Gender pluralism recognizes the existence of multiple gender identities beyond the traditional binary framework, embracing diversity in gender expression and experience. This perspective fosters inclusivity by validating non-binary, genderqueer, and other gender-diverse individuals within social, legal, and cultural contexts. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of how gender pluralism shapes contemporary discussions on identity and rights.
Table of Comparison
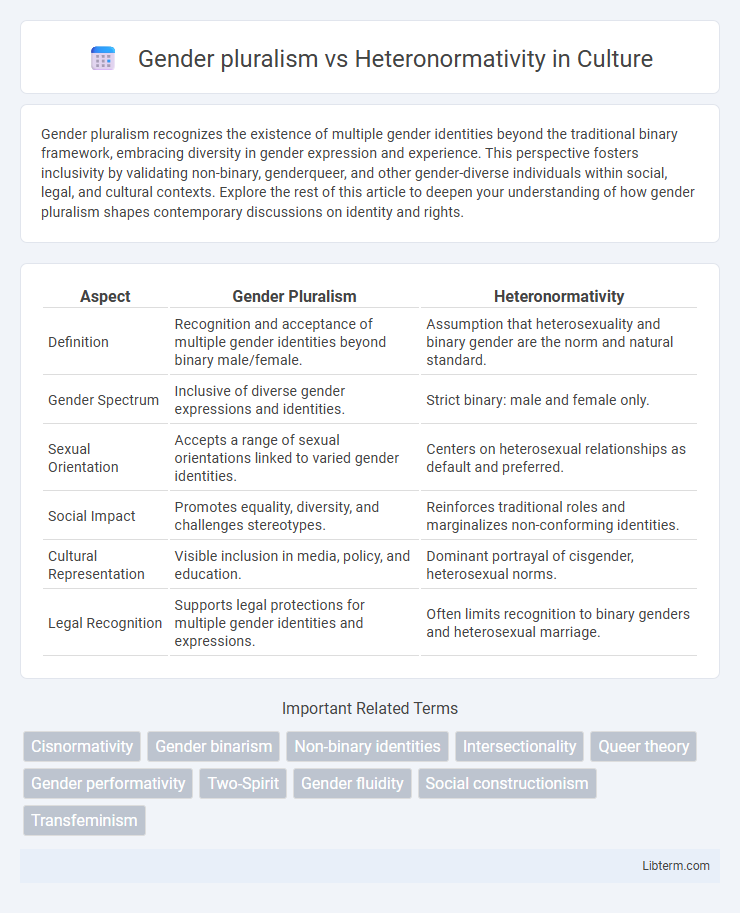
| Aspect | Gender Pluralism | Heteronormativity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognition and acceptance of multiple gender identities beyond binary male/female. | Assumption that heterosexuality and binary gender are the norm and natural standard. |
| Gender Spectrum | Inclusive of diverse gender expressions and identities. | Strict binary: male and female only. |
| Sexual Orientation | Accepts a range of sexual orientations linked to varied gender identities. | Centers on heterosexual relationships as default and preferred. |
| Social Impact | Promotes equality, diversity, and challenges stereotypes. | Reinforces traditional roles and marginalizes non-conforming identities. |
| Cultural Representation | Visible inclusion in media, policy, and education. | Dominant portrayal of cisgender, heterosexual norms. |
| Legal Recognition | Supports legal protections for multiple gender identities and expressions. | Often limits recognition to binary genders and heterosexual marriage. |
Understanding Gender Pluralism
Gender pluralism recognizes a spectrum of gender identities beyond the binary framework, embracing non-binary, genderqueer, and culturally specific gender roles such as Two-Spirit and Hijra. This approach challenges heteronormativity, which assumes heterosexuality and traditional male-female roles as the societal norm. Understanding gender pluralism is crucial for fostering inclusivity and affirming diverse gender experiences in social, legal, and cultural contexts.
