Cultural beliefs shape values, behaviors, and social norms, influencing how individuals perceive the world and interact with others. These deeply ingrained ideas affect traditions, rituals, and everyday decision-making processes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your cultural background impacts your personal and professional life.
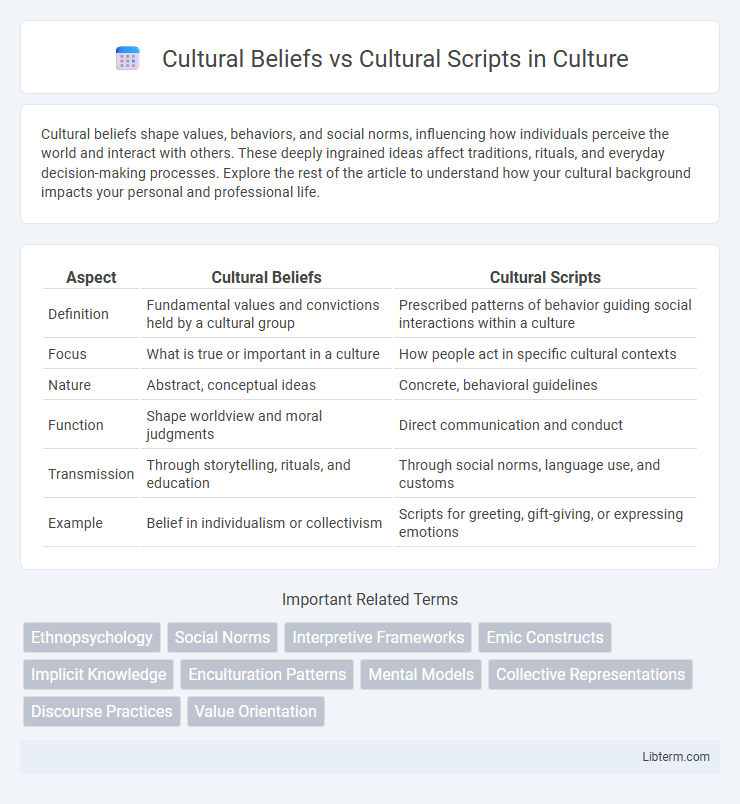
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Beliefs | Cultural Scripts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fundamental values and convictions held by a cultural group | Prescribed patterns of behavior guiding social interactions within a culture |
| Focus | What is true or important in a culture | How people act in specific cultural contexts |
| Nature | Abstract, conceptual ideas | Concrete, behavioral guidelines |
| Function | Shape worldview and moral judgments | Direct communication and conduct |
| Transmission | Through storytelling, rituals, and education | Through social norms, language use, and customs |
| Example | Belief in individualism or collectivism | Scripts for greeting, gift-giving, or expressing emotions |
Defining Cultural Beliefs
Cultural beliefs are deeply held convictions and values shared by a group that shape perceptions, behaviors, and social norms within that culture. These beliefs provide the foundational framework influencing attitudes toward concepts such as family, religion, and morality. Understanding cultural beliefs is essential for interpreting diverse cultural practices and communication styles.
Understanding Cultural Scripts
Cultural scripts represent the tacit, habitual patterns of behavior and communication shaped by cultural norms, influencing how individuals interpret social interactions and respond appropriately. Understanding cultural scripts requires recognizing implicit expectations embedded in language, gestures, and social roles that guide everyday conduct within a specific cultural context. These scripts differ from cultural beliefs, which are explicit values or ideologies; grasping cultural scripts enhances cross-cultural competence by revealing the unspoken rules governing behavior.
Key Differences Between Beliefs and Scripts
Cultural beliefs are deeply held convictions about values, norms, and truths within a society, shaping individuals' perceptions and guiding long-term behavior. Cultural scripts, on the other hand, are socially constructed patterns of behavior and communication that dictate situational interactions and appropriate responses. The key difference lies in beliefs influencing internal attitudes while scripts govern external social conduct and routines.
How Cultural Beliefs Shape Behavior
Cultural beliefs act as foundational convictions shared within a community, guiding individuals' perceptions and actions by defining what is deemed acceptable or unacceptable behavior. These beliefs influence decision-making processes, social norms, and interpersonal interactions, often determining roles, responsibilities, and responses in various contexts. By shaping mental frameworks, cultural beliefs ultimately direct behavior patterns that reinforce the community's values and collective identity.
The Role of Scripts in Social Interactions
Cultural scripts guide predictable patterns of behavior in social interactions, serving as shared, implicit frameworks for communication and etiquette within a culture. They function as mental schemas that shape expectations, responses, and roles, ensuring social cohesion and smooth exchanges by reducing misunderstandings. Unlike broader cultural beliefs, scripts provide actionable sequences for specific social contexts, influencing dialogue structure, nonverbal cues, and ritualized behaviors.
Cultural Transmission: Beliefs vs. Scripts
Cultural transmission involves the passing of cultural beliefs and scripts from one generation to another, shaping societal norms and behaviors. Beliefs consist of deeply held values and worldviews that guide interpretations and judgments, while cultural scripts refer to expected patterns of behavior and interaction within specific contexts. Both elements are encoded through language, rituals, and socialization processes, ensuring the preservation and continuity of culture over time.
Influence on Identity and Worldview
Cultural beliefs shape core values and collective meanings, deeply influencing individual identity by providing a framework for interpreting experiences and guiding behavior. Cultural scripts, as socially shared norms and expected behaviors, reinforce identity through daily practices and communication patterns, affecting how individuals perceive and interact with their environment. Together, these elements create a cohesive worldview by integrating abstract beliefs with concrete social expectations, shaping both self-concept and social reality.
Case Studies: Comparing Global Perspectives
Case studies comparing global perspectives reveal how cultural beliefs shape values, while cultural scripts guide social behaviors and communication patterns across societies. In Japan, cultural scripts emphasize collectivism and harmony in social interactions, contrasting with the United States' cultural beliefs that prioritize individualism and self-expression. These comparisons highlight that understanding both cultural beliefs and scripts is essential for effective intercultural communication and global collaboration.
Challenges in Distinguishing Beliefs and Scripts
Distinguishing cultural beliefs from cultural scripts poses challenges due to their overlapping influence on behavior and thought patterns within societies. While cultural beliefs represent deeply held convictions about reality or values, cultural scripts are normative guides for actions and interactions, making it difficult to separate internal motivations from external expectations. The ambiguity is further compounded in cross-cultural contexts where beliefs may shape scripts differently, complicating accurate interpretation and analysis.
Implications for Cross-Cultural Communication
Cultural beliefs shape fundamental values and worldviews, influencing how individuals interpret messages, while cultural scripts dictate patterned behaviors and communication norms within specific cultural contexts. Misalignment between these elements in cross-cultural communication can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and impaired relationship building. Awareness and adaptation to both cultural beliefs and scripts improve intercultural competence and enhance effective communication across diverse cultural settings.
Cultural Beliefs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com