High culture encompasses the refined arts, literature, music, and intellectual achievements that have shaped civilizations throughout history. It reflects society's highest values and aesthetic standards, influencing education, beliefs, and social norms. Explore the rest of the article to understand how high culture impacts your world and personal growth.
Table of Comparison
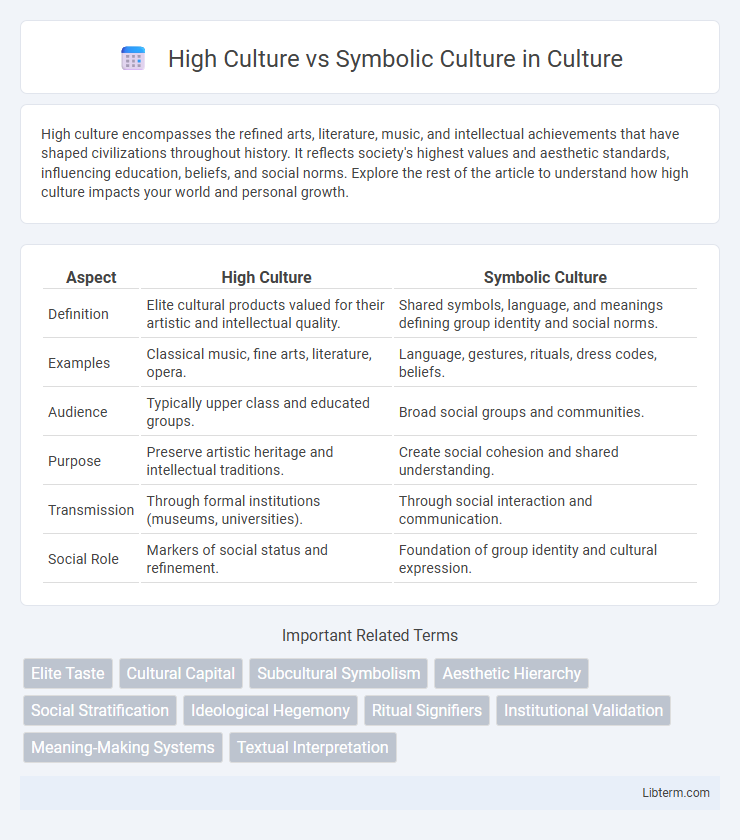
| Aspect | High Culture | Symbolic Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elite cultural products valued for their artistic and intellectual quality. | Shared symbols, language, and meanings defining group identity and social norms. |
| Examples | Classical music, fine arts, literature, opera. | Language, gestures, rituals, dress codes, beliefs. |
| Audience | Typically upper class and educated groups. | Broad social groups and communities. |
| Purpose | Preserve artistic heritage and intellectual traditions. | Create social cohesion and shared understanding. |
| Transmission | Through formal institutions (museums, universities). | Through social interaction and communication. |
| Social Role | Markers of social status and refinement. | Foundation of group identity and cultural expression. |
Defining High Culture: Core Concepts
High culture encompasses the artistic, intellectual, and cultural products deemed valuable by a society's elite, including classical music, fine arts, literature, and philosophy. It often signifies enduring, sophisticated achievements that reflect refined tastes and historical significance, distinguishing it from popular or mass culture. Symbolic culture, on the other hand, involves the meanings, symbols, language, and rituals that shape social experiences and identity, serving as the framework through which high culture gains significance and transmitted value.
Understanding Symbolic Culture: An Overview
Symbolic culture encompasses the ideas, norms, language, and values that a society uses to communicate and interpret reality, serving as a framework for social behavior and identity. Unlike high culture, which emphasizes refined artistic and intellectual achievements often accessible to an elite, symbolic culture includes everyday symbols and rituals that shape collective meaning across all social groups. Understanding symbolic culture involves analyzing how symbols like language, gestures, and artifacts influence perception, social cohesion, and cultural transmission within diverse populations.
Historical Development of High and Symbolic Culture
High culture historically evolved from aristocratic and elite traditions, encompassing classical arts, literature, and formal rituals tied to social status and education. Symbolic culture developed alongside by emphasizing shared symbols, language, and meanings that unify groups beyond elite circles, reflecting collective identities and social cohesion. Both forms have continuously interacted, shaping societal values and cultural narratives throughout history.
Key Differences between High Culture and Symbolic Culture
High culture refers to the set of cultural products, such as classical music, fine arts, and literature, valued by elite or dominant social groups, often associated with established institutions and tradition. Symbolic culture encompasses the broader system of symbols, language, norms, and rituals that shape collective identity and social meanings across all societal levels. The key difference lies in high culture's emphasis on exclusive refinement and aesthetic standards, while symbolic culture emphasizes shared meanings and representations crucial for social cohesion.
Examples of High Culture in Society
High culture in society is exemplified by institutions such as opera houses, classical music orchestras, and fine art museums that showcase works by renowned artists like Beethoven, Picasso, and Shakespeare. Prestigious events such as the Met Gala, the Cannes Film Festival, and the Pulitzer Prize ceremonies also highlight high culture by celebrating achievements in fashion, cinema, and literature. These examples contrast with symbolic culture, which encompasses shared symbols, language, and rituals integral to everyday social interactions rather than elite artistic expression.
Symbols and Meanings: Elements of Symbolic Culture
Symbols in symbolic culture serve as powerful tools conveying complex meanings, shaping social interactions through shared understandings of language, gestures, and rituals. High culture often incorporates these symbols in refined artistic expressions, literature, and ceremonial practices, reflecting societal values and historical continuity. Elements of symbolic culture such as myths, norms, and beliefs function as frameworks that inform both individual identity and collective cultural narratives.
Influence of High Culture on Social Stratification
High culture, characterized by elite art, literature, and classical music, reinforces social stratification by signaling wealth, education, and status, creating barriers to upward mobility. Access to high culture often depends on socioeconomic background, perpetuating class divisions through cultural capital and exclusive institutions. This influence solidifies social hierarchies by associating prestige and power with cultural consumption patterns.
Role of Symbolic Culture in Everyday Life
Symbolic culture encompasses the ideas, beliefs, values, and language that shape social interactions and daily behavior, providing individuals with a framework for interpreting their experiences. It influences everyday life by guiding communication patterns, social norms, and personal identities through shared symbols like language, gestures, and rituals. Unlike high culture, which is often associated with elite art and intellectual pursuits, symbolic culture permeates all social strata, making it essential for understanding group cohesion and cultural continuity.
Globalization and the Evolution of Cultural Forms
High culture and symbolic culture undergo significant transformation through globalization, which facilitates the exchange and hybridization of cultural symbols across diverse societies. The evolution of cultural forms is marked by the blending of elite artistic expressions with popular symbolic practices, creating new cultural dynamics that transcend traditional boundaries. Global communication technologies accelerate the diffusion of cultural symbols, leading to the emergence of transnational identities and reshaped perceptions of cultural heritage.
Impact of High and Symbolic Culture on Identity
High culture, characterized by classical art, literature, and elite cultural practices, profoundly shapes individual and collective identity by reinforcing social status and heritage. Symbolic culture, including language, rituals, and symbols, influences identity by enabling shared meanings and social cohesion within communities. Both forms of culture contribute to identity formation, with high culture often emphasizing prestige and tradition, while symbolic culture fosters everyday communication and group membership.
High Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com