Identity shapes who you are by defining your values, beliefs, and experiences that distinguish you from others. Understanding your identity empowers personal growth and fosters meaningful connections. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how embracing your identity can transform your life.
Table of Comparison
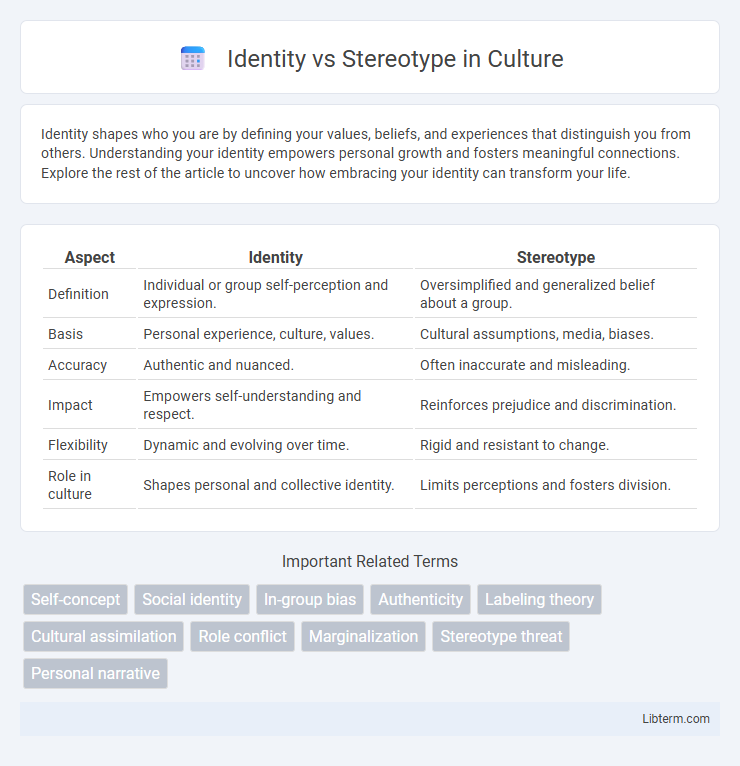
| Aspect | Identity | Stereotype |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or group self-perception and expression. | Oversimplified and generalized belief about a group. |
| Basis | Personal experience, culture, values. | Cultural assumptions, media, biases. |
| Accuracy | Authentic and nuanced. | Often inaccurate and misleading. |
| Impact | Empowers self-understanding and respect. | Reinforces prejudice and discrimination. |
| Flexibility | Dynamic and evolving over time. | Rigid and resistant to change. |
| Role in culture | Shapes personal and collective identity. | Limits perceptions and fosters division. |
Understanding Identity: Beyond Labels
Understanding identity involves recognizing the complex interplay of personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, and individual choices that shape who a person truly is, rather than relying on simplistic or generalized labels. Moving beyond stereotypes requires acknowledging the unique narratives and internal meanings that individuals assign to their identities, which often defy conventional categories. This deeper comprehension fosters authentic connections and challenges societal assumptions by emphasizing the fluid and multifaceted nature of identity.
The Roots and Impact of Stereotypes
Stereotypes originate from cognitive shortcuts that categorize individuals based on perceived group traits, often rooted in cultural, social, and historical contexts. These generalized beliefs influence identity formation by imposing limiting labels that overshadow personal uniqueness and foster bias. The impact of stereotypes manifests in social exclusion, discrimination, and internalized self-doubt, which hinder authentic self-expression and equitable interactions.
Identity Formation in a Diverse World
Identity formation in a diverse world requires navigating complex cultural, social, and personal influences that shape self-perception and group affiliation. Individuals synthesize multiple identities, balancing heritage, values, and societal expectations while resisting reductive stereotypes. Embracing diversity fosters authentic identity development, promoting empathy and challenging monolithic categorizations.
Media Influence: Shaping Stereotypes
Media influence plays a crucial role in shaping stereotypes by consistently portraying specific groups through narrow or exaggerated characteristics, which reinforces simplified identities. These portrayals impact audience perceptions, often leading to widespread acceptance of stereotypical views that overshadow individual diversity. The persistent repetition of such stereotypes in news, films, and advertising limits the recognition of multifaceted identities and perpetuates societal biases.
Navigating Between Self-Image and Social Perceptions
Navigating between self-image and social perceptions involves understanding how identity forms through both personal experiences and societal expectations. Identity represents an individual's authentic self-concept, while stereotypes impose generalized assumptions that can distort social interactions and internal self-view. Balancing these dynamics requires critical self-reflection and social awareness to resist limiting stereotypes and affirm a nuanced, genuine identity.
Cultural Identity vs. Cultural Stereotypes
Cultural identity shapes individuals' sense of belonging through shared traditions, language, and values, fostering a unique collective self-awareness within communities. Cultural stereotypes, often oversimplified and generalized portrayals, distort these identities by reinforcing inaccurate and limiting assumptions about groups. Understanding the nuanced distinctions between authentic cultural identity and reductive stereotypes is essential for promoting respect and inclusivity in diverse societies.
The Role of Education in Challenging Stereotypes
Education plays a crucial role in challenging stereotypes by promoting critical thinking and exposing individuals to diverse perspectives and cultures. Curriculum that includes multicultural content and encourages open dialogue about identity helps dismantle prejudiced beliefs and fosters empathy. Schools that implement inclusive teaching practices create environments where students can question societal stereotypes and develop a more nuanced understanding of personal and collective identities.
Personal Stories: Breaking Free from Labels
Personal stories reveal the complex journey of breaking free from limiting stereotypes and reclaiming authentic identity. Individuals redefine themselves through lived experiences that challenge societal labels, demonstrating resilience and self-discovery. These narratives highlight the transformative power of personal agency in overcoming generalized perceptions and fostering genuine self-expression.
The Psychological Effects of Stereotyping
Stereotyping leads to significant psychological effects, including diminished self-esteem, increased anxiety, and internalized negativity that distort an individual's self-identity. Repeated exposure to stereotypes can cause stereotype threat, impairing cognitive performance and reinforcing identity conflicts. These psychological burdens contribute to social alienation and hinder personal development by limiting authentic self-expression.
Building a Future of Authentic Identity
Building a future of authentic identity requires embracing individual uniqueness beyond societal stereotypes and fostering self-awareness through psychological resilience. Emphasizing personal values, cultural heritage, and diverse experiences empowers individuals to resist homogenizing labels while promoting inclusivity and genuine self-expression. Encouraging education on identity dynamics and challenging bias creates a foundation for communities that respect and celebrate multifaceted identities.
Identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com