Symbolic interactionism explores how individuals create meaning through social interactions using symbols, language, and gestures. This theory highlights the importance of perception and interpretation in shaping human behavior and societal norms. Discover how symbolic interactionism influences communication and relationships in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
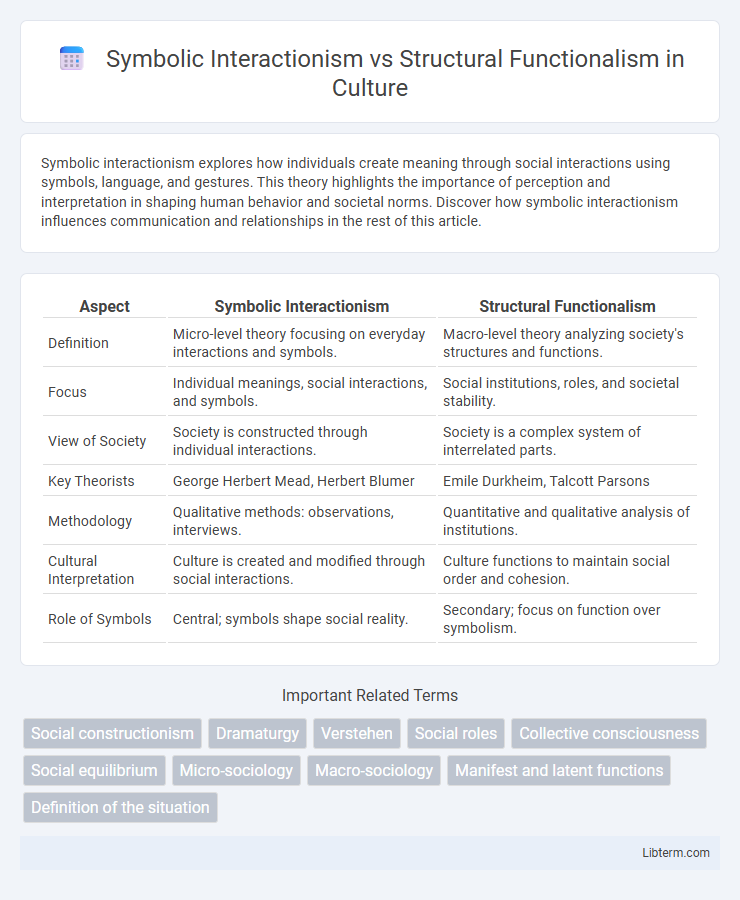
| Aspect | Symbolic Interactionism | Structural Functionalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Micro-level theory focusing on everyday interactions and symbols. | Macro-level theory analyzing society's structures and functions. |
| Focus | Individual meanings, social interactions, and symbols. | Social institutions, roles, and societal stability. |
| View of Society | Society is constructed through individual interactions. | Society is a complex system of interrelated parts. |
| Key Theorists | George Herbert Mead, Herbert Blumer | Emile Durkheim, Talcott Parsons |
| Methodology | Qualitative methods: observations, interviews. | Quantitative and qualitative analysis of institutions. |
| Cultural Interpretation | Culture is created and modified through social interactions. | Culture functions to maintain social order and cohesion. |
| Role of Symbols | Central; symbols shape social reality. | Secondary; focus on function over symbolism. |
Introduction to Symbolic Interactionism and Structural Functionalism
Symbolic Interactionism emphasizes micro-level social interactions, focusing on how individuals create and interpret symbols to construct social reality. Structural Functionalism examines society at a macro level, viewing social institutions as interconnected parts that work together to maintain social stability and order. Both theories offer distinct lenses: Symbolic Interactionism highlights subjective meanings, while Structural Functionalism prioritizes social structures and functions.
Defining Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic Interactionism is a sociological framework that emphasizes the micro-level interactions between individuals and the meanings they assign to symbols, language, and gestures in everyday life. It contrasts with Structural Functionalism, which analyzes society at a macro-level, focusing on social structures and their functional roles in maintaining stability and order. Key theorists in Symbolic Interactionism include George Herbert Mead and Herbert Blumer, who highlight the dynamic and interpretive process of social interaction.
Core Principles of Structural Functionalism
Structural Functionalism centers on the core principle that society is a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability. Key components include social institutions, norms, and roles that function to maintain the social order and fulfill necessary societal needs. This perspective views social structures as interdependent, each contributing to the functioning and equilibrium of society as a whole.
Key Theorists and Historical Development
Symbolic Interactionism, pioneered by George Herbert Mead and further developed by Herbert Blumer in the early 20th century, emphasizes micro-level social interactions and the creation of meaning through symbols. Structural Functionalism, prominently advanced by Emile Durkheim and later Talcott Parsons, focuses on macro-level social systems and their role in maintaining societal stability and cohesion since the mid-20th century. The historical development of these theories reflects a shift from analyzing individual agency in social contexts to understanding the function of social institutions in larger societal structures.
Methods and Approaches Used in Each Theory
Symbolic Interactionism employs qualitative methods such as ethnography, participant observation, and in-depth interviews to explore how individuals create meaning through daily interactions. Structural Functionalism relies on quantitative approaches including surveys, statistical analysis, and large-scale demographic data to examine how social institutions maintain stability and order. Both theories offer distinct analytical frameworks, with Symbolic Interactionism focusing on micro-level social processes and Structural Functionalism emphasizing macro-level social structures.
Understanding Society: Micro vs Macro Perspectives
Symbolic Interactionism examines society through micro-level interactions, highlighting how individuals create and interpret social meanings in daily life. Structural Functionalism analyzes society at the macro level, emphasizing how social institutions work together to maintain stability and social order. Understanding society requires integrating these perspectives to capture both individual agency and systemic structures.
Social Institutions through Different Lenses
Symbolic Interactionism examines social institutions by focusing on individual interactions and the meanings people attach to roles, rituals, and symbols within institutions like family, education, and religion. Structural Functionalism views social institutions as components of a larger societal system, emphasizing their functions in maintaining social order, stability, and cohesion through established norms and roles. These contrasting perspectives highlight micro-level processes of meaning-making versus macro-level functions and structures in understanding the role of social institutions.
Criticisms and Limitations
Symbolic Interactionism faces criticism for its lack of macro-level analysis, making it difficult to address large-scale social structures and systemic issues. Structural Functionalism is often criticized for overlooking social change and inequality by emphasizing social order and stability. Both theories exhibit limitations in fully explaining the complexities of social behavior and interactions across diverse contexts.
Real-world Applications and Examples
Symbolic Interactionism explains how individuals create meaning through social interactions, evident in everyday communication, identity formation, and group dynamics, such as how people interpret gestures or symbols in multicultural workplaces. Structural Functionalism analyzes society as a system of interconnected parts, highlighting institutions like family, education, and religion that maintain social order and stability, demonstrated by how schools socialize children and reinforce societal norms. Real-world applications show Symbolic Interactionism's relevance in understanding micro-level social processes, while Structural Functionalism provides insights into macro-level social structures and their functions in maintaining social cohesion.
Conclusion: Comparing Their Explanatory Power
Symbolic Interactionism offers deep insights into individual behaviors and social interactions through the interpretation of symbols, emphasizing subjective experiences and meanings. Structural Functionalism provides a macro-level analysis, explaining social stability and cohesion by highlighting the roles institutions play in maintaining societal order. Comparing their explanatory power reveals that Symbolic Interactionism excels in understanding micro-level social dynamics, while Structural Functionalism is more effective in addressing large-scale social structures and their functional interrelationships.
Symbolic Interactionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com