Urban culture thrives on the dynamic interplay of diverse communities, arts, and lifestyles that shape city life. This culture influences fashion, music, language, and social interactions, reflecting the vibrancy and complexities of metropolitan areas. Explore the rest of the article to discover how urban culture impacts your daily experiences and social environment.
Table of Comparison
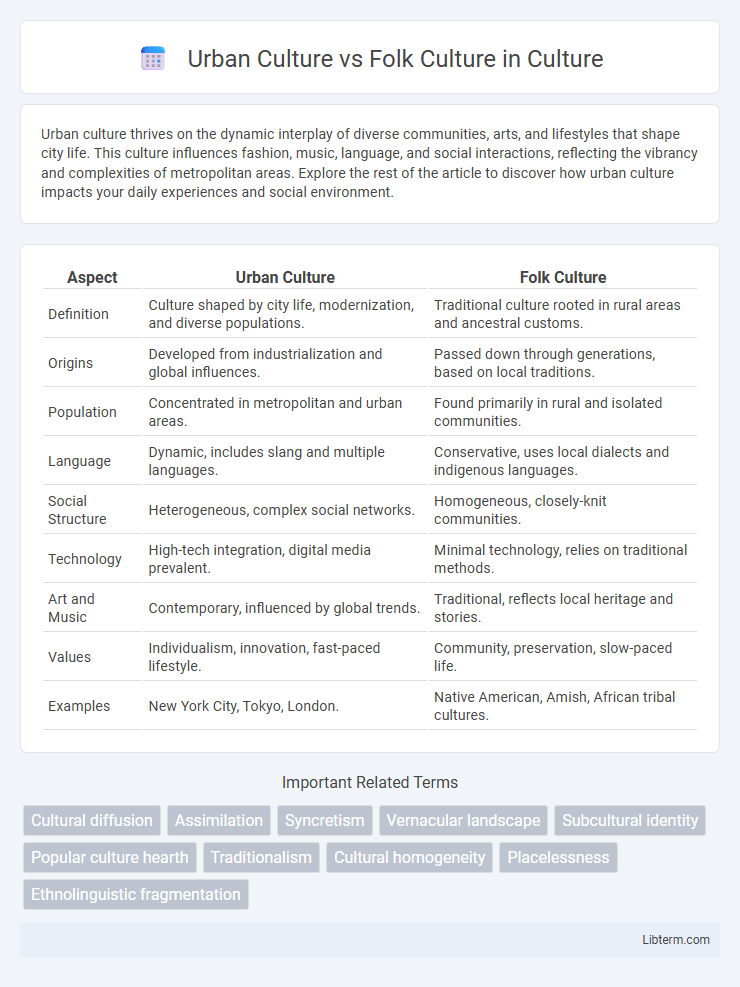
| Aspect | Urban Culture | Folk Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Culture shaped by city life, modernization, and diverse populations. | Traditional culture rooted in rural areas and ancestral customs. |
| Origins | Developed from industrialization and global influences. | Passed down through generations, based on local traditions. |
| Population | Concentrated in metropolitan and urban areas. | Found primarily in rural and isolated communities. |
| Language | Dynamic, includes slang and multiple languages. | Conservative, uses local dialects and indigenous languages. |
| Social Structure | Heterogeneous, complex social networks. | Homogeneous, closely-knit communities. |
| Technology | High-tech integration, digital media prevalent. | Minimal technology, relies on traditional methods. |
| Art and Music | Contemporary, influenced by global trends. | Traditional, reflects local heritage and stories. |
| Values | Individualism, innovation, fast-paced lifestyle. | Community, preservation, slow-paced life. |
| Examples | New York City, Tokyo, London. | Native American, Amish, African tribal cultures. |
Introduction to Urban Culture and Folk Culture
Urban culture thrives in densely populated cities, characterized by diverse lifestyles, advanced technology, and fast-paced social interactions that reflect modernization and globalization. Folk culture originates from rural, homogeneous communities, preserving traditional customs, rituals, and oral histories that embody local heritage and collective identity. Understanding the contrasts between urban and folk cultures involves exploring their distinct social structures, values, and modes of cultural expression.
