Emotional memory plays a crucial role in how experiences influence our feelings and behaviors, often encoding events with strong emotional significance that shape future reactions. This type of memory engages brain regions like the amygdala, enhancing recall of emotionally charged moments compared to neutral ones. Explore the rest of this article to discover how understanding emotional memory can improve your emotional intelligence and cognitive wellbeing.
Table of Comparison
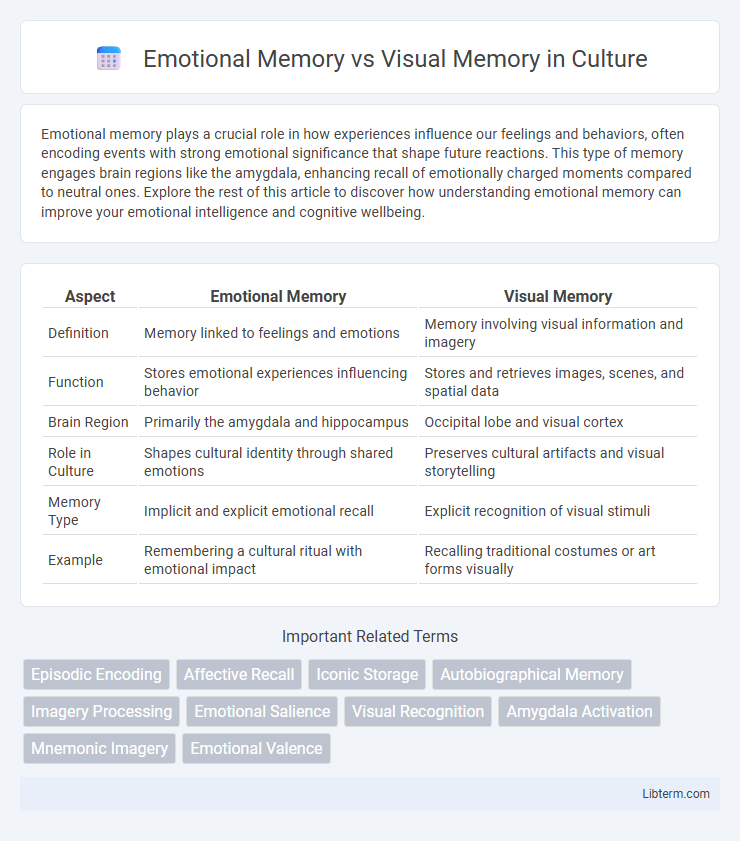
| Aspect | Emotional Memory | Visual Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Memory linked to feelings and emotions | Memory involving visual information and imagery |
| Function | Stores emotional experiences influencing behavior | Stores and retrieves images, scenes, and spatial data |
| Brain Region | Primarily the amygdala and hippocampus | Occipital lobe and visual cortex |
| Role in Culture | Shapes cultural identity through shared emotions | Preserves cultural artifacts and visual storytelling |
| Memory Type | Implicit and explicit emotional recall | Explicit recognition of visual stimuli |
| Example | Remembering a cultural ritual with emotional impact | Recalling traditional costumes or art forms visually |
Understanding Emotional Memory
Emotional memory refers to the brain's ability to store and recall feelings associated with past experiences, primarily processed by the amygdala, which enhances the retention of emotionally charged events. Unlike visual memory, which focuses on the recall of images and spatial details primarily managed by the visual cortex, emotional memory influences decision-making and behavior by triggering automatic responses based on learned emotions. Understanding emotional memory is crucial for fields like psychology and neuroscience, as it plays a key role in trauma, learning, and emotional regulation.
Exploring Visual Memory
Visual memory, a key component of cognitive function, involves the ability to recall or recognize objects, places, and visual details after exposure. This type of memory relies heavily on the occipital lobe and surrounding cortical areas for storing and retrieving images, shapes, colors, and spatial orientations. Studies show that enhancing visual memory can significantly improve everyday tasks such as navigation, reading comprehension, and object recognition.
Key Differences Between Emotional and Visual Memory
Emotional memory encodes and retrieves experiences linked to feelings, heavily involving the amygdala, whereas visual memory processes and stores images, primarily engaging the occipital lobe and visual cortex. Emotional memory often triggers strong unconscious reactions and influences decision-making, while visual memory supports conscious recall of shapes, colors, and spatial arrangements. Key differences include their neural pathways, with emotional memory integrating affective context and visual memory focusing on perceptual details and imagery.
The Science Behind Emotional Memory
Emotional memory involves the brain's amygdala, which enhances the encoding and retrieval of experiences tied to strong emotions, resulting in more vivid and lasting memories compared to visual memory alone. Visual memory relies primarily on the occipital lobe's processing of visual stimuli, storing images and spatial information without the intensified retention linked to emotional significance. Neuroscientific studies demonstrate that emotional arousal triggers neurochemical responses, such as increased norepinephrine, that strengthen synaptic connectivity and memory consolidation in the hippocampus, highlighting why emotionally charged events are more easily recalled.
How Visual Memory Works in the Brain
Visual memory relies heavily on the occipital lobe, particularly the primary visual cortex, where visual information is initially processed and encoded. Neural pathways connect the visual cortex with the hippocampus and other regions involved in memory consolidation, enabling the storage and retrieval of visual scenes and objects. This process allows the brain to maintain detailed mental images and recognize familiar visual stimuli, supporting tasks such as navigation, object identification, and spatial awareness.
Impact of Emotional Memory on Learning
Emotional memory significantly enhances learning by strengthening the retention of information linked to strong feelings, activating the amygdala to prioritize emotionally charged experiences. Unlike visual memory, which primarily involves the processing of images and spatial relationships, emotional memory boosts recall through heightened attention and deeper cognitive connections. This interplay facilitates long-term learning and influences decision-making by embedding emotional context within the memory trace.
Visual Memory’s Role in Daily Life
Visual memory plays a crucial role in daily life by enabling individuals to recognize faces, navigate environments, and recall important visual details such as locations or objects. Effective visual memory supports tasks like reading, driving, and organizing, enhancing overall cognitive function and productivity. Unlike emotional memory, which stores feelings associated with events, visual memory primarily processes and retains images and spatial information essential for everyday decision-making.
Techniques to Improve Emotional Memory
Techniques to improve emotional memory include mindfulness meditation, which enhances awareness and emotional regulation by focusing attention on present experiences. Engaging in vivid storytelling or journaling helps encode emotional experiences more deeply by activating the brain's limbic system. Repeated exposure to emotionally charged stimuli through controlled visualization exercises strengthens neural pathways associated with emotional recall.
Strategies to Enhance Visual Memory
Techniques to enhance visual memory include using visualization exercises that involve mentally picturing objects or scenes in detail, and practicing spatial memory tasks such as map reading or puzzle solving to strengthen neural connections related to visual processing. Employing mnemonic devices like the method of loci links visual information to familiar spatial environments, improving recall. Consistent engagement with activities like drawing, sketching, and memory games can significantly boost the brain's capacity to store and retrieve visual information effectively.
Emotional Memory vs Visual Memory: Practical Implications
Emotional memory enhances retention and recall by linking events to strong feelings, making experiences more vivid and impactful compared to purely visual memory, which relies heavily on imagery without emotional context. In therapeutic settings, emotional memory plays a crucial role in addressing trauma by targeting the affective components of memories, whereas visual memory techniques are often used in educational tools to improve learning through imagery. Understanding the distinction between emotional and visual memory helps optimize strategies in mental health treatment, education, and marketing by tailoring approaches to how individuals process and store different types of information.
Emotional Memory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com