Integration streamlines complex systems by combining multiple components into a unified, efficient workflow that enhances productivity and reduces errors. It supports seamless data exchange, enabling Your business to operate more cohesively and respond faster to market demands. Discover how effective integration can transform your operations by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
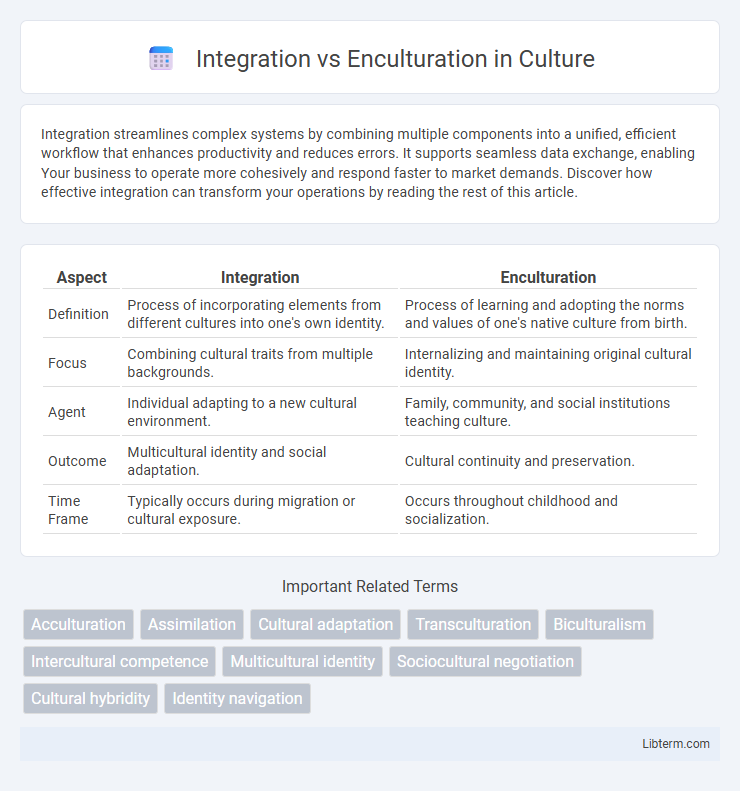
| Aspect | Integration | Enculturation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of incorporating elements from different cultures into one's own identity. | Process of learning and adopting the norms and values of one's native culture from birth. |
| Focus | Combining cultural traits from multiple backgrounds. | Internalizing and maintaining original cultural identity. |
| Agent | Individual adapting to a new cultural environment. | Family, community, and social institutions teaching culture. |
| Outcome | Multicultural identity and social adaptation. | Cultural continuity and preservation. |
| Time Frame | Typically occurs during migration or cultural exposure. | Occurs throughout childhood and socialization. |
Understanding Integration and Enculturation
Integration involves individuals adopting the cultural norms and values of a new society while maintaining aspects of their original culture, leading to bicultural competence and social cohesion. Enculturation refers to the lifelong process through which individuals learn and internalize the beliefs, customs, and behaviors of their native culture, primarily during childhood. Understanding these concepts is essential in fields like anthropology and sociology to analyze how people adapt to cultural environments and preserve cultural identity.
Key Differences Between Integration and Enculturation
Integration involves individuals adopting elements of a new culture while maintaining aspects of their original culture, promoting multicultural coexistence. Enculturation is the lifelong process by which individuals learn and internalize the values, norms, and customs of their native culture from birth. The key difference lies in integration's focus on blending or adjusting within a host culture versus enculturation's emphasis on cultural transmission and identity formation within one's original cultural group.
Historical Perspectives on Cultural Adaptation
Historical perspectives on cultural adaptation differentiate integration as the process where individuals maintain their original cultural identity while participating in the host society, whereas enculturation refers to the gradual internalization of the host culture's norms and values. Early anthropological studies emphasized enculturation as essential for social cohesion, highlighting mechanisms like language acquisition and social rituals in childhood. Integration theories gained prominence in the 20th century, recognizing multiculturalism and dual identity as key factors in successful cultural adaptation within diverse societies.
The Role of Identity in Integration and Enculturation
Identity plays a crucial role in integration and enculturation processes, shaping how individuals adapt to new cultural environments. Integration involves maintaining one's original identity while adopting aspects of the host culture, fostering bicultural competence and social inclusion. Enculturation emphasizes the internalization of cultural norms and values, reinforcing a strong sense of belonging and continuity within the native cultural group.
Social Benefits of Integration vs Enculturation
Integration fosters social cohesion by enabling individuals to participate fully in diverse communities while maintaining their cultural identity, promoting mutual respect and reducing social isolation. Enculturation strengthens cultural continuity and a sense of belonging within a specific cultural group, which supports social stability and identity formation. Both processes contribute uniquely to social benefits: integration enhances cross-cultural understanding and cooperation, while enculturation preserves cultural heritage and reinforces community bonds.
Challenges Faced During Integration and Enculturation
Challenges faced during integration include navigating language barriers, overcoming social exclusion, and adapting to new cultural norms that may conflict with native values. Enculturation difficulties often arise from generational gaps, resistance to change within the community, and conflicting influences from external cultures. Both processes require emotional resilience and cognitive flexibility to balance identity preservation with social adaptation.
Impact on Immigrant Communities
Integration promotes social cohesion by encouraging immigrants to participate in the host society's economic, educational, and cultural systems while maintaining elements of their original identity. Enculturation emphasizes the preservation of native cultural practices and values within immigrant communities, often fostering strong internal solidarity but sometimes limiting broader societal interaction. The impact on immigrant communities varies as integration facilitates access to opportunities and reduces social isolation, whereas enculturation reinforces cultural heritage and community support networks.
Education’s Influence on Cultural Processes
Education significantly shapes cultural integration and enculturation by transmitting shared values, norms, and knowledge across generations. Through formal curricula and social interactions in schools, educational systems facilitate cultural assimilation and the reinforcement of identity within a community. Diverse educational strategies impact how individuals navigate cultural boundaries and maintain or adapt cultural traditions over time.
Policy Approaches: Promoting Integration or Enculturation
Policy approaches to integration emphasize creating inclusive environments through language acquisition programs, employment opportunities, and civic participation initiatives designed to blend immigrants into the host society. Enculturation-focused policies prioritize preserving cultural identities by supporting ethnic schools, community cultural centers, and heritage language programs that maintain distinct traditions. Governments often balance these strategies to promote social cohesion while respecting cultural diversity, fostering both societal inclusion and cultural retention.
Future Trends in Multicultural Societies
Future trends in multicultural societies indicate a shift toward integration strategies that emphasize mutual cultural adaptation and inclusive policies, promoting social cohesion while respecting diversity. Enculturation processes will increasingly leverage digital platforms and immersive experiences to preserve cultural heritage amid globalization. Data-driven approaches and intercultural education programs are expected to enhance understanding and reduce cultural conflicts, fostering sustainable multicultural coexistence.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com