Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, fostering mutual respect and understanding among different ethnic groups. It enriches communities by encouraging the exchange of traditions, languages, and perspectives, creating a more inclusive environment. Explore this article to discover how multiculturalism can positively impact your community and personal growth.
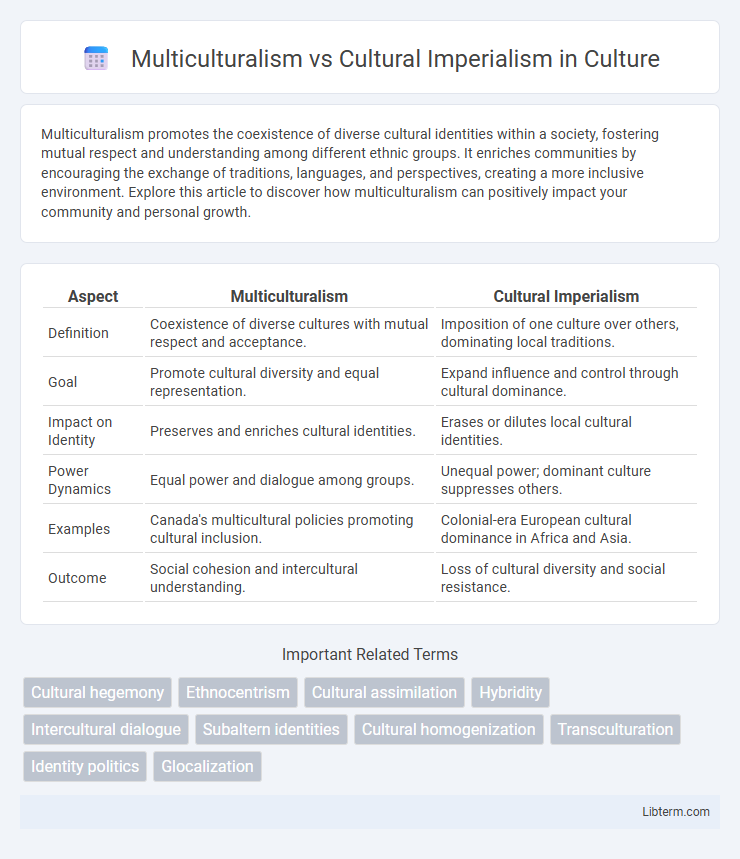
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Cultural Imperialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures with mutual respect and acceptance. | Imposition of one culture over others, dominating local traditions. |
| Goal | Promote cultural diversity and equal representation. | Expand influence and control through cultural dominance. |
| Impact on Identity | Preserves and enriches cultural identities. | Erases or dilutes local cultural identities. |
| Power Dynamics | Equal power and dialogue among groups. | Unequal power; dominant culture suppresses others. |
| Examples | Canada's multicultural policies promoting cultural inclusion. | Colonial-era European cultural dominance in Africa and Asia. |
| Outcome | Social cohesion and intercultural understanding. | Loss of cultural diversity and social resistance. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Definition and Principles
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, emphasizing respect, inclusion, and equal representation of all cultural groups. It encourages the preservation of unique traditions, languages, and customs while fostering intercultural dialogue and cooperation. Rooted in principles of equity and mutual respect, multiculturalism opposes cultural imperialism, which seeks to impose dominant cultural norms on marginalized communities.
What Is Cultural Imperialism? An Overview
Cultural imperialism refers to the dominant culture imposing its values, beliefs, and practices onto other cultures, often through media, language, and economic influence, leading to the erosion of local traditions. This phenomenon typically results in cultural homogenization, where minority cultures lose their distinct identities due to the overwhelming presence of a more powerful culture. The impact of cultural imperialism is evident in global media consumption patterns, language shifts, and changes in social norms driven by dominant Western countries.
Historical Context: Roots of Multiculturalism and Imperialism
Multiculturalism emerged in the 20th century as a response to growing immigration and cultural diversity in Western societies, emphasizing the recognition and celebration of distinct cultural identities within a shared political framework. Cultural imperialism traces its roots to European colonialism from the 15th century onwards, where dominant powers imposed their language, values, and institutions on colonized regions to assert control and exploit resources. Historically, multiculturalism challenges the legacy of cultural imperialism by advocating for pluralism and equality rather than assimilation into a hegemonic culture.
Key Differences Between Multiculturalism and Cultural Imperialism
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence and equal respect of diverse cultural identities within a society, emphasizing inclusion and mutual respect. Cultural imperialism involves imposing one dominant culture's values and practices over others, often leading to cultural homogenization and loss of indigenous traditions. The key difference lies in multiculturalism fostering diversity and harmony, while cultural imperialism enforces cultural dominance and assimilation.
Globalization: Bridge or Barrier for Cultural Diversity?
Globalization acts as a complex force influencing multiculturalism and cultural imperialism by facilitating cross-cultural exchanges while risking the dominance of powerful cultures over marginalized ones. Multiculturalism promotes cultural diversity by encouraging the coexistence of multiple cultural identities within global societies, whereas cultural imperialism often manifests through the widespread dissemination of dominant cultural values, languages, and media, leading to cultural homogenization. The tension between these forces highlights globalization as both a bridge fostering inclusivity and a barrier that can undermine genuine cultural diversity worldwide.
The Impact of Cultural Imperialism on Indigenous Cultures
Cultural imperialism significantly threatens indigenous cultures by imposing dominant values, languages, and practices, leading to erosion of traditional customs and identities. This process often results in the marginalization of indigenous knowledge systems and displacement of local cultural expressions in favor of homogenized global culture. Resistance and revitalization efforts by indigenous communities aim to preserve linguistic diversity and cultural heritage against ongoing external pressures.
Multiculturalism in Modern Societies: Challenges and Benefits
Multiculturalism in modern societies fosters social cohesion by promoting cultural diversity, inclusion, and mutual respect among different ethnic groups, which enhances innovation and economic growth. Challenges include managing cultural conflicts, addressing inequalities, and overcoming resistance to integration within diverse populations. Policies encouraging intercultural dialogue and equitable representation help mitigate these issues while reinforcing the benefits of a pluralistic society.
Media’s Role in Promoting or Undermining Cultural Diversity
Media plays a crucial role in promoting multiculturalism by showcasing diverse narratives, languages, and customs, fostering cross-cultural understanding and respect. However, media conglomerates often perpetuate cultural imperialism by prioritizing dominant cultural values and homogenizing content, which can marginalize minority voices and diminish cultural diversity. The balance between these forces determines whether media serves as a platform for cultural enrichment or a tool for cultural dominance.
Policy Responses: Supporting Multiculturalism, Combating Imperialism
Policy responses supporting multiculturalism promote inclusive frameworks that recognize and celebrate diverse cultural identities through legislation, education, and public programs, enhancing social cohesion and equal rights. Measures combating cultural imperialism include enforcing anti-discrimination laws, protecting indigenous languages and traditions, and regulating media content to prevent cultural homogenization by dominant global influences. Governments and institutions adopt multicultural policies aimed at fostering intercultural dialogue while resisting cultural dominance that threatens minority groups' heritage and autonomy.
The Future of Cultural Interaction: Towards Mutual Respect
The future of cultural interaction emphasizes mutual respect as a cornerstone for peaceful coexistence, challenging the dominance of cultural imperialism that enforces one culture over others. Multiculturalism fosters dialogue and understanding by celebrating diverse traditions and promoting equitable representation in global platforms. Advancing policies that protect cultural identities while encouraging intercultural exchange will create a more inclusive and harmonious international society.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com