Cultural interpretation bridges the gap between diverse traditions and contemporary understanding, enhancing communication in global contexts. It involves decoding symbols, behaviors, and language nuances specific to different societies, which is crucial for effective interaction and collaboration. Explore this article to deepen your insight into cultural interpretation and its significance in today's interconnected world.
Table of Comparison
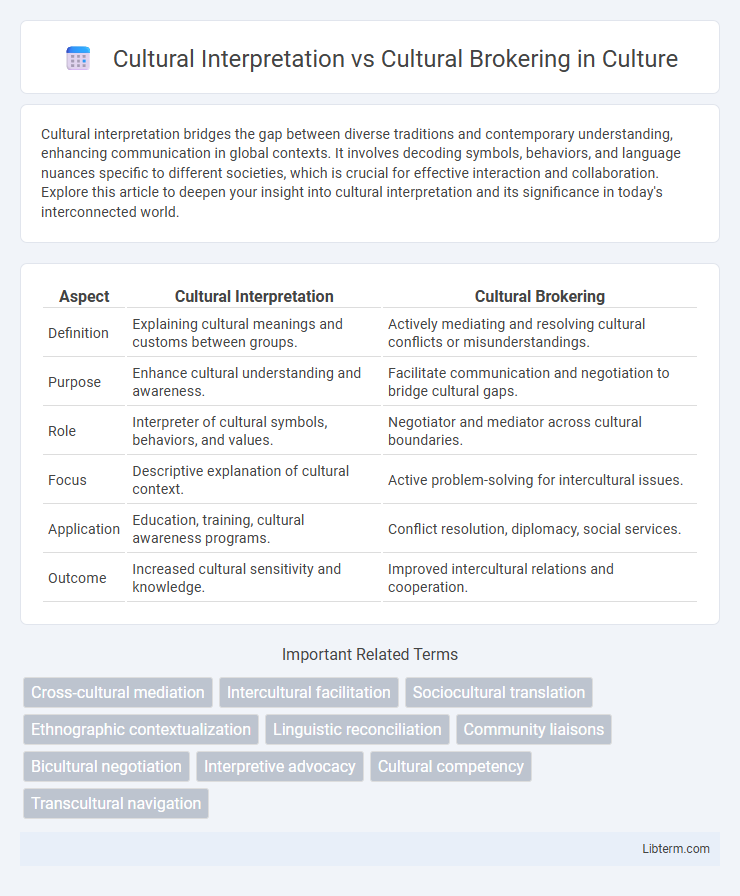
| Aspect | Cultural Interpretation | Cultural Brokering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explaining cultural meanings and customs between groups. | Actively mediating and resolving cultural conflicts or misunderstandings. |
| Purpose | Enhance cultural understanding and awareness. | Facilitate communication and negotiation to bridge cultural gaps. |
| Role | Interpreter of cultural symbols, behaviors, and values. | Negotiator and mediator across cultural boundaries. |
| Focus | Descriptive explanation of cultural context. | Active problem-solving for intercultural issues. |
| Application | Education, training, cultural awareness programs. | Conflict resolution, diplomacy, social services. |
| Outcome | Increased cultural sensitivity and knowledge. | Improved intercultural relations and cooperation. |
Understanding Cultural Interpretation
Cultural interpretation involves accurately conveying verbal and nonverbal communication across cultural boundaries while preserving original meaning and context. It requires deep knowledge of both source and target cultures to avoid misrepresentations and ensure effective intercultural dialogue. Mastery of cultural nuances, including idioms and social norms, is essential for interpreters to facilitate authentic understanding.
Defining Cultural Brokering
Cultural brokering involves mediating between individuals from different cultural backgrounds to resolve misunderstandings and facilitate effective communication. Unlike cultural interpretation, which primarily translates language and cultural nuances, cultural brokering actively bridges gaps by advocating for and negotiating cultural perspectives in health, education, and social services. This role is critical in reducing disparities and promoting culturally competent care.
