Popular culture shapes your daily life through music, movies, fashion, and social media trends that reflect current societal values and interests. It influences how we communicate, express identity, and engage with global communities. Explore the rest of this article to understand the impact of popular culture on your world and society at large.
Table of Comparison
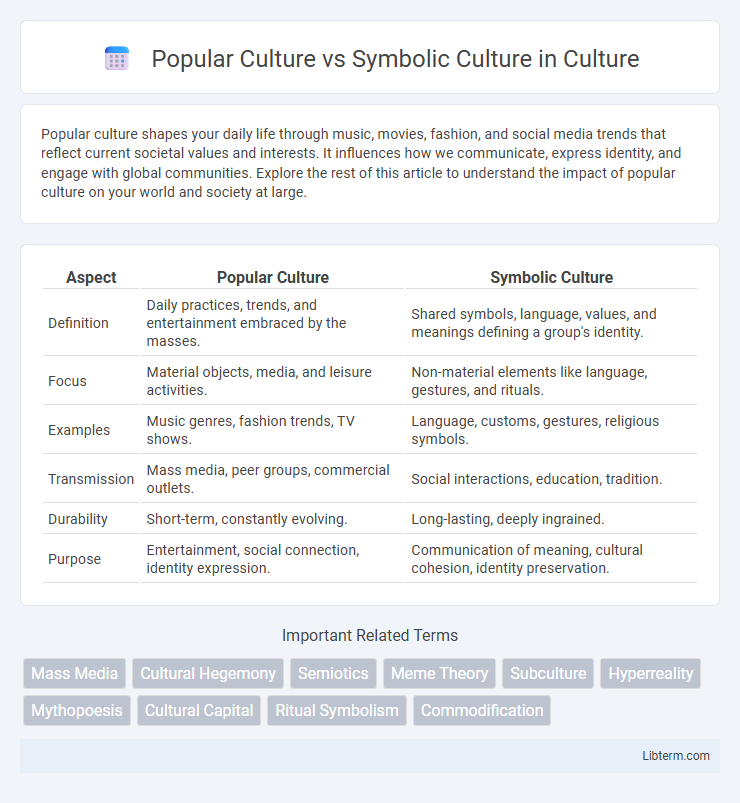
| Aspect | Popular Culture | Symbolic Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Daily practices, trends, and entertainment embraced by the masses. | Shared symbols, language, values, and meanings defining a group's identity. |
| Focus | Material objects, media, and leisure activities. | Non-material elements like language, gestures, and rituals. |
| Examples | Music genres, fashion trends, TV shows. | Language, customs, gestures, religious symbols. |
| Transmission | Mass media, peer groups, commercial outlets. | Social interactions, education, tradition. |
| Durability | Short-term, constantly evolving. | Long-lasting, deeply ingrained. |
| Purpose | Entertainment, social connection, identity expression. | Communication of meaning, cultural cohesion, identity preservation. |
Defining Popular Culture: Meaning and Examples
Popular culture refers to the set of practices, beliefs, objects, and phenomena that dominate mainstream society at a given time, reflecting everyday life and mass appeal. Examples include music genres like pop and hip-hop, television shows such as "Stranger Things," fashion trends, and social media platforms like TikTok. Unlike symbolic culture, which involves deeper meanings conveyed through symbols and rituals, popular culture is more oriented towards entertainment and widespread consumption.
Understanding Symbolic Culture: Key Concepts
Symbolic culture encompasses the beliefs, values, language, rituals, and symbols that shape a society's identity and communication patterns. Unlike popular culture, which includes transient trends and mass media phenomena, symbolic culture represents the deeper meanings and shared understandings that guide social behavior. Key concepts include symbols as carriers of meaning, language as a medium for transmitting culture, and rituals that reinforce collective values and social cohesion.
Historical Evolution of Popular and Symbolic Cultures
Popular culture emerged from mass media and consumerism in the 20th century, reflecting the rapid industrialization and globalization processes that shaped everyday life and social norms. Symbolic culture, rooted in language, values, and rituals, evolved over millennia as human societies developed complex systems of meaning and social cohesion. The historical evolution of these cultures reveals how popular culture responds to contemporary trends and technology, while symbolic culture preserves deep-rooted identities and collective memory across generations.
Core Differences Between Popular and Symbolic Culture
Popular culture consists of widespread, mainstream practices, entertainment, and trends embraced by the general public, often driven by mass media and commercial interests. Symbolic culture encompasses the non-material elements of culture such as beliefs, values, language, and symbols that convey deeper meanings and shape social identity. The core difference lies in popular culture's focus on tangible, consumer-oriented phenomena, whereas symbolic culture centers on abstract, ideological frameworks fundamental to societal cohesion.
How Popular Culture Influences Social Norms
Popular culture shapes social norms by disseminating widely accepted behaviors, values, and trends through media, entertainment, and technology platforms. It creates shared experiences that influence collective attitudes toward fashion, language, and lifestyle, often driving societal acceptance of new practices. The rapid spread of popular culture accelerates social change by challenging traditional symbolic culture rooted in historical beliefs and rituals.
The Role of Symbolic Culture in Identity Formation
Symbolic culture, encompassing language, beliefs, values, and norms, plays a crucial role in identity formation by providing individuals with shared meanings and social frameworks that shape self-concept and group affiliation. Unlike popular culture, which consists of transient trends and entertainment, symbolic culture offers enduring symbols and rituals that connect personal identity to collective heritage and societal values. The internalization of symbolic culture enables people to interpret experiences, establish social roles, and foster a cohesive sense of belonging within cultural communities.
Media’s Impact on Popular and Symbolic Culture
Media profoundly shapes popular culture by rapidly disseminating trends, music, fashion, and entertainment, making them accessible to a broad audience and driving mass consumer behavior. In symbolic culture, media plays a critical role in transmitting and reinforcing shared values, beliefs, rituals, and symbols that define group identities and social norms. Through film, television, and digital platforms, media not only reflects cultural symbols but also transforms and reinterprets them, influencing societal perceptions and cultural continuity.
Interactions and Overlaps: When Pop Culture Becomes Symbolic
Popular culture often transforms into symbolic culture when widely recognized symbols or practices from media, fashion, or entertainment gain deep cultural meanings beyond their original context. Interactions between pop culture and symbolic culture occur as iconic images, phrases, or rituals are adopted by communities to express identity, values, or social movements. This overlap highlights how transient trends can evolve into enduring symbols that shape cultural narratives and collective memory.
Popular Culture vs Symbolic Culture in Globalization
Popular culture in globalization manifests through widespread entertainment, fashion, and consumer trends that transcend borders, shaping a shared cultural experience influenced by mass media and technology. Symbolic culture, comprising language, rituals, and values, persists as a core element of identity, often resisting homogenization by maintaining unique meanings and traditions amid global exchanges. The dynamic interplay between popular and symbolic culture during globalization results in hybrid cultural forms, where global influences intersect with local symbolism to create diversified cultural expressions.
The Future of Cultural Expression: Trends and Predictions
Popular culture, characterized by mass-produced media and consumer-focused trends, will increasingly integrate immersive technologies like virtual reality to shape cultural expression. Symbolic culture, encompassing shared values, beliefs, and symbols, will evolve through digital platforms that enable collective identity formation and real-time cultural dialogue. The future landscape of cultural expression hinges on the convergence of popular content and symbolic meaning, driving dynamic, participatory experiences across global audiences.
Popular Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com