Identity shapes how individuals perceive themselves and connect with the world, encompassing cultural, social, and personal dimensions. It influences behavior, beliefs, and relationships, playing a critical role in personal growth and self-awareness. Explore how understanding your identity can enhance your life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
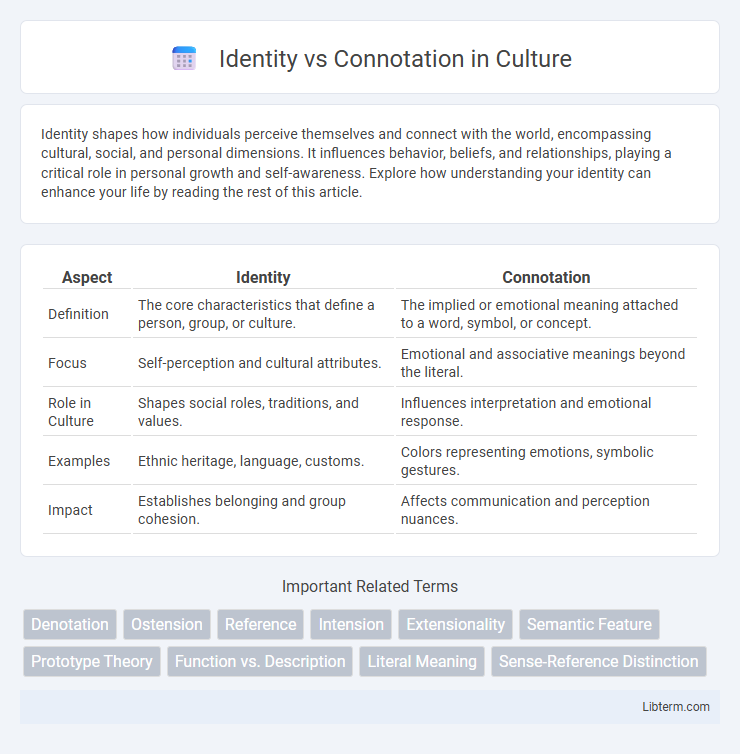
| Aspect | Identity | Connotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The core characteristics that define a person, group, or culture. | The implied or emotional meaning attached to a word, symbol, or concept. |
| Focus | Self-perception and cultural attributes. | Emotional and associative meanings beyond the literal. |
| Role in Culture | Shapes social roles, traditions, and values. | Influences interpretation and emotional response. |
| Examples | Ethnic heritage, language, customs. | Colors representing emotions, symbolic gestures. |
| Impact | Establishes belonging and group cohesion. | Affects communication and perception nuances. |
Understanding Identity: Core Definitions
Identity refers to the distinct characteristics and attributes that define an individual or entity, encompassing aspects such as name, culture, beliefs, and personality traits. Connotation involves the implicit meanings or emotional associations linked to a word or concept beyond its literal definition. Understanding identity requires recognizing both the explicit elements that form one's self-concept and the connotative nuances that influence how identity is perceived and expressed.
Connotation Explained: Beyond Literal Meaning
Connotation refers to the emotions, cultural associations, and implied meanings a word or phrase carries beyond its literal definition. It shapes perception by evoking feelings or ideas that influence interpretation in language, advertising, and communication. Understanding connotation enhances clarity and impact by tapping into shared cultural or emotional undertones.
How Identity Shapes Perception
Identity profoundly influences perception by framing how individuals interpret experiences and social interactions through the lens of their self-concept, cultural background, and personal values. This shaping of perception affects emotional responses, cognitive biases, and the ability to empathize with others, thereby reinforcing or challenging existing identity constructs. Neuroscientific studies suggest that identity-related cues activate specific brain regions responsible for social cognition, highlighting the deep connection between identity and perceptual processes.
The Power of Connotation in Communication
Connotation shapes the emotional and cultural meaning behind words, significantly influencing how messages are interpreted and received in communication. Identity is often communicated implicitly through connotations, revealing values, beliefs, and social affiliations beyond explicit statements. Mastering the power of connotation enables more persuasive and nuanced interactions, fostering deeper understanding and connection between communicators.
Identity vs Connotation in Language
Identity in language defines the inherent characteristics that specify who or what an entity is, while connotation encompasses the associated meanings and emotional nuances that words evoke beyond their literal definitions. Linguistic identity shapes communication by anchoring meaning in cultural, social, or personal contexts, whereas connotation influences perception and interpretation through subjective associations. Understanding the interplay between identity and connotation enhances semantic clarity and effective language use.
The Role of Culture in Identity and Connotation
Culture shapes identity by providing shared symbols, values, and narratives that influence how individuals perceive themselves and are recognized by others. Connotation varies across cultural contexts, as cultural backgrounds assign different emotional and symbolic meanings to words, gestures, and practices. Understanding the cultural underpinnings of identity and connotation enhances communication and fosters intercultural awareness.
Media Influence on Identity and Connotation
Media influence significantly shapes individual and collective identity by framing cultural narratives and societal norms, reinforcing or challenging existing connotations associated with identity markers such as race, gender, and class. Through repeated exposure to media representations, audiences internalize connotative meanings that influence self-perception and social interactions, often perpetuating stereotypes or promoting new identity constructs. The interplay between media-driven connotations and identity formation underscores the power of communication channels in constructing social realities and shaping public consciousness.
Challenges in Distinguishing Identity from Connotation
Distinguishing identity from connotation presents challenges due to the overlapping influence of personal characteristics and societal interpretations on perception. Identity refers to the inherent attributes defining an individual or entity, while connotation encompasses the associated meanings and emotions evoked beyond the literal definition. Misinterpretations arise when societal biases or cultural contexts conflate an individual's true identity with the connotations assigned, complicating accurate understanding and representation.
Real-World Examples: Identity vs Connotation
Brand identity reflects the core attributes and values a company intentionally communicates, such as Nike's emphasis on athletic performance and empowerment. Connotation involves the cultural and emotional associations consumers attach to a brand, seen in how Nike often evokes feelings of motivation and achievement beyond its stated identity. Real-world examples reveal that while Apple's identity centers on innovation and simplicity, the connotation includes creativity and elitism, demonstrating the dynamic interplay between intended image and public perception.
Strategies to Navigate Identity and Connotation
Effective strategies to navigate identity and connotation involve clearly defining brand values and messaging to establish a consistent identity that resonates with target audiences. Employing audience analysis and feedback mechanisms helps align connotations with intended perceptions, reducing misunderstandings. Utilizing narrative storytelling and visual symbolism reinforces identity while managing the connotative impact of brand elements across diverse cultural contexts.
Identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com