Spiritual culture shapes the way individuals connect with their inner selves and the world around them, fostering a sense of purpose and belonging. It encompasses rituals, beliefs, and practices that nurture personal growth and communal harmony. Dive deeper into the article to explore how spiritual culture can enrich your life and perspective.
Table of Comparison
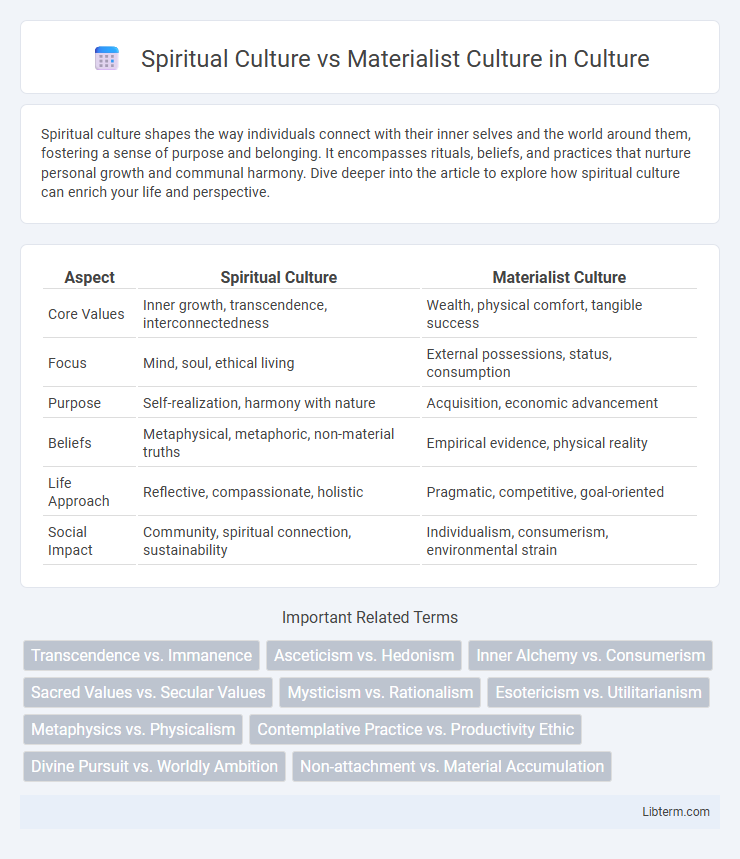
| Aspect | Spiritual Culture | Materialist Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Core Values | Inner growth, transcendence, interconnectedness | Wealth, physical comfort, tangible success |
| Focus | Mind, soul, ethical living | External possessions, status, consumption |
| Purpose | Self-realization, harmony with nature | Acquisition, economic advancement |
| Beliefs | Metaphysical, metaphoric, non-material truths | Empirical evidence, physical reality |
| Life Approach | Reflective, compassionate, holistic | Pragmatic, competitive, goal-oriented |
| Social Impact | Community, spiritual connection, sustainability | Individualism, consumerism, environmental strain |
Defining Spiritual Culture and Materialist Culture
Spiritual culture emphasizes inner values, personal growth, and connection to higher consciousness or universal truths, often rooted in religious, philosophical, or mystical traditions. Materialist culture prioritizes physical possessions, economic success, and tangible achievements, focusing on external wealth and sensory experiences as measures of fulfillment. These cultures represent contrasting worldviews shaping individual behavior and societal development.
Historical Roots of Spiritual and Materialist Philosophies
Spiritual culture traces its roots to ancient religious and metaphysical traditions such as Vedanta, Taoism, and Neoplatonism, emphasizing inner transcendence and the interconnectedness of all life. Materialist culture originates from early Greek atomism, Enlightenment empiricism, and Marxist theory, prioritizing physical reality, scientific inquiry, and economic structures. These historical foundations shaped contrasting worldviews that influence contemporary debates on meaning, existence, and societal values.
Core Values in Spiritual vs Materialist Societies
Spiritual cultures prioritize inner peace, compassion, and interconnectedness as core values, emphasizing personal growth and collective well-being over tangible wealth. Materialist cultures focus on economic success, consumerism, and individual achievement, valuing possessions and status as primary indicators of fulfillment. The divergence in core values influences social behaviors, decision-making processes, and overall life satisfaction within these societies.
The Role of Religion and Spirituality
Religion and spirituality shape spiritual culture by promoting values such as compassion, inner peace, and transcendence, emphasizing personal growth and communal harmony. Materialist culture prioritizes tangible success and consumerism, often sidelining spiritual beliefs in favor of economic and technological advancement. The role of religion in spiritual culture provides moral frameworks and existential meaning, contrasting with the materialist focus on physical wealth and external achievements.
Material Pursuits and Consumerism
Materialist culture emphasizes the accumulation of wealth, possessions, and status as key measures of success, driving consumerism through advertising and societal pressures. This focus on material pursuits often leads to prioritizing short-term gratification and external validation over inner fulfillment and sustainable living. Consumerism fosters a cycle of continuous spending and desire for new products, potentially resulting in environmental degradation and diminished spiritual well-being.
Influence on Personal Identity and Purpose
Spiritual culture shapes personal identity by fostering a sense of inner purpose rooted in values, meaning, and connection beyond the physical world, guiding individuals toward self-awareness and fulfillment. Materialist culture emphasizes external achievements and possessions, influencing identity through social status and measurable success, often linking purpose to wealth and tangible goals. The divergence between these cultures impacts how individuals define themselves and their life's mission, either through transcendental principles or empirical validation.
Social Behaviors and Community Structures
Spiritual culture emphasizes collective well-being, fostering social behaviors centered on empathy, cooperation, and shared rituals that strengthen community bonds. In contrast, materialist culture often promotes individual achievement, competitiveness, and consumption-driven interactions, leading to more fragmented and hierarchical community structures. These differing value systems influence how social support networks and communal responsibilities are organized and maintained.
Impact on Environmental and Ethical Attitudes
Spiritual culture emphasizes interconnectedness with nature, fostering ethical attitudes that prioritize environmental stewardship and sustainable living practices. In contrast, materialist culture often promotes consumption and resource exploitation, resulting in weaker environmental concern and ethical considerations. This divergence significantly influences global efforts toward ecological preservation and social responsibility.
Challenges and Conflicts Between Spiritual and Materialist Cultures
Spiritual culture emphasizes inner growth, values harmony, and prioritizes meaning over wealth, creating tension with materialist culture, which centers on economic success and consumerism. Conflicts arise as materialist values often lead to environmental degradation and social inequality, challenging the spiritual ideals of interconnectedness and ethical living. This clash manifests in societal debates over priorities, lifestyle choices, and the purpose of human existence.
Pathways Toward Cultural Balance and Integration
Pathways toward cultural balance and integration involve recognizing the complementary strengths of spiritual culture's emphasis on inner growth and ethical values with materialist culture's focus on technological advancement and economic development. Fostering dialogues that bridge spirituality and materialism can encourage holistic development, where innovation serves human well-being and ecological sustainability. Integrative frameworks promote education systems and community practices that value both transcendent purpose and practical achievements, leading to a more harmonious societal evolution.
Spiritual Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com