Continuous practice is essential for mastering any skill and achieving lasting improvement. By dedicating time regularly, you build confidence and reinforce your abilities effectively. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical tips that will help you enhance your practice routine.
Table of Comparison
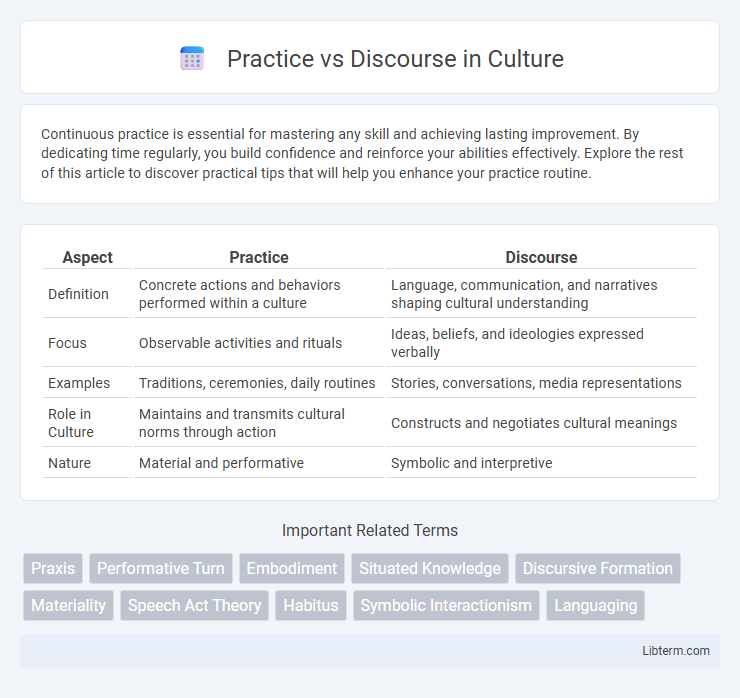
| Aspect | Practice | Discourse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete actions and behaviors performed within a culture | Language, communication, and narratives shaping cultural understanding |
| Focus | Observable activities and rituals | Ideas, beliefs, and ideologies expressed verbally |
| Examples | Traditions, ceremonies, daily routines | Stories, conversations, media representations |
| Role in Culture | Maintains and transmits cultural norms through action | Constructs and negotiates cultural meanings |
| Nature | Material and performative | Symbolic and interpretive |
Understanding Practice and Discourse
Understanding practice involves examining concrete actions and behaviors within specific contexts, emphasizing how individuals apply skills and knowledge in real-world situations. Discourse refers to structured communication that shapes social meanings, norms, and power relations through language use in various settings. Analyzing the interplay between practice and discourse reveals how social realities are constructed and maintained through both action and language.
Historical Perspectives on Practice vs Discourse
Historical perspectives on practice versus discourse reveal shifting academic priorities, with early social theories prioritizing practical actions as drivers of societal change. From the mid-20th century, discourse analysis gained prominence through scholars like Foucault, emphasizing language's role in shaping knowledge and power structures. Contemporary debates integrate both, recognizing the interdependence of social practices and discursive formations in understanding historical developments.
Key Differences Between Practice and Discourse
Practice refers to the habitual actions and behaviors individuals or groups engage in regularly, while discourse encompasses the structured communication, language, and shared meanings that shape social reality. Practices are observable activities rooted in everyday routines, whereas discourse shapes the frameworks and narratives that influence how these activities are understood and interpreted. The key difference lies in practice being action-oriented and discourse being language-oriented, both interdependent in constructing social life.
The Role of Context in Shaping Practice and Discourse
Context critically shapes both practice and discourse by influencing the meanings and actions within social interactions. In practice, context determines how individuals apply skills and knowledge in specific situations, adapting behaviors to fit environmental cues. Discourse reflects and reinforces these contextual dynamics, shaping language use, norms, and power relations that guide collective understanding and social practices.
Intersections of Practice with Discourse
Intersections of practice with discourse reveal how social actions both shape and are shaped by language use within specific contexts. Discourse constructs the frameworks through which practices gain meaning, while practices provide the tangible enactment that sustains and transforms discourse over time. This dynamic interaction underscores the inseparability of practical activities from the communicative structures that legitimize and propagate them.
Practice-Led Approaches in Contemporary Fields
Practice-led approaches in contemporary fields emphasize the creation and reflection of knowledge through active engagement, privileging hands-on experience over purely theoretical discourse. This method integrates doing with critical analysis, fostering innovation in areas such as design, art, and technology by embedding inquiry within the practice itself. Emphasizing tacit knowledge and embodied expertise, practice-led research challenges traditional epistemologies, expanding the boundaries of how knowledge is produced and validated in academic and professional contexts.
Discourse Analysis: Theoretical Foundations
Discourse analysis explores the structures and functions of language beyond isolated sentences, emphasizing how meaning is constructed within social contexts. Theoretical foundations draw from linguistics, sociology, and philosophy, highlighting concepts such as power relations, ideology, and cultural norms embedded in communication. Key frameworks include Michel Foucault's discourse theory, which examines how knowledge and power dynamics shape discourse, and Norman Fairclough's critical discourse analysis, focusing on language's role in social change.
Case Studies: Practice vs Discourse in Action
Case studies of practice versus discourse reveal discrepancies between theoretical language and real-world application, highlighting how discourse shapes but does not always align with actual practices. Analysis of organizational communication shows that while company policies articulate ideal practices, employee behaviors often diverge due to contextual constraints and power dynamics. These case studies underscore the importance of examining both discourse and practice to understand social interactions comprehensively.
Implications for Research and Methodology
The distinction between practice and discourse significantly shapes research methodologies by influencing data collection and analysis strategies, where practice emphasizes observable actions and interactions, while discourse focuses on language use and communication patterns. This duality requires mixed-method approaches to capture both material practices and linguistic structures, enabling comprehensive insights into social phenomena. Researchers must carefully design studies that integrate ethnographic observations with discourse analysis to address complex social realities effectively.
Future Directions: Bridging Practice and Discourse
Future directions in bridging practice and discourse emphasize integrating real-world applications with theoretical communication frameworks to enhance mutual influence and understanding. Emerging methodologies prioritize collaborative platforms that enable continuous feedback loops between practitioners and discourse analysts, facilitating adaptive strategies and innovation. Advances in computational linguistics and data analytics support this integration by providing tools to analyze and apply discourse patterns directly within practice contexts.
Practice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com