Denotation refers to the explicit, literal meaning of a word or phrase, free from any emotions or associations. Understanding denotation helps you interpret texts clearly and avoid miscommunication caused by subjective interpretations. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of denotation and its role in language.
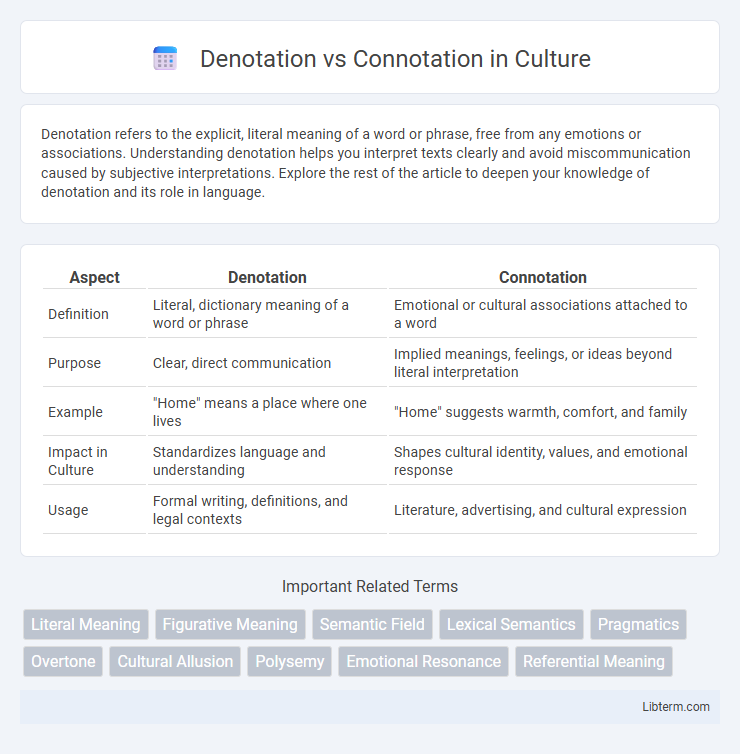
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Denotation | Connotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literal, dictionary meaning of a word or phrase | Emotional or cultural associations attached to a word |
| Purpose | Clear, direct communication | Implied meanings, feelings, or ideas beyond literal interpretation |
| Example | "Home" means a place where one lives | "Home" suggests warmth, comfort, and family |
| Impact in Culture | Standardizes language and understanding | Shapes cultural identity, values, and emotional response |
| Usage | Formal writing, definitions, and legal contexts | Literature, advertising, and cultural expression |
Understanding Denotation: The Literal Meaning
Denotation refers to the explicit, dictionary definition of a word, providing its precise and objective meaning without any emotional or cultural associations. Understanding denotation is essential for clear communication, as it ensures that the intended message is conveyed accurately and unambiguously. This literal meaning serves as the foundation for interpreting language before considering the additional layers of connotation.
Exploring Connotation: The Emotional and Cultural Layer
Connotation involves the emotional and cultural layers that words carry beyond their literal meanings, shaping perception and communication in profound ways. These implied meanings are influenced by historical context, social norms, and personal experiences, making language rich and nuanced. Understanding connotation enhances interpretation in literature, advertising, and everyday conversation by uncovering the deeper significance behind word choices.
Key Differences Between Denotation and Connotation
Denotation refers to the literal, dictionary definition of a word, while connotation involves the emotional or cultural associations it carries beyond its explicit meaning. Key differences include denotation being objective and universally agreed upon, whereas connotation is subjective and varies depending on context, culture, and personal experiences. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective communication, as connotation influences tone and interpretation subtly but powerfully.
Why Word Choice Matters: Impact on Communication
Word choice significantly shapes communication by influencing both the denotation and connotation of language, affecting clarity and emotional response. Denotation provides the precise, literal meaning of a word, establishing clear understanding, while connotation evokes subjective feelings and cultural associations that can alter the message's tone. Selecting words with appropriate denotative accuracy and positive or neutral connotations enhances effective communication, minimizes misunderstandings, and fosters stronger connections with the audience.
Examples of Denotative vs. Connotative Meanings
The word "home" denotes a place where one lives but connotes warmth, security, and family bonds. For instance, a "snake" denotes a legless reptile, while its connotation might evoke danger or deceit. The term "childlike" indicates qualities of a child but often carries positive connotations of innocence and wonder, unlike the neutral denotation.
The Role of Context in Interpreting Meaning
Context shapes the interpretation of denotation and connotation by providing cultural, emotional, and situational cues that influence meaning. Denotation refers to the literal, dictionary definition of a word, while connotation encompasses the associated feelings and implied meanings derived from context. Understanding the surrounding context enables accurate comprehension by distinguishing neutral meanings from subjective, culturally influenced nuances.
Denotation and Connotation in Literature
Denotation in literature refers to the literal, dictionary definition of a word, providing a clear and precise meaning essential for understanding the basic context of a text. Connotation encompasses the emotional, cultural, or symbolic meanings that a word evokes beyond its denotation, enriching the narrative with layers of interpretation and tone. Effective literary analysis distinguishes between denotation and connotation to uncover deeper themes and the author's intent within a work of fiction or poetry.
Effects on Tone and Perception
Denotation refers to the literal meaning of a word, while connotation encompasses the emotional and cultural associations attached to it, significantly influencing tone and perception. Words with positive connotations create a warm, optimistic tone and foster favorable perceptions, whereas negative connotations evoke tension, hostility, or discomfort in the reader. Understanding the interplay between denotation and connotation is essential for writers seeking to shape audience response and effectively convey nuanced meaning.
Avoiding Misunderstandings in Everyday Language
Denotation refers to the literal, dictionary definition of a word, while connotation involves the emotional or cultural associations attached to it. Misunderstandings in everyday language often arise when speakers rely on connotative meanings that differ across contexts or individuals, leading to unintended interpretations. Clarifying both denotative and connotative meanings helps prevent communication breakdowns and promotes clearer interactions.
Tips for Using Denotation and Connotation Effectively
Use denotation to establish clear, unambiguous communication by relying on the literal meanings of words, ensuring your message is straightforward and precise. Incorporate connotation strategically to evoke emotions, create atmosphere, and add depth, selecting words with positive or negative associations that align with your intended tone. Balance both by considering your audience's cultural context and the nuances words may carry to enhance understanding while influencing perception effectively.
Denotation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com