Assimilation is the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits or social patterns of another group, often leading to the blending of customs and languages. This concept plays a crucial role in how societies evolve, influence identity formation, and impact community dynamics. Discover how assimilation shapes cultures and what it means for Your social interactions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
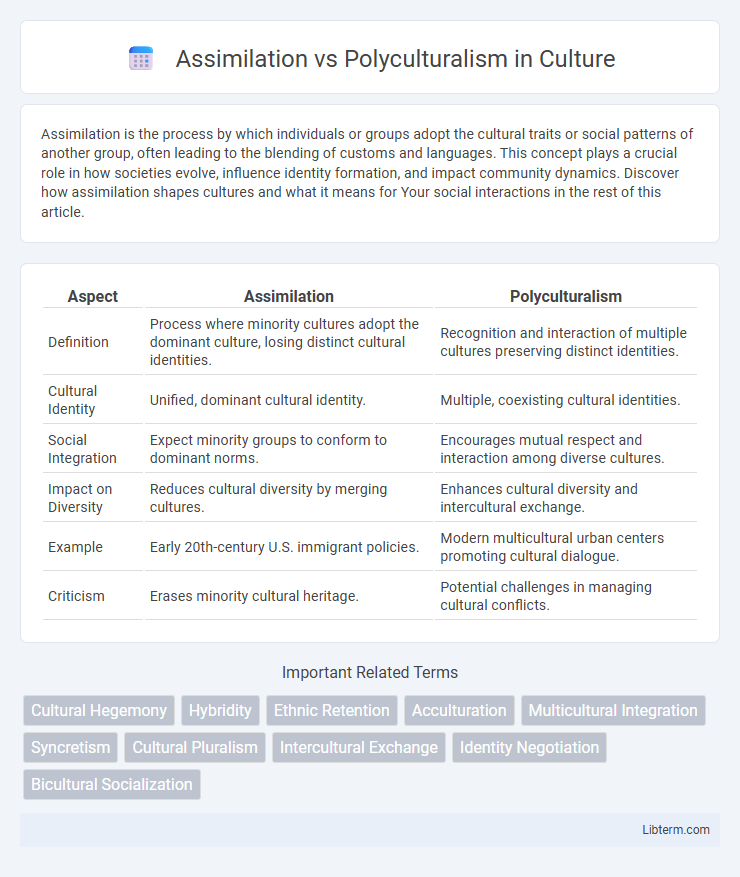
| Aspect | Assimilation | Polyculturalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where minority cultures adopt the dominant culture, losing distinct cultural identities. | Recognition and interaction of multiple cultures preserving distinct identities. |
| Cultural Identity | Unified, dominant cultural identity. | Multiple, coexisting cultural identities. |
| Social Integration | Expect minority groups to conform to dominant norms. | Encourages mutual respect and interaction among diverse cultures. |
| Impact on Diversity | Reduces cultural diversity by merging cultures. | Enhances cultural diversity and intercultural exchange. |
| Example | Early 20th-century U.S. immigrant policies. | Modern multicultural urban centers promoting cultural dialogue. |
| Criticism | Erases minority cultural heritage. | Potential challenges in managing cultural conflicts. |
Understanding Assimilation: Definition and Context
Assimilation involves the process by which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits of a dominant society, often leading to the loss of their original identity and customs. This concept is rooted in contexts where minority groups are expected to conform to the prevailing social norms, language, and values to achieve social integration and acceptance. Understanding assimilation requires examining its historical application in immigration policies and social frameworks that prioritize cultural uniformity over diversity.
Polyculturalism Explained: A Modern Perspective
Polyculturalism emphasizes the interconnectedness of cultures, recognizing the continuous exchange, influence, and blending that shapes identities in multicultural societies. Unlike assimilation, which promotes the absorption of minority cultures into a dominant one, polyculturalism values dynamic cultural interactions that preserve diversity while fostering cooperation and mutual respect. This modern perspective advocates for inclusivity and fluid cultural boundaries, enabling individuals to navigate multiple cultural affiliations simultaneously.
Historical Roots of Assimilation
Assimilation's historical roots trace back to 19th and early 20th century immigration policies in the United States and Europe, where efforts aimed to absorb immigrants into the dominant culture by encouraging language adoption, cultural conformity, and social integration. These policies were often driven by the ideology of cultural homogeneity as a pathway to national unity and economic efficiency. Polyculturalism emerged later as a critique of assimilation's limitations, emphasizing the coexistence and interaction of diverse cultures within a shared society.
The Evolution of Polycultural Societies
Polycultural societies evolve by recognizing and valuing the interconnectedness of diverse cultural identities, contrasting with assimilation's emphasis on conforming to a dominant culture. This evolution promotes dynamic intercultural exchange, fostering social cohesion through mutual respect and the blending of traditions. The ongoing development of polycultural frameworks supports innovation and adaptability in increasingly multicultural environments.
Key Differences Between Assimilation and Polyculturalism
Assimilation involves individuals adopting the dominant culture's values, language, and behaviors, often resulting in the loss of their original cultural identity. Polyculturalism emphasizes the interconnectedness and interaction of multiple cultures, encouraging mutual respect and the blending of cultural traits without erasing distinct identities. Key differences include assimilation's focus on cultural uniformity versus polyculturalism's celebration of cultural diversity and hybridity.
Cultural Identity: Preservation vs. Integration
Assimilation emphasizes the absorption of minority cultures into the dominant society, often leading to the erosion of original cultural identities in favor of a unified national identity. Polyculturalism supports the coexistence and interaction of diverse cultures, promoting the preservation and mutual influence of distinct cultural identities within a shared social framework. This approach encourages integration through cultural exchange while maintaining the uniqueness of each group's heritage.
Social Impacts of Assimilation Policies
Assimilation policies often lead to the erosion of cultural identities and create social tension by marginalizing minority groups, resulting in reduced social cohesion and increased discrimination. These policies can undermine mental health and self-esteem within affected communities due to the pressure to conform to dominant cultural norms. The loss of cultural diversity also diminishes the societal benefits of multicultural interaction, weakening the fabric of inclusive social networks.
Benefits and Challenges of Polyculturalism
Polyculturalism enriches societies by promoting mutual respect and understanding among diverse cultural groups, fostering innovation through the blending of different perspectives. Challenges include managing potential cultural conflicts and overcoming resistance to change from communities accustomed to homogenous norms. Effective polyculturalism requires inclusive policies and open dialogue to harness its benefits while addressing integration complexities.
Contemporary Debates: Which Approach Works Best?
Assimilation emphasizes a unified national identity by encouraging immigrants to adopt the dominant culture, which can enhance social cohesion but risks erasing cultural diversity. Polyculturalism values the coexistence and interaction of multiple cultures, fostering mutual respect and innovation yet challenging traditional notions of national unity. Contemporary debates highlight that hybrid models balancing cultural integration with identity preservation often yield the most effective outcomes in multicultural societies.
Future Trends: Moving Beyond Assimilation and Polyculturalism
Future trends in cultural integration emphasize dynamic intercultural dialogue over rigid assimilation and static polyculturalism models. Emerging approaches prioritize hybrid identities and fluid cultural exchange, leveraging digital platforms and global connectivity to foster inclusive societies. Urban multiculturalism and policy innovation aim to balance individual cultural expression with collective social cohesion, redefining diversity in the 21st century.
Assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com