Art transcends mere aesthetics by evoking emotions and provoking thought through visual, auditory, or performative expressions. It serves as a powerful medium for cultural storytelling, personal reflection, and social commentary, connecting people across time and space. Explore the rest of this article to discover how art shapes our world and inspires your creativity.
Table of Comparison
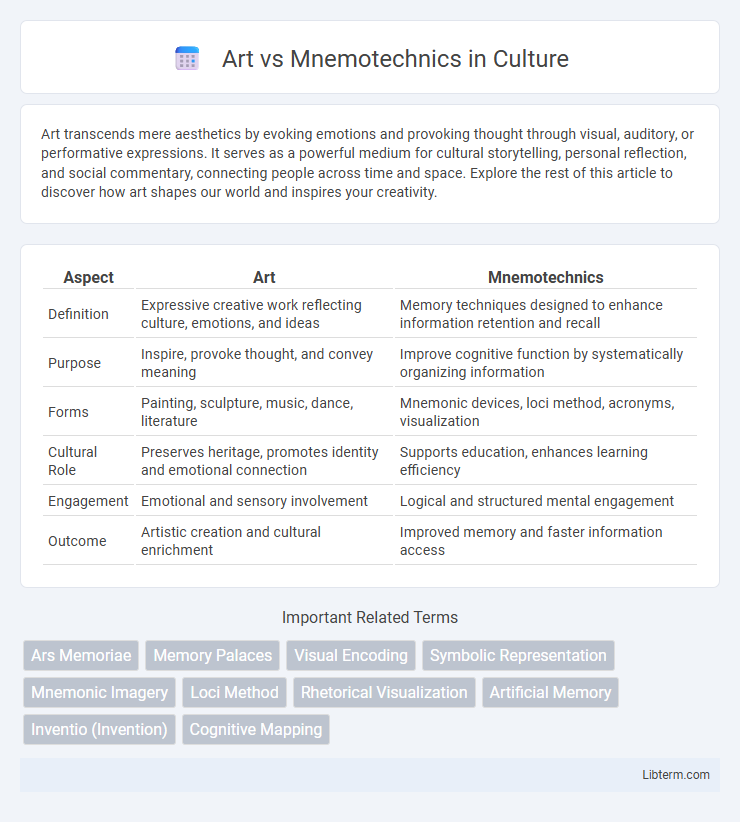
| Aspect | Art | Mnemotechnics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expressive creative work reflecting culture, emotions, and ideas | Memory techniques designed to enhance information retention and recall |
| Purpose | Inspire, provoke thought, and convey meaning | Improve cognitive function by systematically organizing information |
| Forms | Painting, sculpture, music, dance, literature | Mnemonic devices, loci method, acronyms, visualization |
| Cultural Role | Preserves heritage, promotes identity and emotional connection | Supports education, enhances learning efficiency |
| Engagement | Emotional and sensory involvement | Logical and structured mental engagement |
| Outcome | Artistic creation and cultural enrichment | Improved memory and faster information access |
Defining Art and Mnemotechnics
Art encompasses creative expression through various mediums such as painting, sculpture, music, and literature, aiming to evoke emotions and provoke thought. Mnemotechnics, or mnemonic techniques, involve strategies and methods specifically designed to improve memory retention and recall, often employing visualization, association, and structured organization. While art appeals to aesthetic and emotional sensibilities, mnemotechnics prioritizes cognitive enhancement and practical application in learning processes.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Art and mnemotechnics have distinct historical origins, with art tracing back to prehistoric cave paintings over 40,000 years ago, reflecting early human creativity and expression. Mnemotechnics, or mnemonic techniques, originated in ancient Greece around 500 BCE, notably attributed to Simonides of Ceos, who developed memory systems to enhance oral tradition and rhetoric. Over centuries, art evolved through movements like Renaissance, Baroque, and Modernism, while mnemotechnics advanced with methods such as the Method of Loci and the Major System, integrating into educational and cognitive sciences.
Core Principles: Creativity vs. Memory Aids
Art emphasizes creativity, expression, and emotional resonance as core principles, fostering innovation and unique perspectives through imaginative techniques. Mnemotechnics centers on structured memory aids and cognitive strategies designed to enhance recall and information retention using patterns, imagery, and association methods. Balancing creative interpretation in art with systematic mnemonic devices highlights the fundamental distinction between imaginative exploration and efficient memory optimization.
Techniques and Methodologies Compared
Art relies on intuitive creativity, emotional expression, and spontaneous techniques such as brushwork, color theory, and composition to convey meaning and evoke responses. Mnemotechnics employs structured cognitive strategies like visualization, association, and the method of loci to enhance memory retention and recall efficiency. While art techniques emphasize sensory engagement and aesthetic experience, mnemotechnics prioritize systematic encoding and retrieval processes for learning and information management.
Cognitive Impact: Expression vs. Retention
Art enhances cognitive function by engaging emotional and sensory pathways, fostering creative expression and deeper understanding of complex ideas. Mnemotechnics primarily improve memory retention through structured techniques like visualization and association, strengthening neural connections for efficient recall. Combining both leverages expressive engagement with robust memory, optimizing cognitive performance.
Role in Education and Learning
Art enhances education by stimulating creativity, critical thinking, and emotional engagement, facilitating deeper understanding and retention of complex concepts. Mnemotechnics employs structured memory techniques, such as acronyms and visualization, to improve recall accuracy and learning efficiency. Both play complementary roles in education; art fosters holistic cognitive development, while mnemotechnics provides practical tools for systematic memorization.
Cultural Significance and Applications
Art and mnemotechnics both serve crucial cultural roles, with art expressing human creativity through diverse mediums while mnemotechnics enhances memory retention using structured techniques such as loci and visualization. Cultural significance in art is evident in its ability to convey historical narratives, social values, and collective identities, whereas mnemotechnics underpins educational practices and oral traditions by improving information recall and transmission. Applications of art range from galleries and public installations to therapeutic settings, while mnemotechnics is widely used in academic learning, competitive memory sports, and cognitive therapy.
Notable Figures and Pioneers
Giulio Camillo revolutionized memory techniques with his "Theater of Memory," blending art and mnemonics for knowledge retention. Frances Yates extensively researched Renaissance mnemotechnics, highlighting the interplay of art, imagination, and memory. Giordano Bruno further advanced mnemonic art through complex memory systems combining symbolic imagery and philosophical ideas.
Modern Usage and Digital Transformation
Modern usage of art in digital transformation integrates immersive technologies such as virtual reality and AI-generated content to enhance creativity and user engagement. Mnemotechnics, traditionally mnemonic devices, have evolved into digital memory aids like apps and software that optimize information retention through interactive and personalized learning experiences. Both fields leverage advanced algorithms and data analytics to tailor experiences, blending aesthetics with cognitive enhancement in contemporary digital environments.
Future Perspectives: Integration or Divergence
Future perspectives on Art vs Mnemotechnics highlight the potential integration of creative expression with advanced memory techniques through emerging technologies like AI and neuroenhancement. The fusion of artistic approaches and cognitive science could enhance memory retention and experiential learning, fostering innovative educational tools. However, divergent paths remain possible as art emphasizes subjective interpretation while mnemotechnics prioritizes systematic memory improvement, leading to distinct evolutionary trajectories in each field.
Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com