Status reflects the current condition or state of an object, person, or situation, often indicating progress, availability, or position. Understanding status is crucial for effective communication, decision-making, and tracking changes over time. Explore the rest of the article to learn how your awareness of status can enhance productivity and clarity.
Table of Comparison
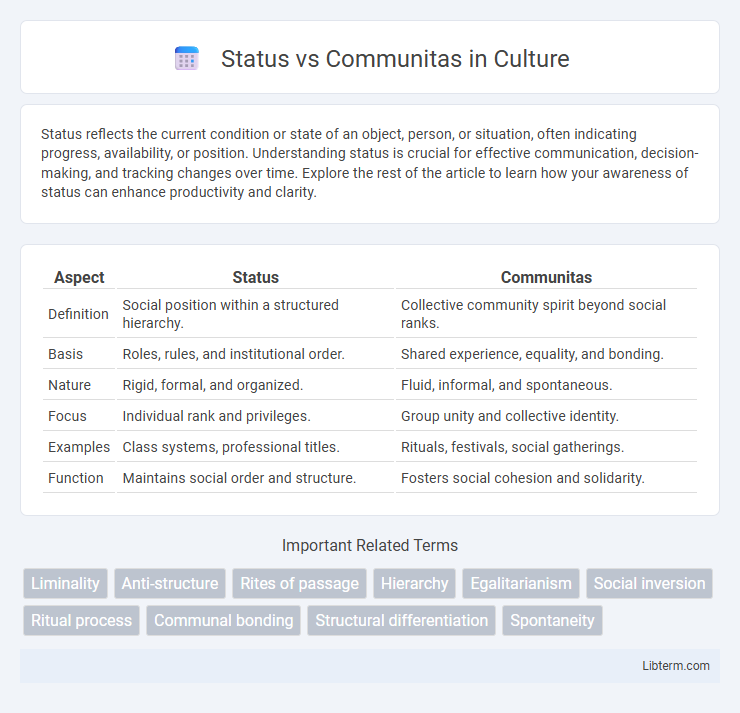
| Aspect | Status | Communitas |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social position within a structured hierarchy. | Collective community spirit beyond social ranks. |
| Basis | Roles, rules, and institutional order. | Shared experience, equality, and bonding. |
| Nature | Rigid, formal, and organized. | Fluid, informal, and spontaneous. |
| Focus | Individual rank and privileges. | Group unity and collective identity. |
| Examples | Class systems, professional titles. | Rituals, festivals, social gatherings. |
| Function | Maintains social order and structure. | Fosters social cohesion and solidarity. |
Defining Status and Communitas
Status refers to a socially recognized position or rank within a structured hierarchy, often associated with roles, titles, and responsibilities that define one's place in a community. Communitas, in contrast, describes a sense of collective unity and equality experienced during moments of shared ritual or liminality, where social distinctions temporarily dissolve. The distinction between status as a fixed social stratification and communitas as an ephemeral communal bonding highlights their complementary roles in social organization and human experience.
Historical Perspectives on Social Hierarchies
Historical perspectives on social hierarchies emphasize the contrast between status, defined by fixed social roles and institutionalized power, and communitas, representing spontaneous, equalizing communal bonds. Status systems were prominent in feudal societies where rigid class distinctions structured political and economic relationships. Communitas emerged in ritualistic or liminal contexts, challenging hierarchical order through shared experiences that fostered social cohesion.
Status: The Structure of Social Order
Status in social theory refers to the hierarchical organization of individuals within a society based on roles, privileges, and power. It structures social order through recognized positions that dictate expected behaviors and relationships, reinforcing norms and institutions. This formalized system contrasts with communitas by emphasizing stability, roles, and social differentiation.
Communitas: The Emergence of Collective Unity
Communitas represents a profound form of social cohesion characterized by spontaneous, unstructured communal unity that arises during shared experiences, transcending formal status hierarchies. This collective unity fosters equality, mutual support, and a sense of belonging that contrasts with the rigid roles and expectations inherent in structured social statuses. Emphasizing Communitas reveals its essential role in strengthening social bonds and enabling transformative communal dynamics beyond conventional social order.
Status and Communitas in Rituals
Status in rituals refers to the structured social positions individuals occupy, often defined by hierarchy, roles, and expectations within the community. Communitas represents the spontaneous, egalitarian bond that forms among participants during rituals, transcending social distinctions to create a shared sense of unity and belonging. Rituals balance status and communitas by simultaneously reinforcing social order and fostering collective emotional experiences.
Power Dynamics: Authority vs. Equality
Status represents a hierarchical power dynamic where authority is derived from social roles and institutional positions, often reinforcing control and obedience. In contrast, communitas embodies an egalitarian power structure characterized by shared experiences and mutual support, dissolving conventional authority boundaries. This tension between authority and equality highlights how power is negotiated differently in structured versus spontaneous social contexts.
Community Building: From Hierarchy to Togetherness
Status in traditional social structures often emphasizes hierarchy and individual roles, while communitas fosters a sense of collective identity and equal belonging within communities. Community building shifts from rigid status distinctions to shared experiences that promote mutual trust and solidarity. This transformation enhances social cohesion and encourages collaborative engagement among diverse members.
Challenges of Balancing Status and Communitas
Balancing status and communitas presents the challenge of maintaining individual recognition while fostering collective belonging, often leading to tension between hierarchical roles and egalitarian group dynamics. The pursuit of status can create divisions or competition that undermine the spontaneous, inclusive nature of communitas. Navigating these dynamics requires careful negotiation to ensure that status does not disrupt the shared sense of community essential for communitas to thrive.
Modern Examples: Status and Communitas Today
In contemporary society, status often manifests through social media followers, job titles, and material wealth, reflecting individual achievements and hierarchical positioning. Communitas emerges in movements like social activism, music festivals, and online communities where shared experiences and collective identity transcend formal structures. These examples highlight the contrast between institutionalized social roles and moments of spontaneous, inclusive togetherness.
Toward a Harmonious Society: Bridging Hierarchy and Unity
Status represents structured social hierarchy defined by roles and institutional power, while communitas embodies spontaneous, egalitarian unity experienced during shared social moments. Bridging status and communitas fosters a harmonious society by integrating order with collective belonging, enabling diverse groups to collaborate without eroding individual dignity. Emphasizing mutual respect and inclusive participation, this balance cultivates social cohesion through both organized roles and shared human connection.
Status Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com