Norms are unwritten rules that guide behavior within societies and groups, shaping expectations and promoting social order. Understanding these norms can help you navigate social interactions more effectively and avoid misunderstandings. Discover how norms influence daily life and why they are essential by reading the full article.
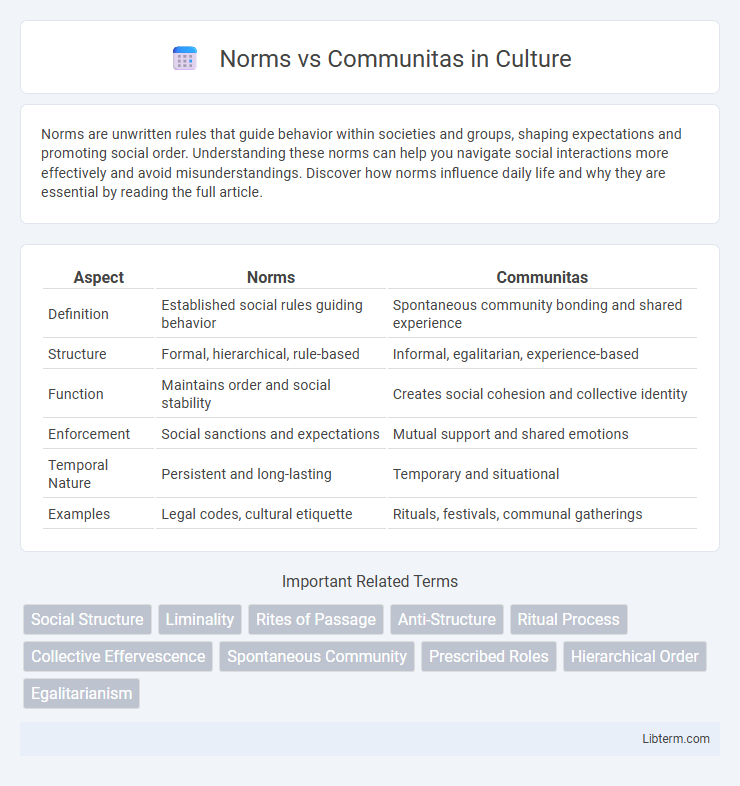
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Norms | Communitas |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Established social rules guiding behavior | Spontaneous community bonding and shared experience |
| Structure | Formal, hierarchical, rule-based | Informal, egalitarian, experience-based |
| Function | Maintains order and social stability | Creates social cohesion and collective identity |
| Enforcement | Social sanctions and expectations | Mutual support and shared emotions |
| Temporal Nature | Persistent and long-lasting | Temporary and situational |
| Examples | Legal codes, cultural etiquette | Rituals, festivals, communal gatherings |
Understanding Norms: Definition and Importance
Norms are established social rules and expectations that guide individual behavior within a group, providing structure and predictability essential for social order. They function as shared standards that regulate interactions and maintain cultural cohesion by defining acceptable and unacceptable conduct. Understanding norms is crucial because they influence social compliance, shape identity, and help prevent conflicts by aligning group members with common values and practices.
What is Communitas? Core Concepts Explained
Communitas refers to an intense community spirit, characterized by equal and spontaneous social bonds that emerge during shared experiences, often outside structured societal norms. Core concepts of communitas include a profound sense of togetherness, collective joy, and a temporary suspension of hierarchical roles or formal rules. It contrasts with norms by emphasizing fluid, organic social interactions instead of rigid, institutionalized expectations.
Historical Origins of Norms and Communitas
Norms have historical origins rooted in structured societies where codified rules and laws governed behavior to maintain order and predictability. Communitas arises from anthropological contexts, notably from Victor Turner's studies of rites of passage, emphasizing spontaneous, egalitarian social bonds formed during collective liminal experiences. The contrast highlights the evolution from formalized norms to organic communal connections as foundational elements in social cohesion.
Norms: Structure, Stability, and Social Expectations
Norms provide the foundational structure and stability necessary for societal functioning by defining consistent social expectations and behaviors. These unwritten rules guide individual actions, ensuring predictability and cohesion within communities. By reinforcing shared values, norms maintain order and facilitate cooperation across diverse social settings.
Communitas: Spontaneity, Equality, and Transformation
Communitas represents a state of spontaneous social togetherness where individuals experience equality, breaking free from structured norms and hierarchies. This collective unity fosters a transformative experience, enabling participants to connect deeply and challenge established social roles. The essence of communitas lies in its ability to create moments of shared humanity that transcend conventional societal boundaries.
Norms vs Communitas: Key Differences
Norms are established social rules and expectations that regulate individual behavior within structured societies, emphasizing order and predictability. Communitas represents spontaneous, collective experiences that foster deep social bonds and a sense of equality, often emerging during rituals or shared crises. The key difference lies in norms enforcing conformity and social roles, while communitas dissolves hierarchies, promoting unity and shared identity.
The Role of Rituals in Shaping Social Dynamics
Rituals serve as a crucial mechanism in balancing norms and communitas by reinforcing established social structures while fostering moments of collective unity and equality. Through repeated ceremonial acts, rituals solidify community values and expectations, embedding norms into social consciousness. Simultaneously, these shared experiences dissolve hierarchies temporarily, generating communitas that enhances group cohesion and transformative social connections.
Norms and Communitas in Modern Society
Norms in modern society function as established rules guiding behavior, maintaining social order and predictability across diverse groups and institutions. Communitas represents spontaneous, collective experiences of equality and togetherness, often emerging during events that temporarily dissolve social hierarchies. The dynamic interplay between norms and communitas shapes social cohesion, influencing how individuals balance conformity with moments of shared communal identity.
Challenges When Norms Clash with Communitas
Conflicts arise when established social norms contradict the fluid, collective spirit of communitas, generating tension between structured expectations and spontaneous group unity. These clashes challenge individuals to navigate between conformity and authentic shared experiences, often causing social fragmentation or resistance. Managing the balance requires adaptive frameworks that respect both normative order and the transformative potential of communitas.
Balancing Structure and Spontaneity for Social Harmony
Balancing norms and communitas is essential for social harmony as norms provide structured guidelines that maintain order, while communitas fosters spontaneous, collective bonding that strengthens community ties. Effective social systems integrate these elements by regulating behavior through norms without stifling the organic, egalitarian interactions characteristic of communitas. This dynamic interplay helps communities adapt, ensuring stability alongside the vitality of shared human experiences.
Norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com