Defining Heteronormativity
Heteronormativity is a societal framework that assumes heterosexuality as the default or normal sexual orientation, reinforcing binary gender roles and traditional family structures. This ideology marginalizes non-heterosexual identities and non-binary gender expressions by promoting conformity to established norms. In contrast, gender pluralism values the diversity of gender identities and expressions, challenging the restrictive assumptions of heteronormativity.
Historical Roots of Gender Norms
Historical roots of gender norms trace back to rigid binary classifications reinforced by religious, legal, and social institutions, which promoted heteronormativity as a dominant framework. Gender pluralism challenges these norms by recognizing diverse gender identities beyond male and female, reflecting Indigenous, non-Western, and pre-colonial cultures that historically embraced fluid and multiple gender roles. The persistence of heteronormativity limits gender expression by privileging heterosexuality and cisgender identities, overshadowing the complexity and legitimacy of gender pluralism throughout history.
The Impact of Heteronormativity on Society
Heteronormativity enforces binary gender roles and reinforces traditional heterosexual relationships, marginalizing non-conforming identities and perpetuating systemic discrimination. This cultural norm influences social institutions, shaping laws, education, and media to maintain gender hierarchies and limit diverse gender expressions. Challenging heteronormativity through gender pluralism promotes inclusivity, equality, and the recognition of multiple gender identities, fostering social acceptance and reducing stigma.
Gender Pluralism: Benefits and Challenges
Gender pluralism promotes acceptance of diverse gender identities beyond the binary male-female framework, enhancing social inclusion and mental health for marginalized groups. This approach fosters equitable policies and representation, supporting non-binary, genderqueer, and transgender individuals in various societal sectors, including education and healthcare. Challenges include overcoming entrenched heteronormative norms, addressing legal recognition gaps, and ensuring broad access to gender-affirming resources while combating discrimination.
Intersectionality in Gender Identities
Gender pluralism recognizes a spectrum of gender identities beyond the binary framework, challenging heteronormativity's restrictive norms that prioritize male-female roles and heterosexual relationships. Intersectionality in gender identities highlights how overlapping social categories such as race, class, sexuality, and disability shape unique experiences of marginalization or privilege within gender pluralism. Addressing these intersecting factors is crucial for developing inclusive policies and social frameworks that validate and protect diverse gender expressions and identities.
Media Representation and Gender Narratives
Media representation plays a crucial role in challenging heteronormativity by showcasing diverse gender identities and expressions that embody gender pluralism. Inclusive storytelling and character development expand societal understanding by normalizing non-binary, transgender, and gender-fluid experiences. This shift in gender narratives fosters broader acceptance and counters entrenched binary gender norms often perpetuated by traditional media frameworks.
Legal Frameworks: Equality vs. Exclusion
Legal frameworks that uphold gender pluralism emphasize comprehensive anti-discrimination laws and policies recognizing non-binary and transgender identities, promoting equality and protection under the law. In contrast, heteronormative legal systems often enforce binary gender classifications and traditional family structures, resulting in exclusionary practices that marginalize LGBTQ+ individuals. Progressive jurisdictions are increasingly adopting inclusive legal definitions and rights, challenging heteronormativity and fostering social justice.
Promoting Inclusive Social Policies
Promoting inclusive social policies requires addressing gender pluralism by recognizing and validating diverse gender identities beyond the binary framework upheld by heteronormativity. Policies that incorporate gender pluralism foster equality, reduce discrimination, and ensure access to healthcare, education, and legal protections for all genders. Emphasizing intersectional approaches within these policies enhances social acceptance and supports marginalized communities effectively.
The Future of Gender Diversity
Emerging trends in gender pluralism challenge the entrenched norms of heteronormativity by advocating for broader recognition of non-binary, genderqueer, and transgender identities in social, legal, and cultural frameworks. The future of gender diversity involves integrating inclusive policies, educational curricula, and healthcare practices that validate and support diverse gender expressions beyond traditional male-female binaries. Organizations and governments are increasingly implementing measures to combat gender discrimination and promote acceptance, signaling a societal shift towards embracing expansive understandings of gender identity.
Gender pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com