Tradition shapes cultures and communities by preserving values, customs, and beliefs passed down through generations. It offers a sense of identity and continuity, reinforcing social bonds and guiding behavior in familiar ways. Explore the rest of the article to understand how tradition influences your life and society today.
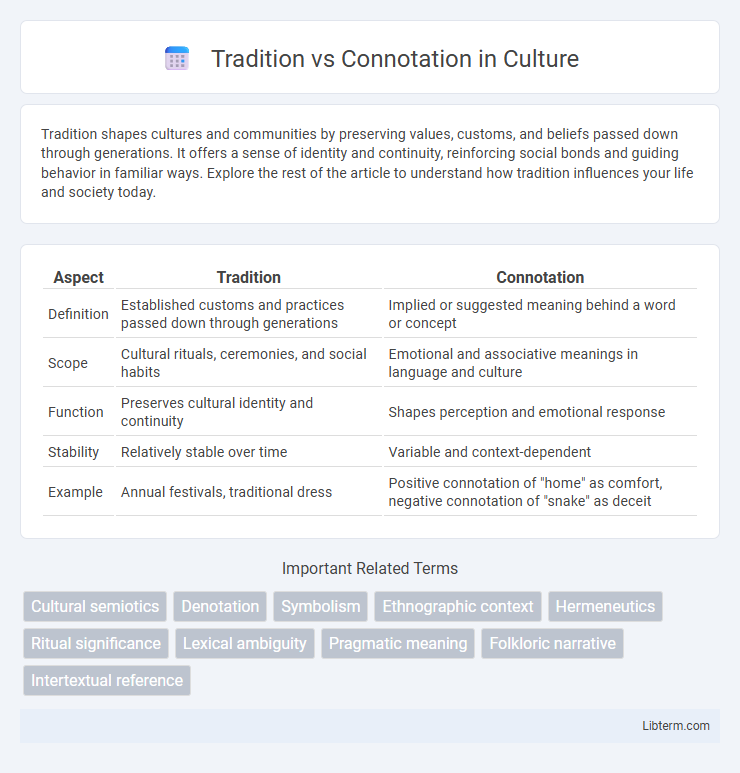
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tradition | Connotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Established customs and practices passed down through generations | Implied or suggested meaning behind a word or concept |
| Scope | Cultural rituals, ceremonies, and social habits | Emotional and associative meanings in language and culture |
| Function | Preserves cultural identity and continuity | Shapes perception and emotional response |
| Stability | Relatively stable over time | Variable and context-dependent |
| Example | Annual festivals, traditional dress | Positive connotation of "home" as comfort, negative connotation of "snake" as deceit |
Understanding Tradition: Roots and Roles
Tradition represents the inherited customs, beliefs, and practices passed down through generations, serving as a foundation for cultural identity and social continuity. Understanding tradition involves exploring its historical roots and the roles it plays in shaping community values, rituals, and social norms. This deep comprehension highlights how traditions influence behavior, reinforce group cohesion, and provide a sense of belonging within societies.
The Evolution of Connotation in Society
The evolution of connotation in society reflects shifting cultural values and social dynamics, transforming traditional meanings into new associations that influence communication and perception. Words and symbols once rooted in fixed traditions acquire nuanced interpretations as collective experiences and historical contexts change. This semantic shift demonstrates how language adapts to contemporary societal norms, shaping identity and influencing social interactions.
Tradition vs Connotation: Defining the Terms
Tradition refers to the long-established customs, beliefs, or practices passed down through generations, forming a collective cultural identity. Connotation involves the implied or emotional meanings associated with a word or concept beyond its literal definition. Understanding the distinction between tradition and connotation reveals how cultural practices carry both explicit functions and nuanced symbolic interpretations.
Historical Perspectives on Tradition
Historical perspectives on tradition reveal its role as a repository of collective memory, shaping cultural identity through rituals, customs, and social norms passed down generations. Traditions often embody symbolic meanings that influence contemporary values and behaviors, reflecting a community's interpretations and adaptations over time. This dynamic interplay between maintaining continuity and evolving connotations highlights tradition's function as both a stabilizing force and a subject to redefinition within historical contexts.
How Connotation Shapes Cultural Norms
Connotation profoundly influences cultural norms by attaching emotional and associative meanings to traditions, thus shaping collective behavior and societal values. Over time, the positive or negative connotations linked to certain customs can reinforce or alter their acceptance within a community. This dynamic interaction between connotation and tradition helps maintain cultural identity while allowing for gradual adaptation to changing social contexts.
The Impact of Tradition on Modern Values
Tradition shapes modern values by preserving cultural identities and providing continuity across generations, influencing societal norms and behaviors. While traditions often establish foundational principles, evolving interpretations and connotations lead to the redefinition of these values in contemporary contexts. This dynamic interplay between tradition and connotation drives the adaptation and modernization of ethical frameworks in today's society.
Connotation’s Influence on Language and Perception
Connotation significantly shapes language by imbuing words with emotional and cultural associations beyond their literal meanings, influencing how individuals perceive and interpret communication. These implied meanings affect societal attitudes and biases, molding public opinion and interpersonal understanding through subtle nuances in speech and writing. The power of connotation extends to branding, literature, and media, where carefully chosen words evoke specific feelings and imagery that resonate deeply with audiences.
Navigating Conflicts: When Tradition Meets Connotation
Navigating conflicts between tradition and connotation requires a nuanced understanding of cultural values and contemporary interpretations. Traditions carry historical significance that shapes communal identity, while connotations evolve with language and social context, often leading to reinterpretations or challenges to established norms. Effective resolution hinges on balancing respect for traditional practices with awareness of modern connotative shifts to foster mutual understanding and adaptation.
Tradition, Connotation, and Social Change
Tradition embodies long-established customs and practices that shape cultural identity and social continuity, while connotation involves the emotional and associative meanings attached to traditional symbols and rituals. Social change challenges and transforms these traditions by altering their connotations, leading to shifts in collective values and behaviors. The dynamic interplay between tradition and connotation reflects evolving societal norms, where reinterpretation of symbols influences the persistence or adaptation of cultural practices.
Bridging the Gap: Harmonizing Tradition and Connotation
Bridging the gap between tradition and connotation involves understanding how historical practices influence contemporary meanings and social perceptions. Cultural rituals rooted in tradition often carry connotations that evolve over time, reflecting shifts in societal values and language usage. Harmonizing these elements requires a dynamic approach that respects inherited customs while adapting to modern interpretive contexts, ensuring relevance and continuity across generations.
Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com