Key Differences Between Cultural Interpretation and Brokering
Cultural interpretation primarily involves translating language and context accurately between cultures to ensure clear communication, while cultural brokering extends beyond translation by actively mediating and negotiating between cultural groups to resolve conflicts or facilitate mutual understanding. Interpretation focuses on conveying messages faithfully, whereas brokering requires cultural expertise to bridge gaps in values, beliefs, and practices. The key difference lies in interpretation's role as a linguistic mediator and brokering's role as a cultural intermediary addressing deeper social and interpersonal dynamics.
Roles and Responsibilities of Cultural Interpreters
Cultural interpreters facilitate communication by conveying not only linguistic content but also cultural nuances, ensuring accurate understanding between diverse groups. Their roles and responsibilities include mediating cultural differences, explaining contextual meanings, and preventing misunderstandings in healthcare, legal, or social services settings. Unlike cultural brokers who advocate and negotiate on behalf of clients, cultural interpreters primarily focus on clarifying cultural contexts while maintaining neutrality and confidentiality.
The Function of Cultural Brokers in Diverse Settings
Cultural brokers serve as vital intermediaries in diverse settings by facilitating understanding and communication between disparate cultural groups, thereby reducing misunderstandings and fostering collaboration. Their function extends beyond mere language translation to include the interpretation of cultural norms, values, and behaviors, ensuring that interactions are respectful and contextually appropriate. By navigating complex cultural landscapes, cultural brokers enhance the effectiveness of services in healthcare, education, and social work, promoting inclusivity and equity.
Skills Required for Effective Cultural Mediation
Effective cultural mediation requires advanced cross-cultural communication skills, including deep cultural awareness, empathy, and the ability to recognize nuanced cultural differences. Cultural interpretation demands linguistic accuracy and context-sensitive translation skills, while cultural brokering involves negotiation, conflict resolution, and the capacity to bridge cultural gaps by facilitating mutual understanding. Strong interpersonal skills and adaptability are essential in both roles to navigate complex social dynamics and promote collaborative interactions.
Case Studies: Interpretation vs Brokering in Practice
Case studies demonstrate that cultural interpretation primarily facilitates clear communication between parties by translating language and cultural nuances, while cultural brokering actively bridges gaps by negotiating and mediating cultural misunderstandings to achieve mutual understanding. For instance, in healthcare settings, interpreters enable accurate information exchange, whereas cultural brokers assist patients and providers in navigating cultural beliefs and practices influencing medical decisions. These practical distinctions highlight that brokering involves a more proactive role in managing cultural dynamics beyond mere translation.
Challenges Faced by Interpreters and Brokers
Cultural interpreters and brokers face significant challenges in maintaining accuracy while navigating complex cultural nuances and avoiding misrepresentation. They must balance fidelity to the source language with sensitivity to cultural context, which often requires deep cultural competence and adaptability. Ethical dilemmas arise when mediators encounter conflicting cultural norms, making it difficult to fulfill dual roles without bias or loss of meaning.
The Impact on Cross-Cultural Communication
Cultural interpretation bridges language gaps by conveying not only words but also cultural nuances, enhancing mutual understanding in diverse settings. Cultural brokering extends this role by actively mediating conflicts and negotiating cultural differences to facilitate collaboration and trust between parties. Both practices significantly improve cross-cultural communication by addressing linguistic and cultural barriers, fostering more effective and respectful interactions.
Choosing the Right Approach: Interpretation or Brokering
Choosing the right approach between cultural interpretation and cultural brokering depends on the context and complexity of the interaction. Cultural interpretation focuses on accurate language translation and conveying meaning between parties, essential in medical or legal settings where precision is critical. Cultural brokering involves mediating broader cultural differences and addressing systemic barriers, making it ideal for situations requiring negotiation, advocacy, or conflict resolution across diverse cultural perspectives.
Cultural Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com