A regiocentric approach focuses on understanding and integrating the cultural, economic, and social characteristics of a specific geographic region to enhance business strategies and operations. This method balances global efficiency with local responsiveness, optimizing decision-making for regional markets. Discover how adopting a regiocentric mindset can transform your organization's regional success by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
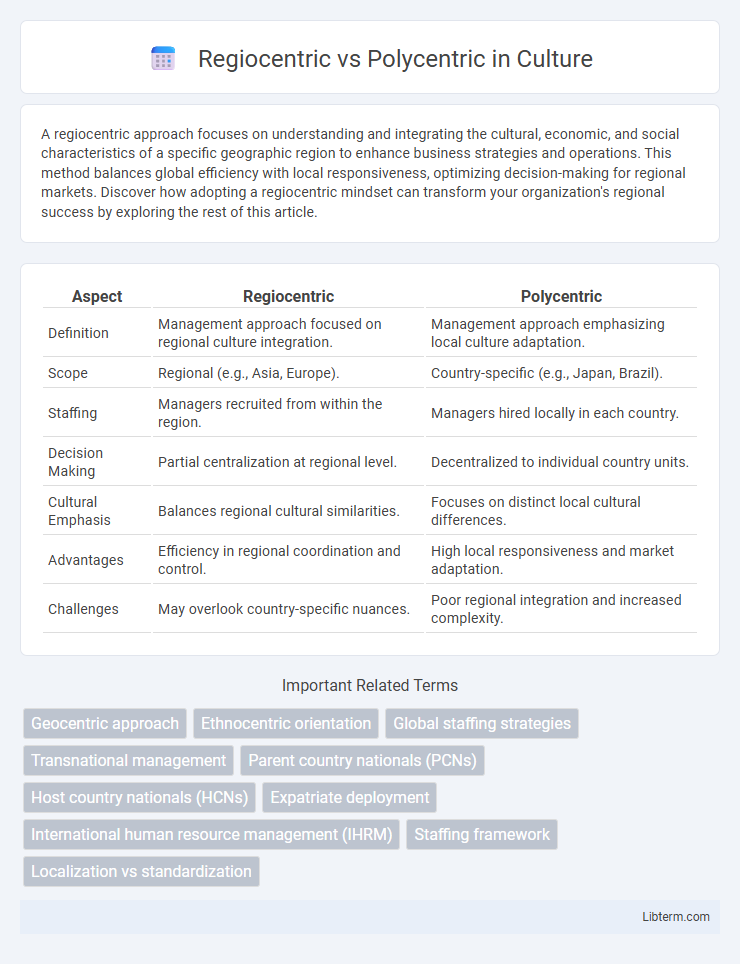
| Aspect | Regiocentric | Polycentric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management approach focused on regional culture integration. | Management approach emphasizing local culture adaptation. |
| Scope | Regional (e.g., Asia, Europe). | Country-specific (e.g., Japan, Brazil). |
| Staffing | Managers recruited from within the region. | Managers hired locally in each country. |
| Decision Making | Partial centralization at regional level. | Decentralized to individual country units. |
| Cultural Emphasis | Balances regional cultural similarities. | Focuses on distinct local cultural differences. |
| Advantages | Efficiency in regional coordination and control. | High local responsiveness and market adaptation. |
| Challenges | May overlook country-specific nuances. | Poor regional integration and increased complexity. |
Introduction to Regiocentric and Polycentric Approaches
Regiocentric and polycentric approaches represent strategic frameworks in international business management focused on balancing global integration with local responsiveness. The regiocentric approach clusters countries into regions, enabling companies to develop strategies tailored to regional similarities and shared market characteristics. In contrast, the polycentric approach treats each country as unique, promoting decentralized decision-making and allowing subsidiaries to adapt products and practices to local preferences and cultural nuances.
Defining Regiocentric Strategy
A regiocentric strategy focuses on integrating and coordinating operations within a specific region to achieve regional responsiveness and efficiency. Companies adopting this approach tailor products and marketing strategies to regional preferences while leveraging regional economies of scale. This strategy balances global standardization and local adaptation by treating the region as the primary geographic unit for strategic decisions.
