Syncretism blends diverse religious, cultural, or philosophical beliefs into a unified system, often leading to innovative practices and ideas. This phenomenon plays a significant role in shaping societies by fostering tolerance, adaptability, and enriched traditions. Discover how syncretism influences your world and history by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
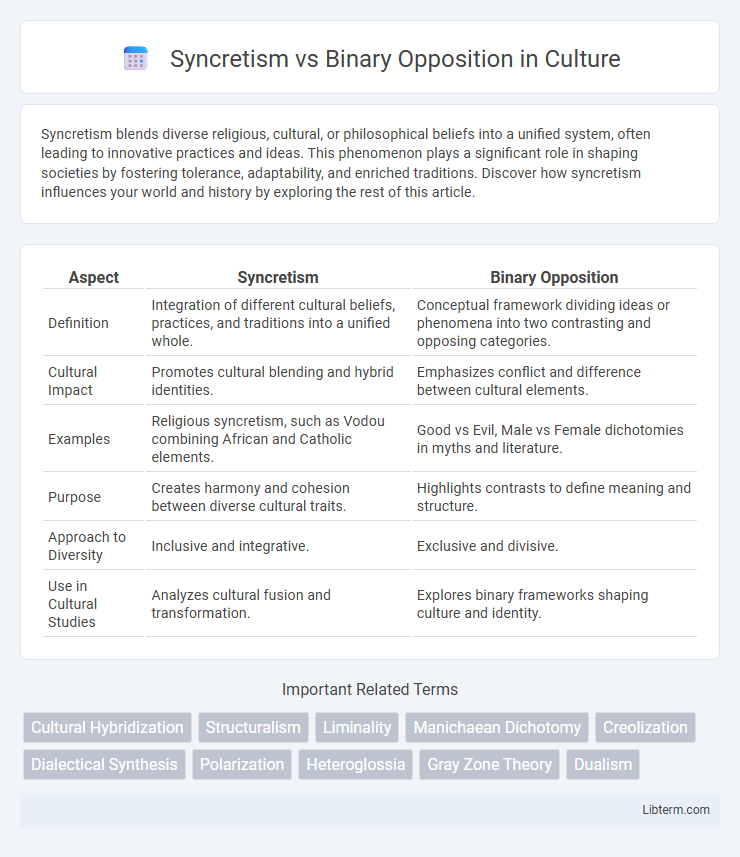
| Aspect | Syncretism | Binary Opposition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of different cultural beliefs, practices, and traditions into a unified whole. | Conceptual framework dividing ideas or phenomena into two contrasting and opposing categories. |
| Cultural Impact | Promotes cultural blending and hybrid identities. | Emphasizes conflict and difference between cultural elements. |
| Examples | Religious syncretism, such as Vodou combining African and Catholic elements. | Good vs Evil, Male vs Female dichotomies in myths and literature. |
| Purpose | Creates harmony and cohesion between diverse cultural traits. | Highlights contrasts to define meaning and structure. |
| Approach to Diversity | Inclusive and integrative. | Exclusive and divisive. |
| Use in Cultural Studies | Analyzes cultural fusion and transformation. | Explores binary frameworks shaping culture and identity. |
Understanding Syncretism: A Conceptual Overview
Syncretism involves the blending of diverse beliefs, practices, or cultural elements into a cohesive whole, transcending traditional boundaries. It challenges binary opposition by integrating opposing concepts rather than maintaining strict contrasts. This process fosters cultural hybridity, enabling societies to adapt and evolve through the fusion of religious, social, or ideological frameworks.
Defining Binary Opposition in Philosophy and Culture
Binary opposition in philosophy and culture refers to the conceptual framework that divides ideas, beliefs, or phenomena into two contrasting and mutually exclusive categories, such as good versus evil, light versus darkness, or nature versus culture. This dualistic structure often shapes narratives, ideologies, and social identities by framing meaning through opposition and hierarchical relationships. Understanding binary opposition reveals how cultural texts and philosophical arguments mobilize difference to produce meaning and influence power dynamics within societies.
