Popular culture shapes the way society communicates, influences trends, and reflects collective values through music, films, fashion, and social media. Understanding these elements helps you grasp the evolving dynamics that define modern lifestyles. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how popular culture impacts your daily life and social environment.
Table of Comparison
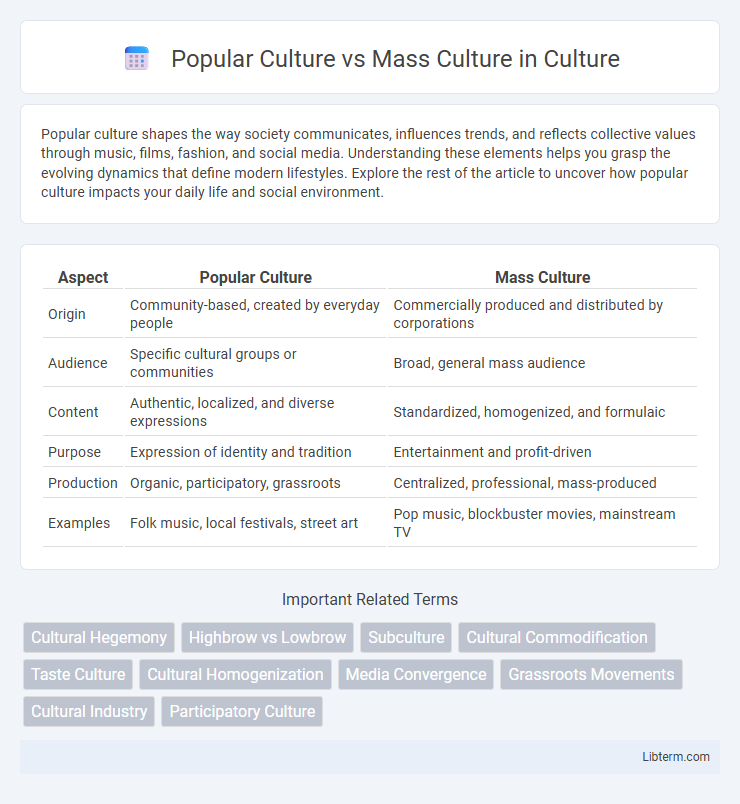
| Aspect | Popular Culture | Mass Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Community-based, created by everyday people | Commercially produced and distributed by corporations |
| Audience | Specific cultural groups or communities | Broad, general mass audience |
| Content | Authentic, localized, and diverse expressions | Standardized, homogenized, and formulaic |
| Purpose | Expression of identity and tradition | Entertainment and profit-driven |
| Production | Organic, participatory, grassroots | Centralized, professional, mass-produced |
| Examples | Folk music, local festivals, street art | Pop music, blockbuster movies, mainstream TV |
Introduction to Popular Culture and Mass Culture
Popular culture encompasses the everyday practices, beliefs, and objects that are widely accepted and enjoyed by the general population, often reflecting societal values and trends. Mass culture, by contrast, is produced and distributed through mass media channels, designed to appeal to a broad audience for commercial purposes. The distinction lies in popular culture's organic, grassroots origin versus mass culture's top-down, manufactured nature driven by corporations.
Defining Popular Culture: Origins and Evolution
Popular culture originated from everyday social practices and shared experiences, evolving through folklore, music, and communal traditions. Distinct from mass culture, which is produced and distributed by commercial media for broad consumption, popular culture emerges organically from grassroots movements and local identities. Its evolution reflects societal changes, adapting continuously to technological advancements and shifting cultural dynamics.
Understanding Mass Culture: Characteristics and Development
Mass culture is characterized by widespread accessibility and uniform consumption patterns driven by mass media, commercial production, and standardization. It emerged alongside industrialization, technological advancements, and urbanization, facilitating the rapid dissemination of cultural products to large audiences. The development of mass culture reflects an emphasis on entertainment, consumerism, and passive audience reception, contrasting with the diversity and grassroots nature of popular culture.
Key Differences Between Popular Culture and Mass Culture
Popular culture embodies the shared experiences, practices, and values organically developed and embraced by diverse social groups, often reflecting grassroots creativity and identity. Mass culture, in contrast, is typically produced and disseminated by large-scale commercial enterprises aiming for widespread consumer appeal and uniformity. Key differences include popular culture's bottom-up origin versus mass culture's top-down production, the emphasis on authenticity and community in popular culture, and mass culture's focus on mass consumption and standardized content.
Historical Perspectives: Shifts in Cultural Consumption
Historical shifts in cultural consumption reveal distinct trajectories for popular culture and mass culture, with popular culture emerging from localized, community-based practices and mass culture developing through industrialization and mass media proliferation. Popular culture traditionally reflects grassroots creativity and shared social experiences, whereas mass culture often aligns with commodification and standardized products designed for wide audiences. The 20th century's technological advancements, such as radio and television, accelerated the dominance of mass culture, transforming consumption patterns and cultural production globally.
The Role of Media in Shaping Both Cultures
Media plays a crucial role in shaping both popular culture and mass culture by disseminating content that reflects and influences societal values, trends, and behaviors. Popular culture thrives on the interactive and participatory nature of media platforms, where audiences actively engage with and reshape cultural narratives. Mass culture is often characterized by standardized, widely distributed media products designed to appeal to large audiences, fostering shared cultural experiences but sometimes limiting diversity and individual expression.
Influence of Technology on Popular and Mass Culture
Technology has revolutionized both popular culture and mass culture by enabling rapid dissemination and creation of content across digital platforms. Social media, streaming services, and mobile devices facilitate immediate access to diverse cultural expressions, influencing trends and consumer behavior globally. This technological integration accelerates the globalization of culture while blurring distinctions between popular culture's grassroots origins and mass culture's commercial production.
Criticisms and Debates Surrounding Popular vs Mass Culture
Popular culture often faces criticism for lacking depth and originality, being perceived as overly commercialized and driven by consumer demand rather than artistic value. Debates surrounding mass culture focus on its role in homogenizing cultural expressions, potentially diminishing regional and individual creativity through standardized media content. Scholars argue that while popular culture reflects grassroots interests, mass culture is predominantly shaped by corporate interests, raising concerns about cultural manipulation and loss of authentic community voices.
Case Studies: Examples from Music, Film, and Art
Popular culture showcases grassroots trends and diverse expressions in music, film, and art, as seen in the indie music movement, auteur-driven films like Wes Anderson's works, and street art exemplified by Banksy. Mass culture is characterized by widespread commercial distribution and standardized content, exemplified by blockbuster franchises like Marvel movies, top-charting pop music produced by major labels, and mass-produced art prints of iconic works. The interplay of these cultures reveals how niche creativity influences mainstream media while mass culture shapes consumer accessibility and global reach.
The Future of Culture: Blurring Boundaries and Emerging Trends
Popular culture and mass culture increasingly intersect as digital platforms democratize content creation and distribution, fostering hybrid cultural forms that defy traditional categorizations. Emerging trends like virtual reality experiences and influencer-driven communities reshape audience engagement, making cultural consumption more personalized and interactive. The future of culture lies in this seamless fusion, where grassroots creativity blends with mass media reach, driving innovation in entertainment, fashion, and social discourse.
Popular Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com