Understanding Polycentric Orientation
Polycentric orientation emphasizes tailoring management practices to fit each host country's unique cultural, economic, and legal environment, promoting local responsiveness and autonomy in multinational corporations. This approach facilitates effective adaptation by employing local managers who understand regional markets and consumer behavior, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and market acceptance. Businesses with a polycentric orientation prioritize decentralized decision-making to capitalize on local expertise and foster stronger relationships with local stakeholders.
Key Differences Between Regiocentric and Polycentric Approaches
The regiocentric approach emphasizes managing operations within a specific geographic region, allowing companies to leverage regional similarities and customize strategies accordingly, whereas the polycentric approach focuses on adapting management and marketing practices to each individual host country, promoting local responsiveness and autonomy. Regiocentric management often results in regional headquarters coordinating activities across countries within the region, while polycentric management decentralizes decision-making to local subsidiaries to better address unique market conditions. These differences impact organizational structure, resource allocation, and control mechanisms, with regiocentric models balancing global integration and regional responsiveness, whereas polycentric models prioritize localized adaptation at the expense of global coordination.
Advantages of a Regiocentric Approach
The regiocentric approach enhances regional integration by leveraging shared cultural, economic, and regulatory similarities within a defined geographic area, promoting efficient resource allocation and market responsiveness. It fosters stronger regional innovation and collaboration, enabling companies to tailor strategies that suit regional consumer preferences and competitive dynamics more effectively than global or purely local approaches. Adopting a regiocentric perspective reduces operational complexities and costs by standardizing processes across neighboring countries while maintaining enough flexibility to adapt to regional nuances.
Benefits of Adopting a Polycentric Strategy
Adopting a polycentric strategy benefits multinational corporations by enabling better alignment with local market preferences, regulatory environments, and cultural nuances, which enhances customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. This approach fosters increased employee motivation and retention by empowering local management teams who possess deeper regional expertise. Companies also reduce risks related to market misunderstandings and improve agility in responding to local competitive pressures through decentralized decision-making.
Challenges in Implementing Regiocentric and Polycentric Models
Implementing regiocentric models challenges firms with balancing regional standardization and local responsiveness, often leading to complexity in coordination and higher management costs due to diverse market needs across countries within a region. Polycentric models face difficulties in maintaining consistent corporate culture and strategic alignment as subsidiaries operate with significant autonomy, risking inefficiencies and conflicting objectives. Both models require robust communication systems and skilled regional or local managers to overcome barriers such as cultural differences, resource allocation issues, and control mechanisms.
Real-World Examples: Regiocentric vs Polycentric Companies
Regiocentric companies like Toyota operate by adapting their management and marketing strategies to specific regions, balancing global efficiency with local responsiveness in markets such as North America, Europe, and Asia. Polycentric firms such as Unilever empower local subsidiaries to independently tailor products and business practices to individual countries, enhancing cultural sensitivity and local market penetration. Both approaches illustrate distinct methods multinational corporations use to optimize global operations while respecting regional and national differences.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Global Expansion
Choosing between regiocentric and polycentric strategies significantly impacts a company's global expansion success. A regiocentric approach centralizes management within a specific geographic region, enhancing regional integration and efficiency, while a polycentric strategy empowers local subsidiaries with autonomy, fostering adaptation to diverse cultural and market conditions. Selecting the right strategy depends on factors such as the level of cultural diversity, market heterogeneity, and the company's objectives for control versus local responsiveness.
Future Trends in International Management Approaches
Future trends in international management reveal a shift from regiocentric to polycentric approaches, driven by increasing globalization and local market complexities. Companies adopt polycentric strategies to enhance cultural adaptability and responsiveness by empowering local subsidiaries with decision-making autonomy. Advanced technologies and data analytics further support polycentric models by enabling real-time, localized management insights, fostering agility in diverse international markets.
Regiocentric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com