Hierarchical governance organizes decision-making through a clear chain of command, ensuring accountability and streamlined communication within organizations. This structure supports efficient policy implementation by defining specific roles and responsibilities at each level. Explore the rest of the article to understand how hierarchical governance can enhance your organization's management and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
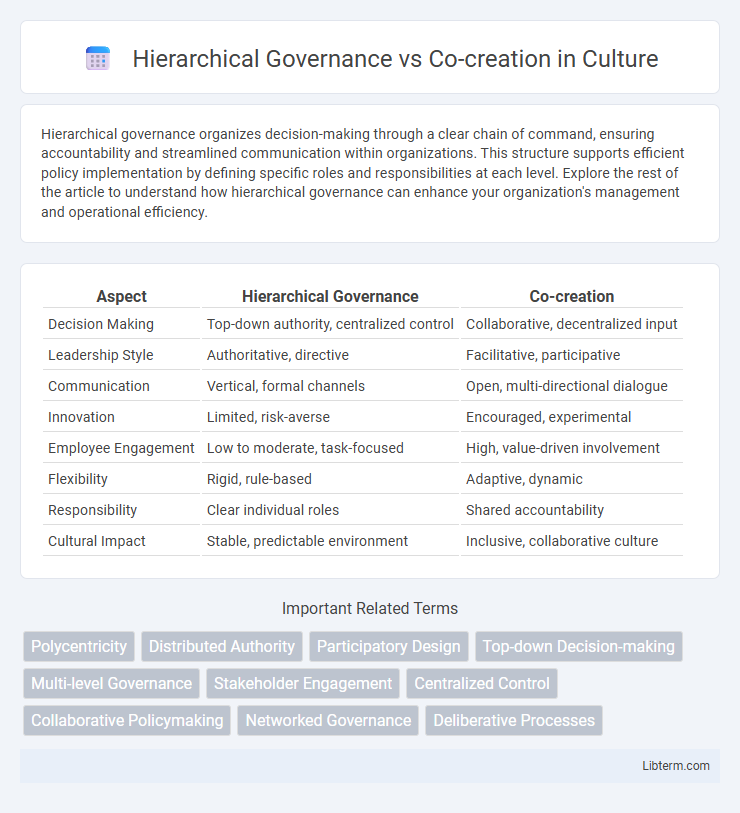
| Aspect | Hierarchical Governance | Co-creation |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Top-down authority, centralized control | Collaborative, decentralized input |
| Leadership Style | Authoritative, directive | Facilitative, participative |
| Communication | Vertical, formal channels | Open, multi-directional dialogue |
| Innovation | Limited, risk-averse | Encouraged, experimental |
| Employee Engagement | Low to moderate, task-focused | High, value-driven involvement |
| Flexibility | Rigid, rule-based | Adaptive, dynamic |
| Responsibility | Clear individual roles | Shared accountability |
| Cultural Impact | Stable, predictable environment | Inclusive, collaborative culture |
Understanding Hierarchical Governance
Hierarchical governance involves a structured framework where authority flows top-down, enabling efficient decision-making through clearly defined roles and responsibilities within organizations or governments. This model prioritizes control, accountability, and consistency, often resulting in streamlined processes but limited stakeholder participation. Understanding hierarchical governance is crucial to recognizing its strengths in maintaining order and its challenges in adapting to complex, dynamic environments requiring collaborative input.
Defining Co-creation in Modern Organizations
Co-creation in modern organizations involves collaborative processes where stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, actively contribute to decision-making and value creation, fostering innovation and responsiveness. Unlike hierarchical governance, which relies on top-down control and structured authority, co-creation emphasizes shared responsibility and decentralized input to enhance organizational agility. This participatory approach leverages diverse perspectives to develop products, services, and strategies that better meet market demands and enhance stakeholder engagement.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical Governance and Co-creation
Hierarchical governance relies on top-down decision-making processes with clearly defined roles and authority levels, ensuring efficient control and accountability. Co-creation emphasizes collaborative engagement among diverse stakeholders, fostering innovation and shared ownership through decentralized participation. Key differences include the concentration of power in hierarchical governance versus distributed influence in co-creation, and the contrasting approaches to stakeholder involvement and decision-making dynamics.
Historical Evolution of Governance Models
Hierarchical governance has origins in early centralized administrations where authority was concentrated in top-down structures, primarily driven by bureaucratic control and formalized decision-making processes. In contrast, co-creation emerged as a response to the limitations of hierarchical models, emphasizing collaborative stakeholder engagement and participatory governance during the late 20th and early 21st centuries. The historical evolution reflects a shift from rigid authority to more inclusive, networked governance frameworks that prioritize shared value creation and adaptive problem-solving.
Advantages of Hierarchical Structures
Hierarchical governance offers clear authority lines, enhancing decision-making speed and accountability within organizations. Structured tiers facilitate efficient resource allocation and consistent policy implementation across departments. This model supports scalability and stability, ensuring uniform compliance and reducing ambiguities in responsibility.
Benefits of Co-creation Approaches
Co-creation approaches enhance stakeholder engagement by fostering collaboration among diverse participants, leading to more innovative and context-sensitive solutions. These approaches improve decision-making transparency and trust, increasing the legitimacy and acceptance of policies or products. Through continuous feedback loops and shared ownership, co-creation drives adaptability and resilience in governance systems compared to rigid hierarchical structures.
Challenges in Shifting from Hierarchical to Co-creative Models
Shifting from hierarchical governance to co-creative models faces challenges such as resistance to change from established power structures, the need for developing trust and shared vision among diverse stakeholders, and the complexity of coordinating collaborative decision-making. Existing bureaucratic processes often hinder flexibility and slow down innovation, while unclear roles and responsibilities can lead to conflicts and inefficiencies. Successfully overcoming these obstacles requires comprehensive capacity building, transparent communication, and adaptive mechanisms that embrace participation and collective intelligence.
Case Studies: Real-world Implementations
Hierarchical governance structures emphasize top-down decision-making, with case studies like Singapore's urban planning demonstrating efficiency in policy enforcement and rapid implementation. In contrast, co-creation models prioritize stakeholder engagement and collaboration, as seen in Porto Alegre's participatory budgeting, which enhances community involvement and transparency. Comparative analysis reveals that while hierarchical governance excels in control and consistency, co-creation fosters innovation and social inclusion through shared authority and collective problem-solving.
Impact on Organizational Culture and Innovation
Hierarchical governance often enforces top-down decision-making, which can limit employee autonomy and stifle creative problem-solving, thus constraining innovation within organizational culture. In contrast, co-creation fosters collaboration and shared ownership, enhancing trust and openness that drive innovative thinking and adaptive cultural shifts. Organizations leveraging co-creation experience increased engagement and a stronger innovation pipeline due to diverse perspectives and collective ideation.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Organization
Choosing the right governance model depends on your organization's size, goals, and culture; hierarchical governance offers clear authority and streamlined decision-making, ideal for large or structured entities. Co-creation emphasizes collaboration and shared power, fostering innovation and stakeholder engagement, which suits dynamic and creative environments. Evaluating factors like project complexity, stakeholder diversity, and desired agility helps in selecting a governance approach that aligns with organizational objectives and operational efficiency.
Hierarchical Governance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com