Norms represent the unwritten rules and shared expectations that govern behavior within a group or society, shaping social order and cooperation. They influence how individuals interact, guiding acceptable conduct and fostering a sense of community. Explore the article to understand how norms impact your daily life and social dynamics.
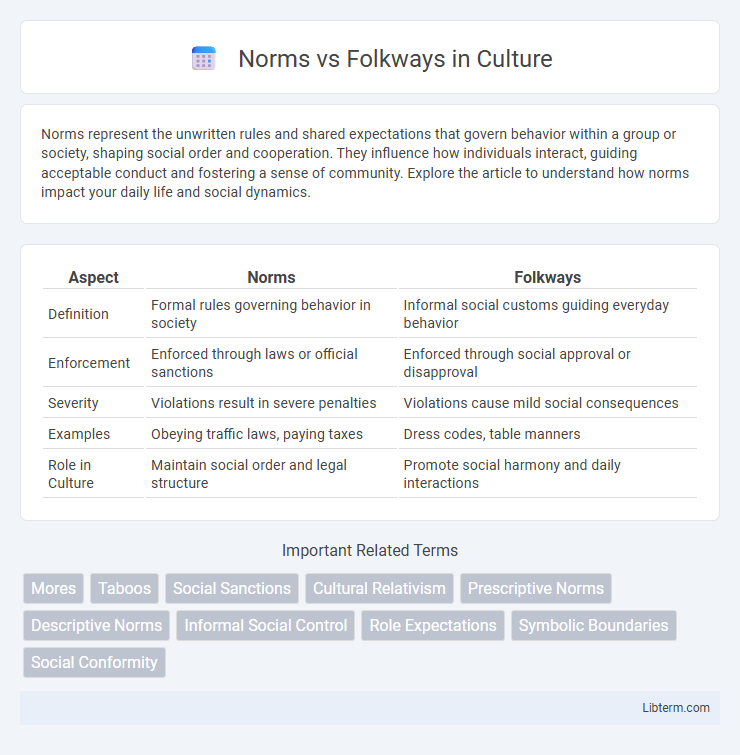
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Norms | Folkways |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal rules governing behavior in society | Informal social customs guiding everyday behavior |
| Enforcement | Enforced through laws or official sanctions | Enforced through social approval or disapproval |
| Severity | Violations result in severe penalties | Violations cause mild social consequences |
| Examples | Obeying traffic laws, paying taxes | Dress codes, table manners |
| Role in Culture | Maintain social order and legal structure | Promote social harmony and daily interactions |
Understanding Social Norms
Social norms guide behavior by establishing expected standards within a community, distinguishing between formal rules (norms) and informal customs (folkways). Norms often carry sanctions when violated, reflecting societal values, while folkways represent everyday practices shaping social interaction without strict enforcement. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing social order and cultural cohesion.
Defining Folkways in Society
Folkways are informal social norms that govern everyday behavior and customs within a society, shaping routines like dress codes, greetings, and meal practices. Unlike laws, folkways carry mild social sanctions when violated, such as ridicule or disapproval, rather than legal penalties. These unwritten rules maintain social order by fostering predictability and cohesion in daily interactions.
Key Differences between Norms and Folkways
Norms are established social rules that govern behavior and carry formal sanctions when violated, while folkways are informal customs guiding everyday behavior without strict enforcement. Norms often reflect moral principles and laws, whereas folkways involve routine social practices like dress codes or dining etiquette. The key difference lies in the severity of consequences and the level of societal expectation linked to norms compared to the more flexible, customary nature of folkways.
The Role of Norms in Shaping Behavior
Norms are established rules and expectations that govern behavior within a society, providing clear guidelines for what is considered acceptable or unacceptable. They play a crucial role in maintaining social order by promoting predictability and conformity, influencing individuals to align their actions with collective standards. Unlike folkways, which are informal everyday customs, norms carry stronger social sanctions and are essential in shaping consistent behavioral patterns across communities.
Folkways as Everyday Customs
Folkways represent everyday customs that guide casual social interactions and are typically followed without formal enforcement. Unlike norms that may have legal or moral significance, folkways include practices such as greetings, dress codes, and table manners, which help maintain social order and predictability. These informal rules vary widely across cultures and evolve gradually over time as societal behaviors change.
Examples of Norms in Modern Culture
Norms in modern culture include laws against theft, traffic regulations, and workplace dress codes, which guide acceptable behavior to maintain social order. For instance, adhering to speed limits prevents accidents, while professional attire helps establish a respectful work environment. These formal norms are enforced by institutions, distinguishing them from informal folkways like table manners or greetings.
Examples of Folkways in Daily Life
Folkways in daily life include behaviors such as saying "please" and "thank you," dressing appropriately for different social settings, and following customary table manners like using utensils correctly. These informal norms guide everyday interactions and help maintain social harmony without strict enforcement or severe consequences for violations. Unlike formal norms or laws, folkways reflect cultural habits that vary widely across communities and influence social cohesion through routine practices.
Consequences of Breaking Norms
Breaking norms results in formal sanctions such as fines, legal penalties, or imprisonment due to their codification in laws and regulations. Violating folkways typically leads to informal social consequences like ridicule, ostracism, or subtle social disapproval, reflecting their basis in everyday customs rather than formal rules. The severity of consequences depends on the cultural context and the norm's significance in maintaining social order.
How Folkways Influence Social Interactions
Folkways shape social interactions by guiding everyday behaviors and establishing informal expectations within a community. These customary norms influence how individuals dress, greet, and communicate, promoting social harmony and coherence. Compliance with folkways helps maintain group identity and smooth social exchanges by minimizing conflict in routine situations.
The Importance of Norms and Folkways in Social Cohesion
Norms and folkways are crucial in maintaining social cohesion by establishing expected behaviors within a community, guiding individuals on how to act appropriately. Norms carry stronger social sanctions and enforce core values, while folkways regulate everyday customs and polite behaviors, together creating a framework for predictable interactions. This shared understanding fosters trust and cooperation, essential elements for a stable and functioning society.
Norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com