Hypernymy is a fundamental semantic relationship where one word, the hypernym, encompasses the meaning of more specific words known as hyponyms. This structure helps organize vocabulary and clarify how concepts relate, such as "vehicle" being a hypernym of "car" and "bicycle." Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of hypernymy and its applications in language.
Table of Comparison
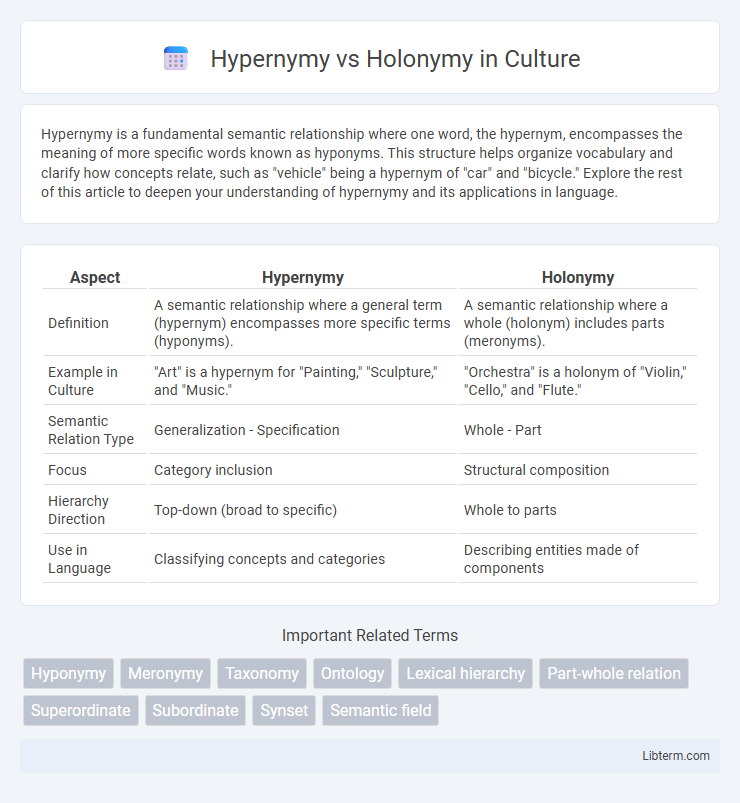
| Aspect | Hypernymy | Holonymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A semantic relationship where a general term (hypernym) encompasses more specific terms (hyponyms). | A semantic relationship where a whole (holonym) includes parts (meronyms). |
| Example in Culture | "Art" is a hypernym for "Painting," "Sculpture," and "Music." | "Orchestra" is a holonym of "Violin," "Cello," and "Flute." |
| Semantic Relation Type | Generalization - Specification | Whole - Part |
| Focus | Category inclusion | Structural composition |
| Hierarchy Direction | Top-down (broad to specific) | Whole to parts |
| Use in Language | Classifying concepts and categories | Describing entities made of components |
Introduction to Semantic Relationships
Hypernymy refers to a relationship where a word represents a general category encompassing more specific instances, such as "vehicle" being a hypernym of "car." Holonymy describes a part-whole relationship where one term denotes the whole and the other its part, for example, "tree" is a holonym of "branch." Understanding these semantic relationships is essential for natural language processing tasks like word sense disambiguation and ontology development.
Defining Hypernymy
Hypernymy is a semantic relationship where a word serves as a general category encompassing more specific terms, known as hyponyms; for example, "animal" is a hypernym of "dog" and "cat." This hierarchical structure enables efficient organization of vocabulary by linking broad concepts to their narrower instances. Understanding hypernymy is essential in natural language processing for tasks like semantic search and word sense disambiguation.
Understanding Holonymy
Holonymy refers to a semantic relationship where a term denotes a whole that includes the parts represented by other terms, such as "tree" being a holonym of "branch" and "leaf." This concept is crucial in natural language understanding and ontology development, enabling machines to accurately interpret hierarchical structures of entities. Unlike hypernymy, which relates to general-to-specific classification, holonymy emphasizes part-whole connections vital for detailed semantic representation.
Key Differences Between Hypernymy and Holonymy
Hypernymy denotes a hierarchical relationship where one term (hypernym) represents a broad category encompassing more specific instances (hyponyms), such as "vehicle" for "car" and "bicycle." Holonymy, by contrast, describes a part-whole relationship where the holonym is the whole entity containing parts (meronyms), for example, "car" as the holonym of "wheel" and "engine." The key difference lies in hypernymy addressing category inclusion based on type, while holonymy emphasizes physical or functional inclusion based on parts and wholes.
Real-World Examples of Hypernymy
Hypernymy involves a hierarchical relationship where a general term (hypernym) encompasses specific instances called hyponyms, such as "vehicle" including cars, trucks, and bicycles. Real-world examples include "animal" as a hypernym for dogs, cats, and elephants, or "fruit" covering apples, bananas, and cherries. This semantic structure aids in categorizing knowledge, improving search algorithms and natural language understanding systems.
Real-World Examples of Holonymy
Holonymy describes a relationship where a term denotes a whole that includes the parts represented by other terms, such as "car" being a holonym of "wheel," "engine," and "door." Real-world examples include "tree" as a holonym of "branch," "leaf," and "trunk," and "computer" as a holonym of "keyboard," "monitor," and "processor." Understanding holonymy is essential for natural language processing tasks that involve part-whole hierarchies in knowledge representation and semantic analysis.
Functions and Uses in Linguistics
Hypernymy and holonymy serve distinct functions in linguistics by organizing vocabulary through hierarchical relationships: hypernymy defines a general category encompassing more specific subcategories (hyponyms), aiding in semantic classification and lexical retrieval. Holonymy establishes part-whole relationships, linking a whole entity to its parts (meronyms), facilitating understanding of compositional structure and semantic integration. Both relations enhance lexicon organization, semantic parsing, and natural language processing tasks by enabling nuanced meaning representation and disambiguation.
Hypernymy and Holonymy in Natural Language Processing
Hypernymy in Natural Language Processing (NLP) involves identifying hierarchical relationships where a word (hypernym) represents a general category encompassing more specific instances (hyponyms), enabling tasks like ontology building and semantic search. Holonymy, by contrast, captures part-whole relationships between words, where a holonym denotes the whole to which other words (meronyms) belong, which is crucial for understanding context in text comprehension and information extraction. Effective modeling of hypernymy and holonymy enhances NLP applications such as word sense disambiguation and knowledge graph construction by providing rich semantic context.
Common Confusions and How to Avoid Them
Hypernymy involves a relationship where one term is a general category encompassing more specific instances, such as "vehicle" for "car" and "bike," whereas holonymy refers to a whole-part relationship, like "car" being the whole of which "engine" is a part. Common confusions arise when learners mistake hyponymy (instances under a category) for meronymy (parts of a whole), leading to errors in semantic categorization and language comprehension. To avoid these mistakes, focus on identifying whether the relationship describes class inclusion (hypernymy) or part-whole composition (holonymy), using clear examples and context to distinguish the semantic boundaries.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Semantic Relations
Understanding semantic relations like hypernymy and holonymy is crucial for language processing, knowledge representation, and improving search algorithms. Hypernymy reveals hierarchical relationships by linking general categories to specific instances, while holonymy connects whole objects to their parts, enriching comprehension of object structures. Mastery of these distinctions enhances natural language understanding and supports advanced AI applications in linguistics and information retrieval.
Hypernymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com