-based, and systematic. | Informal, intuitive, and based on leader's vision. |
| Succession | Clear, based on established procedures. | Uncertain, often tied to leader's personal influence. |
| Examples | Government agencies, corporations. | Religious prophets, revolutionary leaders. |
Understanding Bureaucratic Authority
Bureaucratic authority is grounded in a formalized system of rules, roles, and procedures that ensure consistency and predictability in organizational operations. It emphasizes hierarchical structures where power is distributed through clearly defined offices rather than individual personalities. Max Weber's theory identifies bureaucratic authority as the most efficient form for managing large, complex organizations due to its reliance on standardized regulations and impersonal decision-making.
Defining Charismatic Authority
Charismatic authority is defined by the personal charm and exceptional qualities of a leader, which inspire devotion and obedience from followers independent of formal rules or legal frameworks. This form of authority contrasts with bureaucratic authority, which is rooted in established laws, procedures, and hierarchical structures. Max Weber identified charismatic authority as revolutionary, often leading to transformational social change driven by the leader's vision and personal appeal.
Origins and Development of Authority Types
Bureaucratic authority originates from formal structures and established rules, emphasizing hierarchy and rational-legal legitimacy, prominently developed through Max Weber's sociological theories in the early 20th century. Charismatic authority arises from an individual's exceptional personal qualities and the devotion they inspire, often emerging during periods of social crisis or transformation. These authority types evolve differently: bureaucratic authority stabilizes organizations through codified regulations, while charismatic authority drives change through personal influence and emotional appeal.
Key Characteristics: Bureaucratic vs Charismatic
Bureaucratic authority is characterized by a formalized hierarchy, clear rules, and impersonal relationships ensuring predictable and consistent decision-making. Charismatic authority relies on the personal charm, vision, and influence of a leader, inspiring loyalty and devotion based on individual qualities rather than codified regulations. Bureaucratic systems emphasize stability and rational-legal order, whereas charismatic authority thrives on emotional appeal and transformational leadership.
Structures and Hierarchies in Leadership
Bureaucratic authority relies on formalized structures and clear hierarchies where leadership is based on established rules, roles, and procedures to ensure consistency and efficiency. Charismatic authority centers on the exceptional personal qualities and vision of a leader, often resulting in more fluid and personalized organizational structures without rigid hierarchies. This distinction influences how power is exercised, with bureaucratic leadership emphasizing systematic control and charismatic leadership promoting dynamic, follower-driven influence.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Bureaucratic authority relies on formal rules and hierarchical structures to guide decision-making processes, ensuring consistency, predictability, and procedural fairness. Charismatic authority centers on the personal qualities and vision of a leader, enabling swift, flexible decisions often driven by individual judgment and emotional appeal. The bureaucratic approach emphasizes systematic evaluation and adherence to established norms, while charismatic decision-making prioritizes inspiration and adaptability in dynamic contexts.
Advantages of Bureaucratic Authority
Bureaucratic authority ensures consistent decision-making through clearly defined rules and hierarchical structures, promoting efficiency and predictability in organizations. It eliminates personal biases by emphasizing formal procedures and merit-based advancement, enhancing fairness and accountability. This type of authority is scalable, allowing large institutions to function smoothly with standardization and clarity in roles and responsibilities.
Strengths of Charismatic Leadership
Charismatic leadership excels in inspiring loyalty and enthusiasm through personal magnetism and vision, effectively motivating followers beyond formal rules or established procedures. Its strength lies in fostering strong emotional bonds and driving innovative change during times of uncertainty. This leadership style encourages creativity and commitment by appealing directly to individual values and aspirations, often leading to high levels of dedication and performance.
Challenges and Risks of Each Authority
Bureaucratic authority faces challenges such as rigid hierarchies that can impede innovation and slow decision-making processes, often leading to inefficiency and employee dissatisfaction. Charismatic authority risks dependency on a single leader's personal appeal, making the organization vulnerable to instability and loss of direction if that leader departs or loses influence. Both forms of authority present risks of power concentration, but bureaucratic structures struggle with adaptability, while charismatic systems face challenges in maintaining continuity and institutional legitimacy.
Impact on Organizational Culture
Bureaucratic authority emphasizes formal rules and hierarchical structures, fostering a culture of consistency, predictability, and clear accountability within organizations. Charismatic authority relies on personal appeal and vision, cultivating an innovative, flexible, and inspirational organizational culture that thrives on individual influence. The impact on organizational culture varies, where bureaucratic authority often limits creativity but ensures stability, while charismatic authority drives dynamic change but may risk inconsistency and dependency on the leader.
Bureaucratic Authority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com