Digitality transforms how we interact, communicate, and access information by embedding technology into everyday life. It fosters innovation across industries by enabling seamless connectivity and data-driven solutions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how digitality shapes your world and future opportunities.
Table of Comparison
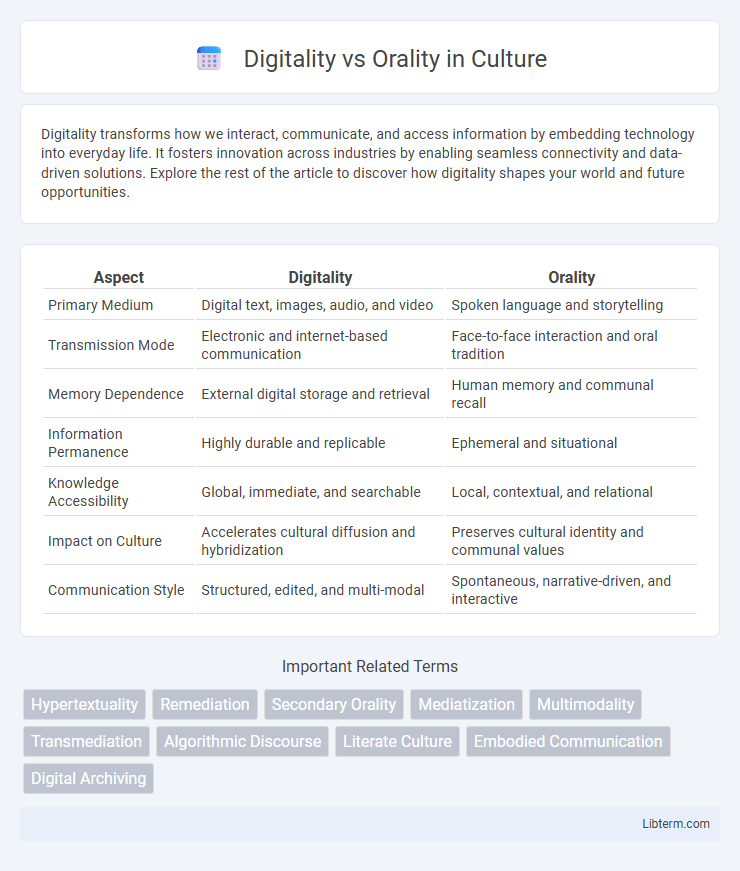
| Aspect | Digitality | Orality |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Medium | Digital text, images, audio, and video | Spoken language and storytelling |
| Transmission Mode | Electronic and internet-based communication | Face-to-face interaction and oral tradition |
| Memory Dependence | External digital storage and retrieval | Human memory and communal recall |
| Information Permanence | Highly durable and replicable | Ephemeral and situational |
| Knowledge Accessibility | Global, immediate, and searchable | Local, contextual, and relational |
| Impact on Culture | Accelerates cultural diffusion and hybridization | Preserves cultural identity and communal values |
| Communication Style | Structured, edited, and multi-modal | Spontaneous, narrative-driven, and interactive |
Defining Digitality and Orality
Digitality refers to the state or condition of expressing, processing, and transmitting information through digital formats, leveraging binary code and electronic technologies for data storage and communication. Orality denotes the tradition and practice of spoken communication, emphasizing memory, face-to-face interaction, and the communal sharing of knowledge without reliance on written or digital records. Understanding digitality involves analyzing digital media's capacity for manipulation and reproduction, while orality centers on immediacy and the performative aspects of spoken word.
Historical Contexts of Communication
The historical contexts of communication reveal a shift from orality, characterized by spoken word and memory-based storytelling in pre-literate societies, to digitality, which emphasizes digitized information and electronic media. Oral cultures relied on communal interaction and mnemonic techniques, whereas digital communication enables rapid, global information exchange and data storage. This transition marks a fundamental change in how knowledge is produced, preserved, and transmitted across generations.
Key Characteristics of Orality
Orality is characterized by the use of spoken language as the primary mode of communication, relying heavily on memory, repetition, and communal participation. Oral cultures emphasize face-to-face interaction, storytelling, and mnemonic devices, fostering collective knowledge through shared experiences rather than written records. The temporal and situational context plays a crucial role in orality, as meaning is often constructed in the moment and tied to social dynamics.
Key Features of Digitality
Digitality is characterized by the encoding, storage, and transmission of information in binary format, enabling rapid and efficient data processing. It facilitates multimedia integration, hypertextuality, and network connectivity, which allow for interactive and non-linear communication. Key features include scalability, replicability without degradation, and the capacity for algorithmic manipulation of content.
Cognitive Effects: Orality vs Digitality
Orality engages cognitive processes such as memory, imagination, and storytelling, fostering strong auditory and interpersonal skills through direct, continuous interaction. Digitality reshapes cognition by emphasizing visual processing, multitasking, and hyperlinked information access, which can alter attention spans and reduce deep, linear thinking. The shift from oral traditions to digital media transforms neural pathways, influencing how individuals encode, retrieve, and prioritize knowledge in everyday communication.
Memory, Storytelling, and Knowledge Transmission
Digitality reshapes memory by externalizing information storage, allowing instantaneous access and extensive archiving beyond human cognitive limits. Storytelling evolves through multimedia integration, blending text, audio, and visuals to enhance narrative engagement and retention across diverse platforms. Knowledge transmission accelerates globally via digital networks, facilitating collaborative learning while challenging traditional oral methods reliant on communal and mnemonic practices.
Social Dynamics and Community Formation
Digitality transforms social dynamics by enabling instantaneous communication and widespread connectivity, reshaping how communities form and interact beyond physical boundaries. Orality fosters community through shared, face-to-face interactions and oral traditions, emphasizing trust, cultural transmission, and collective memory. The shift from orality to digitality introduces new modes of identity construction and social cohesion, often prioritizing virtual presence and networked participation over direct interpersonal contact.
Impact on Language and Expression
Digitality transforms language by enabling rapid, multimedia-rich communication that blends text, images, and sounds, enhancing expression beyond traditional verbal forms. Orality emphasizes face-to-face interaction, relying on tone, gesture, and memory, which fosters spontaneity and communal bonding in storytelling. The shift from orality to digitality alters linguistic structures, favoring brevity, immediacy, and interactivity, thereby reshaping how meaning is constructed and shared.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Digital Age
Digitality transforms traditional orality by enabling instantaneous global communication while challenging the preservation of nuanced oral traditions and cultural contexts. The shift to digital platforms presents opportunities for enhanced accessibility, multimedia storytelling, and interactive engagement in knowledge transmission. However, it raises concerns about digital literacy gaps, information overload, and the potential erosion of deep interpersonal connections found in face-to-face oral exchanges.
Future Trends in Communication Modalities
Future trends in communication modalities will increasingly favor digitality due to advancements in artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and real-time data transmission, enhancing interactive and immersive experiences. Orality will persist in contexts where personal connection, emotional nuance, and cultural traditions are paramount, supported by emerging voice technologies and speech recognition systems. Hybrid communication models combining digital and oral elements are expected to dominate, fostering seamless integration across virtual and physical environments.
Digitality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com