Historical Contexts: Syncretism vs Binary Opposition
Syncretism historically emerges in cultural and religious contexts where disparate beliefs and practices merge, such as the Hellenistic period blending Greek and Eastern traditions or the spread of Christianity incorporating pagan rituals. Binary opposition, rooted in structuralist theory especially from Claude Levi-Strauss, frames human thought and culture through contrasting pairs like good vs evil or sacred vs profane, often influencing interpretations of history as conflicts between opposing forces. Understanding these concepts in historical contexts reveals how syncretism fosters cultural integration and hybridity, while binary opposition highlights dichotomous frameworks shaping historical narratives and ideological divisions.
The Role of Syncretism in Cultural Integration
Syncretism plays a crucial role in cultural integration by blending diverse beliefs, practices, and traditions to create new, cohesive cultural expressions that transcend binary oppositions such as us versus them or tradition versus modernity. This process facilitates mutual understanding and adaptation, allowing previously antagonistic or incompatible cultural elements to coexist and interact harmoniously. Through syncretism, societies can overcome rigid dualisms and foster inclusive identities that reflect complex, layered histories and social dynamics.
Binary Opposition: Foundation of Structuralist Thought
Binary opposition serves as a fundamental principle in structuralist thought, organizing human cognition through paired opposites such as good/evil, light/dark, and life/death. This concept highlights how meaning is generated by the relationship and contrast between these opposing elements within cultural texts and symbols. Structuralists like Claude Levi-Strauss argue that binary oppositions underpin mythologies, language structures, and social systems, revealing deep patterns in human understanding and cultural expression.
Syncretism in Religious and Spiritual Traditions
Syncretism in religious and spiritual traditions merges diverse beliefs, rituals, and symbols to create unified systems that transcend rigid dogmas. This process fosters cultural exchange and adaptation, blending elements from multiple faiths to form new, dynamic practices that reflect complex identities. Unlike binary opposition, which categorizes beliefs into mutually exclusive pairs, syncretism emphasizes synthesis and coexistence, promoting spiritual inclusivity and innovation.
Binary Opposition in Language and Semiotics
Binary opposition in language and semiotics structures meaning through contrasting pairs such as good/evil, male/female, or presence/absence, forming essential frameworks for interpretation and communication. This dualistic thinking underlies linguistic systems and cultural codes, influencing how signs are decoded and understood within different contexts. Scholars like Claude Levi-Strauss and Roland Barthes highlight binary opposition as a foundational mechanism shaping narratives, myths, and symbolism across diverse semiotic landscapes.
Comparative Analysis: Syncretism and Binary Opposition
Syncretism blends distinct cultural or religious elements into a unified system, emphasizing integration and synthesis, while binary opposition divides concepts into contrasting, mutually exclusive categories, highlighting duality and conflict. Syncretism promotes harmony and fluidity by reconciling differences, whereas binary opposition reinforces clear boundaries and opposition between ideas or groups. Comparative analysis reveals that syncretism fosters inclusivity and transformation, contrasting with binary opposition's tendency to establish rigid dichotomies and hierarchical structures.
Impacts on Identity and Social Dynamics
Syncretism fosters inclusive identities by blending diverse cultural, religious, or ideological elements, promoting social cohesion and reducing conflict through shared symbols and practices. Binary opposition reinforces rigid group distinctions, often intensifying social polarization and identity-based conflicts by emphasizing exclusive, opposing categories. The interplay between syncretism and binary opposition shapes social dynamics by either bridging divides or deepening fractures within communities.
Future Perspectives: Moving Beyond Polarities and Blending Traditions
Future perspectives on syncretism emphasize transcending binary opposition by fostering dynamic integrations of cultural, religious, and philosophical traditions. Innovations in intercultural dialogue promote hybrid frameworks that dissolve rigid dualities, creating inclusive spaces where diverse worldviews coexist and evolve. This shift toward blending traditions encourages adaptive paradigms that reflect global interconnectedness and complex identity formations, moving beyond simplistic either/or categorizations.
Syncretism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com