Cultural diffusion plays a crucial role in shaping societies by spreading ideas, customs, and technologies across different regions and communities. This exchange fosters innovation, understanding, and diversity, enriching cultural landscapes globally. Explore the rest of this article to discover how cultural diffusion influences your world today.
Table of Comparison
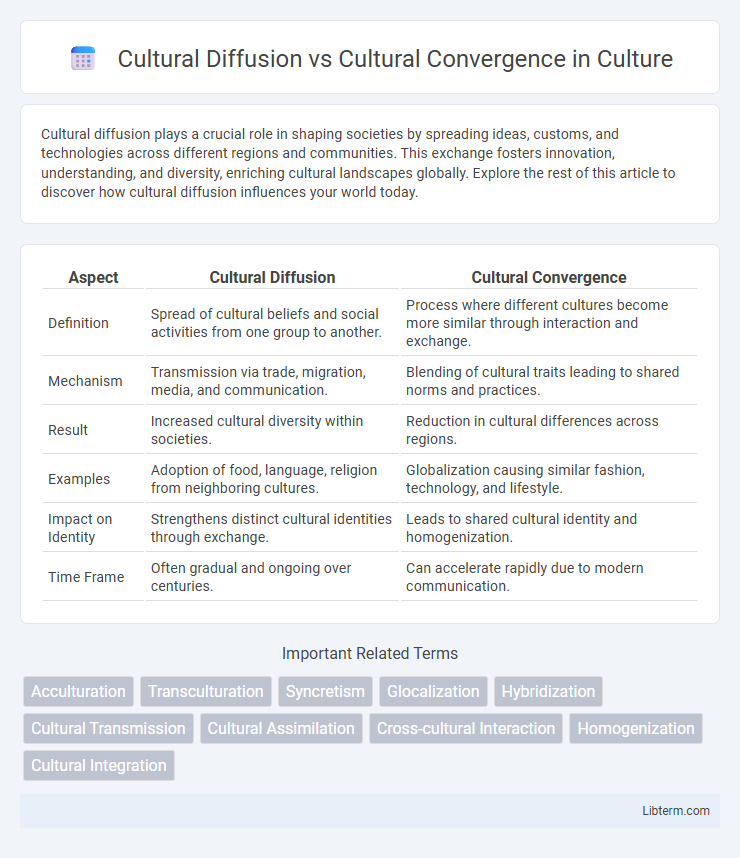
| Aspect | Cultural Diffusion | Cultural Convergence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another. | Process where different cultures become more similar through interaction and exchange. |
| Mechanism | Transmission via trade, migration, media, and communication. | Blending of cultural traits leading to shared norms and practices. |
| Result | Increased cultural diversity within societies. | Reduction in cultural differences across regions. |
| Examples | Adoption of food, language, religion from neighboring cultures. | Globalization causing similar fashion, technology, and lifestyle. |
| Impact on Identity | Strengthens distinct cultural identities through exchange. | Leads to shared cultural identity and homogenization. |
| Time Frame | Often gradual and ongoing over centuries. | Can accelerate rapidly due to modern communication. |
Introduction to Cultural Diffusion and Cultural Convergence
Cultural diffusion involves the spread of cultural beliefs and social activities from one group to another, leading to the exchange of languages, traditions, and technologies across regions. Cultural convergence occurs when different cultures become more alike through increased communication and interaction, often resulting in shared values, practices, and norms. Both processes play critical roles in shaping multicultural societies and influencing global cultural dynamics.
Defining Cultural Diffusion: Meaning and Mechanisms
Cultural diffusion refers to the process through which cultural elements such as ideas, beliefs, technologies, and customs spread from one society or group to another, facilitating intercultural exchange and adaptation. Mechanisms of cultural diffusion include relocation diffusion, where people migrate and carry cultural traits to new areas; expansion diffusion, involving the spread of cultural elements through direct or indirect contact; and hierarchical diffusion, which occurs when cultural traits spread from larger or influential groups to smaller or less prominent ones. This process plays a critical role in shaping global cultural landscapes by promoting diversity and innovation while enabling societies to integrate new practices and knowledge.
Understanding Cultural Convergence: Key Concepts
Cultural convergence refers to the process where different cultures become more similar due to increased interaction through trade, technology, or communication. Key concepts include globalization, which accelerates cultural exchange, and homogenization, where distinct cultural elements blend into shared practices, norms, and values. Understanding cultural convergence highlights how digital media and transnational corporations promote shared lifestyles, influencing cultural identities worldwide.
Historical Examples of Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion is exemplified by the Silk Road, where goods, ideas, and technologies such as papermaking and gunpowder spread from China to the West, influencing societies along the trade route. The Columbian Exchange represents another significant case, transferring crops like potatoes and maize between the Americas and Europe, reshaping diets and economies globally. These historical examples highlight how cultural diffusion facilitates the transmission of knowledge, innovation, and customs across diverse civilizations.
Instances of Cultural Convergence in Modern Society
Cultural convergence is evident in modern society through global phenomena such as the widespread adoption of technology, international cuisine, and popular media like music and film, which blend diverse cultural elements. Social media platforms facilitate the rapid exchange of ideas and trends, fostering a shared global culture despite geographic boundaries. Multinational corporations also play a crucial role by promoting standardized products and services, further driving cultural similarities worldwide.
Factors Influencing Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion is driven by factors such as trade, migration, technology, and communication, which facilitate the spread of ideas, customs, and innovations across societies. Geographic proximity and political relations further influence how cultures exchange and adopt elements from one another, enhancing interconnectedness. In contrast, cultural convergence occurs when distinct cultures increasingly resemble each other due to sustained interaction, often accelerated by globalization and mass media.
Drivers Behind Cultural Convergence
Technological advancements and globalization serve as primary drivers behind cultural convergence, facilitating the rapid exchange of ideas, values, and practices across borders. Mass media, social networks, and international trade contribute to homogenizing cultural expressions, promoting shared lifestyles and consumer behaviors. Urbanization and educational systems also play critical roles by exposing diverse populations to common cultural norms and practices.
Impact of Technology on Cultural Exchange
Technology accelerates cultural diffusion by enabling instantaneous sharing of ideas, customs, and products across global digital platforms. This rapid exchange fosters cultural convergence as diverse societies adopt similar technologies, media, and lifestyles, creating blended cultural identities. Innovations such as social media, artificial intelligence, and high-speed internet drive unprecedented levels of intercultural communication and hybridization in the 21st century.
Challenges and Criticisms of Cultural Homogenization
Cultural homogenization, a key outcome of cultural diffusion and convergence, faces challenges such as the erosion of local traditions and loss of cultural diversity. Critics argue that globalization-driven cultural blending often results in dominant cultures overshadowing smaller, indigenous ones, leading to a monocultural world. This uniformity risks diminishing unique cultural identities and heritage, creating resistance among communities striving to preserve their distinct customs.
The Future of Global Cultures: Diffusion or Convergence?
Global cultures face a dynamic interplay between cultural diffusion, which spreads unique traditions and ideas across borders, and cultural convergence, where increasing interaction leads to more homogenized cultural traits. Advances in digital communication, international trade, and migration accelerate cultural diffusion by facilitating the exchange of diverse cultural elements, while simultaneously promoting convergence through shared global media, language standardization, and multinational corporations. The future of global cultures likely involves a complex balance where cultural diffusion enriches diversity, yet cultural convergence fosters common global identities and interconnected social norms.
Cultural Diffusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com