Defining Urban Culture
Urban culture encompasses the lifestyles, customs, arts, and social behaviors that emerge from densely populated cities and metropolitan areas, reflecting diversity and rapid innovation. It is characterized by dynamic interactions among heterogeneous populations, technological advancements, and contemporary trends influenced by globalization and mass media. Urban culture often contrasts with folk culture by emphasizing modernity, multiculturalism, and continuous change rather than tradition and community-specific practices.
Understanding Folk Culture
Folk culture encompasses traditional practices, customs, and beliefs passed down through generations within small, homogeneous communities, often rural or isolated. It is characterized by strong community bonds, oral traditions, and a deep connection to historical heritage, contrasting with the dynamic and diverse nature of urban culture. Understanding folk culture involves studying its role in maintaining social cohesion and preserving unique identities amid globalization.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Urban culture originated from the complex social structures and diverse populations in cities, evolving through trade, industrialization, and globalization since ancient Mesopotamia and the Roman Empire. Folk culture, deeply rooted in rural traditions and indigenous practices, has been passed down through generations via oral storytelling, rituals, and community events, often remaining localized and resistant to rapid change. The evolution of urban culture is characterized by constant innovation and cultural fusion, while folk culture emphasizes preservation and continuity of heritage.
Key Differences Between Urban and Folk Culture
Urban culture is characterized by diverse lifestyles, fast-paced environments, and technological advancements, often reflecting contemporary values and global influences. Folk culture revolves around traditional practices, localized customs, and community-based activities passed down through generations, emphasizing continuity and shared heritage. Key differences include urban culture's emphasis on innovation and individualism versus folk culture's focus on preservation and collective identity.
Influence of Technology and Media
Urban culture is heavily shaped by advanced technology and mass media platforms, enabling rapid dissemination of trends and ideas across global cities. Folk culture, in contrast, relies more on oral traditions and localized practices, with limited technological influence preserving its authenticity and historical continuity. The pervasive impact of digital media in urban areas fosters cultural convergence, while folk culture resists homogenization through community-based storytelling and ritual performances.
Identity and Community in Urban vs Folk Culture
Urban culture often reflects a diverse and dynamic identity shaped by multicultural influences, fostering a sense of belonging through shared experiences in fast-paced, interconnected environments. Folk culture centers on traditional practices and collective memory, strengthening community bonds via rituals, language, and customs passed down through generations. The contrast highlights urban culture's fluid and inclusive identity versus folk culture's rooted and cohesive communal identity.
Transmission and Preservation Methods
Urban culture primarily transmits and preserves itself through digital media, formal education, and mass communication, enabling rapid dissemination and adaptation across diverse populations. Folk culture relies heavily on oral traditions, rituals, and community-based practices, ensuring preservation through face-to-face interactions and localized activities. The contrast in transmission methods highlights urban culture's dependence on technology for widespread influence, whereas folk culture maintains its authenticity via direct, intergenerational exchange.
Challenges Facing Folk Culture in Urban Settings
Folk culture experiences significant challenges in urban settings due to rapid modernization, which often leads to the erosion of traditional practices and indigenous knowledge. The dominance of mass media and commercial entertainment further diminishes the transmission of folk traditions among younger urban populations. Limited spaces for communal gatherings and the influence of globalized lifestyles disrupt the preservation of authentic folk cultural expressions in cities.
The Future of Urban and Folk Cultures
Urban culture continues to evolve rapidly due to technological advancements and globalization, driving dynamic changes in lifestyle, art, and social interactions. Folk culture, rooted in traditional practices and local identity, faces challenges from modernization but remains vital through cultural preservation efforts and community engagement. The future of both cultures depends on balancing innovation with heritage, fostering coexistence that enriches diversity in rapidly urbanizing societies.
Urban Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com