High culture encompasses sophisticated artistic expressions such as classical music, fine arts, and literature that represent the intellectual achievements of society. It reflects the values, traditions, and heritage that shape cultural identity and influence social norms. Discover how understanding high culture can enrich your appreciation of the arts in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
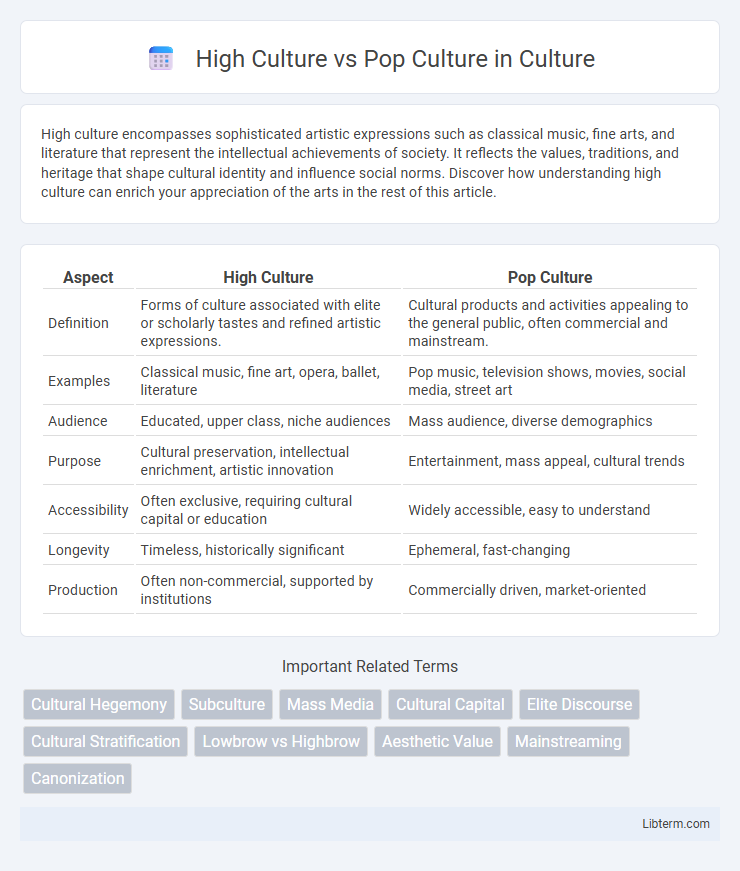
| Aspect | High Culture | Pop Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forms of culture associated with elite or scholarly tastes and refined artistic expressions. | Cultural products and activities appealing to the general public, often commercial and mainstream. |
| Examples | Classical music, fine art, opera, ballet, literature | Pop music, television shows, movies, social media, street art |
| Audience | Educated, upper class, niche audiences | Mass audience, diverse demographics |
| Purpose | Cultural preservation, intellectual enrichment, artistic innovation | Entertainment, mass appeal, cultural trends |
| Accessibility | Often exclusive, requiring cultural capital or education | Widely accessible, easy to understand |
| Longevity | Timeless, historically significant | Ephemeral, fast-changing |
| Production | Often non-commercial, supported by institutions | Commercially driven, market-oriented |
Defining High Culture and Pop Culture
High culture encompasses sophisticated artistic expressions such as classical music, fine art, literature, and theater, often associated with elite societal groups and intellectual refinement. Pop culture includes mainstream entertainment forms like television, popular music, social media trends, and mass-market films, reflecting contemporary societal interests and accessible to a wide audience. These cultural categories reveal differences in artistic value, social status, and audience reach, highlighting the dynamic relationship between tradition and mass appeal.
Historical Origins of High and Pop Culture
High culture originated in the Renaissance period, deeply rooted in classical art, philosophy, and literature, reflecting the tastes of the aristocracy and intellectual elite. Pop culture emerged in the 20th century, influenced by mass media, industrialization, and urbanization, making cultural expressions accessible to the broader public. Both cultural forms illustrate distinct historical trajectories shaped by social class, technological advancements, and evolving cultural consumption patterns.
Key Characteristics of High Culture
High culture is characterized by its association with classical art forms, including literature, fine arts, and classical music, which are traditionally regarded as intellectually and aesthetically superior. It often emphasizes complexity, historical significance, and the cultivation of refined tastes among educated elites. This cultural tier prioritizes enduring artistic value and often requires specialized knowledge for full appreciation.
Core Elements of Pop Culture
Pop culture centers around core elements such as mass media, trends, and entertainment that are accessible and widely consumed by the general public. It includes music, television, fashion, and social media, reflecting contemporary societal values and collective experiences. These elements drive popular engagement and influence daily life, differentiating pop culture from the more exclusive and refined expressions of high culture.
Influence on Society and Identity
High culture, characterized by classical music, fine arts, and literature, shapes societal values by promoting intellectual engagement and traditional aesthetic standards that influence identity formation among elite and academic circles. Pop culture, encompassing music, fashion, and social media trends, fosters mass identity through shared experiences and accessible symbols that reflect contemporary social dynamics and collective values. The interplay between high culture and pop culture drives cultural evolution, influencing social norms, community belonging, and individual self-expression across diverse demographic groups.
The Role of Media in Shaping Culture
Media serves as a powerful conduit in shaping both high culture and pop culture by determining visibility and accessibility. High culture often benefits from curated media platforms such as art galleries, classical music broadcasts, and literary journals that target niche audiences, preserving prestige and exclusivity. Pop culture thrives through mass media channels like television, social media, and streaming services, rapidly influencing trends and democratizing cultural consumption across global audiences.
Accessibility and Audience Engagement
High culture often appeals to a niche audience with specialized knowledge, making it less accessible due to its complex themes and traditional formats. Pop culture thrives on broad accessibility, using media channels like television, social media, and music to engage diverse audiences quickly and interactively. Accessibility in pop culture drives higher audience engagement, while high culture emphasizes depth and exclusivity, creating distinct experiences for their respective followers.
Cultural Value and Social Perception
High culture often carries cultural value associated with sophistication, tradition, and intellectual depth, reflecting elite tastes in art, literature, and music. Pop culture embodies mass appeal and accessibility, shaping social perception through trends, media, and entertainment that resonate with broader audiences. The distinction between high and pop culture influences societal hierarchies and informs debates on cultural legitimacy and identity formation.
The Blurring Lines Between High and Pop Culture
The blurring lines between high culture and pop culture reflect a growing convergence where traditional distinctions fade, driven by increased accessibility and digital media platforms. Iconic artworks and classical music increasingly influence mainstream entertainment, while pop culture elements gain recognition in academic and artistic institutions. This fusion challenges conventional hierarchies, promoting a more inclusive cultural landscape that values both elite and popular expressions.
Future Trends in Cultural Evolution
Future trends in cultural evolution indicate a blurring of boundaries between high culture and pop culture, driven by digital media and global connectivity. Emerging technologies like virtual reality and AI-generated art are democratizing cultural production, enabling broader participation beyond traditional elite circles. This convergence fosters hybrid cultural forms that challenge conventional definitions and shape inclusive, diverse cultural landscapes worldwide.
High Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com