Cultural exchange fosters understanding and appreciation between diverse communities by sharing traditions, languages, and customs. Engaging in such exchanges enriches your worldview and promotes global empathy. Discover how cultural exchange can transform relationships and broaden horizons in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
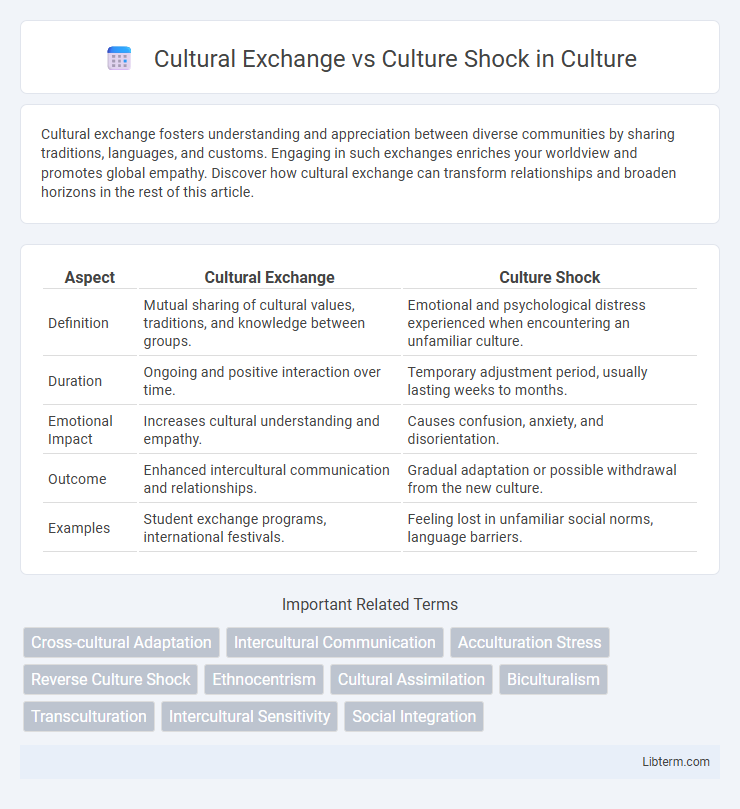
| Aspect | Cultural Exchange | Culture Shock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mutual sharing of cultural values, traditions, and knowledge between groups. | Emotional and psychological distress experienced when encountering an unfamiliar culture. |
| Duration | Ongoing and positive interaction over time. | Temporary adjustment period, usually lasting weeks to months. |
| Emotional Impact | Increases cultural understanding and empathy. | Causes confusion, anxiety, and disorientation. |
| Outcome | Enhanced intercultural communication and relationships. | Gradual adaptation or possible withdrawal from the new culture. |
| Examples | Student exchange programs, international festivals. | Feeling lost in unfamiliar social norms, language barriers. |
Defining Cultural Exchange and Culture Shock
Cultural exchange involves the mutual sharing and learning of traditions, values, and practices between individuals or groups from different cultural backgrounds, enhancing cross-cultural understanding and collaboration. Culture shock refers to the psychological disorientation and stress experienced when encountering an unfamiliar cultural environment, often characterized by confusion, anxiety, and homesickness. Recognizing the distinct nature of cultural exchange as a positive, interactive process contrasts with the challenging emotional adjustment inherent in culture shock.
Key Differences Between Cultural Exchange and Culture Shock
Cultural exchange involves the mutual sharing and learning of customs, traditions, and values between individuals or groups from different cultural backgrounds, fostering understanding and global connection. Culture shock refers to the psychological and emotional discomfort experienced when encountering a new and unfamiliar culture, often characterized by confusion, anxiety, and homesickness. Key differences include cultural exchange being a proactive and enriching experience promoting adaptation, whereas culture shock is a reactive response to cultural disorientation requiring adjustment and coping strategies.
The Process of Cultural Exchange
The process of cultural exchange involves the mutual sharing and learning of traditions, values, and customs between different cultures, fostering understanding and respect. Participants actively engage in dialogues, cultural activities, and immersive experiences that promote empathy and reduce stereotypes. This dynamic interaction contrasts with culture shock, which is an individual's initial psychological and emotional reaction to unfamiliar cultural environments.
Stages of Culture Shock
Cultural exchange fosters mutual understanding and adaptation through shared experiences, while culture shock occurs in distinct stages: the honeymoon phase, characterized by excitement and fascination; the frustration phase, marked by confusion and anxiety due to cultural differences; the adjustment phase, where coping mechanisms develop; and the mastery phase, in which individuals achieve cultural competence and comfort. Recognizing these stages helps individuals navigate the psychological and emotional challenges encountered when immersing in a new culture. Effective management of culture shock enhances the success of cultural exchange programs by promoting resilience and empathy.
Benefits of Cultural Exchange
Cultural exchange fosters mutual understanding, enhances communication skills, and broadens global perspectives by immersing individuals in diverse traditions and customs. It promotes empathy and tolerance, reducing prejudices and cultural stereotypes through firsthand experiences. Exposure to new languages and social norms during cultural exchange contributes to personal growth and adaptability in multicultural environments.
Common Triggers of Culture Shock
Common triggers of culture shock include language barriers, unfamiliar social norms, and differing communication styles that create confusion and frustration for individuals in new cultural environments. Differences in food, climate, and daily routines often lead to feelings of discomfort and anxiety. Emotional challenges arise from isolation or misunderstanding, impacting one's ability to adapt and engage in cultural exchange effectively.
Coping Strategies for Culture Shock
Coping strategies for culture shock emphasize building social connections, practicing mindfulness, and maintaining routines to foster stability in unfamiliar environments. Immersing oneself in local customs while setting realistic expectations helps reduce anxiety and enhances cultural adaptation. Access to support networks, including expatriate groups and counseling services, further aids emotional resilience during cultural adjustment.
Real-life Examples of Cultural Exchange
Cultural exchange involves sharing traditions, food, language, and customs between communities to foster understanding and appreciation, as seen in international student programs where participants live with host families and experience daily life firsthand. Examples include the Japanese tea ceremony practiced by Western visitors or American volunteers participating in Indian festivals, illustrating immersive learning rather than disorientation. These experiences contrast with culture shock, which often involves feelings of confusion and anxiety when encountering unfamiliar cultural norms for the first time.
How to Maximize Cultural Exchange Experiences
Maximizing cultural exchange experiences requires embracing open-mindedness and active participation in local customs, traditions, and languages to foster genuine understanding. Engaging with diverse communities through shared activities and meaningful conversations helps mitigate culture shock by building familiarity and connection. Documenting experiences and reflecting on cultural differences promotes personal growth and deepens intercultural competence.
Overcoming Culture Shock for Effective Cultural Integration
Overcoming culture shock is essential for effective cultural integration, involving adapting to new social norms, language, and customs while maintaining an open mindset. Engaging in cultural exchange programs enhances understanding, reduces anxiety, and fosters meaningful connections with locals by promoting empathy and active communication. Developing resilience through immersive experiences and support networks accelerates adjustment, ensuring smoother integration into diverse cultural environments.
Cultural Exchange Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com