Pragmatics explores how context influences the interpretation of meaning beyond the literal words spoken or written. This field examines factors like speaker intent, social norms, and conversational implicatures to understand real-world language use effectively. Discover how pragmatics shapes your communication by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
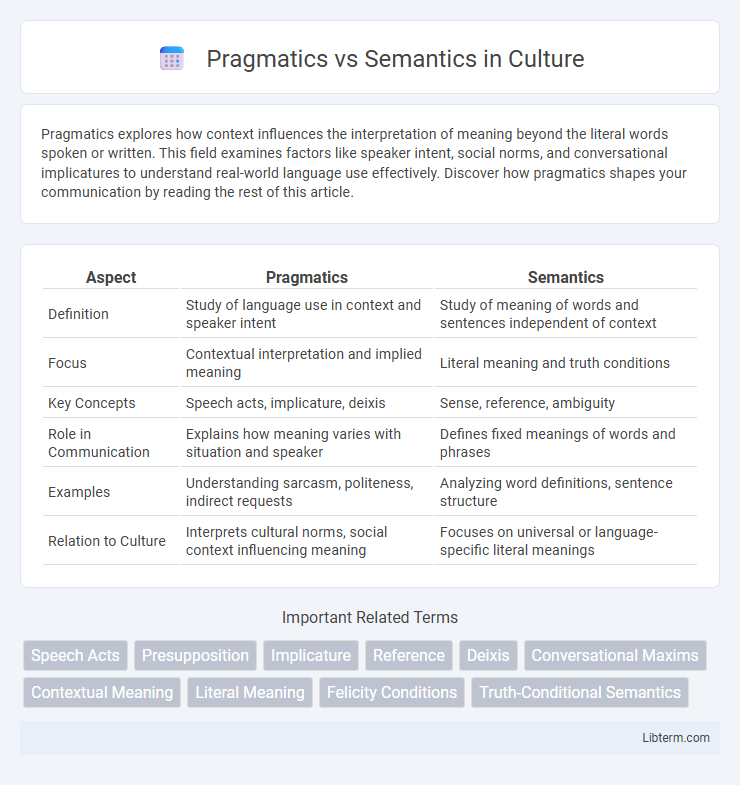
| Aspect | Pragmatics | Semantics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of language use in context and speaker intent | Study of meaning of words and sentences independent of context |
| Focus | Contextual interpretation and implied meaning | Literal meaning and truth conditions |
| Key Concepts | Speech acts, implicature, deixis | Sense, reference, ambiguity |
| Role in Communication | Explains how meaning varies with situation and speaker | Defines fixed meanings of words and phrases |
| Examples | Understanding sarcasm, politeness, indirect requests | Analyzing word definitions, sentence structure |
| Relation to Culture | Interprets cultural norms, social context influencing meaning | Focuses on universal or language-specific literal meanings |
Introduction to Pragmatics and Semantics
Pragmatics studies how context influences the interpretation of meaning, focusing on speaker intentions, social cues, and situational factors. Semantics analyzes the inherent meaning of words, phrases, and sentences independent of context, emphasizing literal definitions and truth conditions. Understanding the distinction between pragmatics and semantics is essential for linguistic analysis, language processing, and communication theory.
Defining Semantics: Meaning in Language
Semantics studies the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences by analyzing their inherent relationships and interpretations within language systems. It focuses on the literal meaning encoded in linguistic expressions, independent of context or speaker intention. Key concepts include sense, reference, truth conditions, and semantic roles that define how meaning is constructed and understood.
Understanding Pragmatics: Context in Communication
Pragmatics studies how context influences the interpretation of meaning beyond the literal semantics of words and sentences. It examines factors such as speaker intention, social cues, and situational context to understand implied meanings and conversational implicatures. This field is essential for analyzing how meaning shifts dynamically in real-life communication and discourse.
Key Differences Between Pragmatics and Semantics
Pragmatics studies how context influences the interpretation of meaning in communication, while semantics focuses on the inherent meaning of words and sentences independent of context. Key differences include pragmatics addressing implied meanings, speaker intentions, and social cues, whereas semantics deals with literal meanings, truth conditions, and syntactic structures. Understanding pragmatics requires knowledge of situational factors and cultural norms, which are not necessary for semantic analysis.
The Role of Context in Interpreting Meaning
Pragmatics centers on how context influences the interpretation of meaning beyond the literal sense of words, emphasizing speaker intent, situational factors, and shared knowledge. Semantics deals with the inherent meaning of linguistic expressions and their truth conditions regardless of context. Understanding the role of context in pragmatics enables accurate decoding of utterances in communication, highlighting how meaning shifts in different environments and social interactions.
Examples Illustrating Semantics vs Pragmatics
Semantics examines the literal meaning of words and sentences, such as "The cat is on the mat" indicating a specific spatial relationship. Pragmatics studies how context influences interpretation, for example, the phrase "Can you pass the salt?" functions as a polite request rather than a question about ability. Understanding the distinction is crucial in language processing, where semantics deals with static meanings and pragmatics with dynamic, context-dependent meanings.
Common Misunderstandings in Language Analysis
Pragmatics and semantics are often confused, but semantics focuses on the literal meaning of words and sentences, while pragmatics examines how context influences interpretation. A common misunderstanding is treating semantic meaning as fixed, ignoring that pragmatic factors like speaker intention and social cues shape actual communication. Analysts must differentiate between encoded meanings and inferred meanings to accurately interpret language use.
Importance of Pragmatics and Semantics in Linguistics
Pragmatics explores how context influences meaning in communication, making it essential for interpreting implied intentions and social cues beyond literal language. Semantics focuses on the inherent meaning of words and sentences, providing a foundation for understanding language structure and vocabulary. Both are crucial in linguistics for decoding effective communication: semantics clarifies what is said, while pragmatics explains why and how it is understood in real-world interactions.
Real-World Applications of Pragmatics and Semantics
Pragmatics focuses on the interpretation of meaning based on context, which is crucial in natural language processing applications such as chatbots, where understanding user intent and conversational implicature enhances communication accuracy. Semantics deals with the inherent meaning of words and sentences, playing a key role in information retrieval systems that rely on precise content understanding to improve search relevance. Both fields synergize in AI-driven translation and sentiment analysis, enabling systems to accurately decode meaning beyond literal text and adapt responses to real-world scenarios.
Conclusion: Integrating Semantics and Pragmatics in Language Study
Integrating semantics and pragmatics in language study enhances the understanding of meaning by combining the literal interpretation of words with contextual nuances. This approach enables more accurate communication analysis, capturing both the explicit content and the implied intentions behind utterances. Emphasizing the interplay between semantics and pragmatics is essential for advancing linguistic theory, natural language processing, and effective human-computer interaction.
Pragmatics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com