Narrative logic weaves events and ideas into a coherent and compelling story, allowing readers to follow the progression naturally. It ensures each element connects meaningfully, enhancing understanding and engagement. Explore the rest of this article to master how narrative logic can transform your storytelling skills.
Table of Comparison
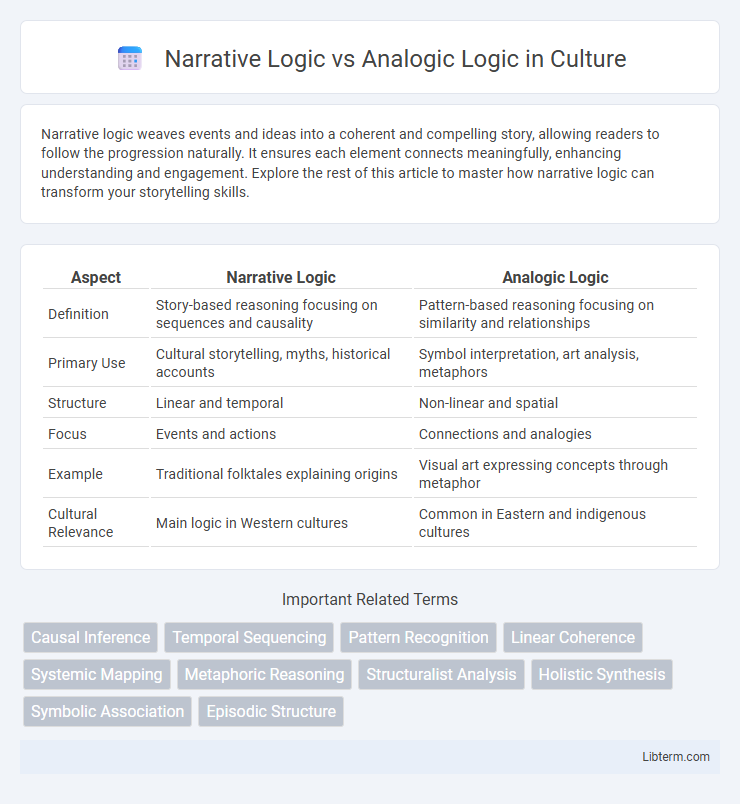
| Aspect | Narrative Logic | Analogic Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Story-based reasoning focusing on sequences and causality | Pattern-based reasoning focusing on similarity and relationships |
| Primary Use | Cultural storytelling, myths, historical accounts | Symbol interpretation, art analysis, metaphors |
| Structure | Linear and temporal | Non-linear and spatial |
| Focus | Events and actions | Connections and analogies |
| Example | Traditional folktales explaining origins | Visual art expressing concepts through metaphor |
| Cultural Relevance | Main logic in Western cultures | Common in Eastern and indigenous cultures |
Introduction to Narrative Logic and Analogic Logic
Narrative logic structures information through temporal and causal sequences, emphasizing storytelling and human experience, making it essential for understanding human communication and decision-making. In contrast, analogic logic relies on similarity and comparison between concepts or objects to draw conclusions, playing a crucial role in problem-solving and creativity across disciplines such as art, science, and law. Both logics provide complementary frameworks: narrative logic offers coherence in events and actions over time, while analogic logic facilitates pattern recognition and conceptual connections.
Defining Narrative Logic: Concepts and Frameworks
Narrative logic centers on the structured progression of events and experiences, emphasizing cause-and-effect relationships within stories to construct coherent meaning. It employs frameworks like Labov's narrative model and Freytag's pyramid to analyze how narratives unfold through temporal sequencing and thematic coherence. This approach contrasts with analogic logic by prioritizing temporal causality and subjective interpretation in understanding human communication and cognition.
Understanding Analogic Logic: Key Principles
Analogic logic operates through pattern recognition and holistic understanding, relying on visual and sensory analogies rather than linear sequences. It emphasizes the relationship between elements, fostering intuitive comprehension through metaphor and symbolic representation. Key principles include context-dependent reasoning, simultaneous processing of multiple cues, and tolerance for ambiguity, distinguishing it from the sequential, cause-effect approach of narrative logic.
Historical Context: Evolution of Logic Types
Narrative logic emerged from early human storytelling traditions, functioning as a means to structure events in a coherent sequence, crucial for cultural transmission and historical understanding. Analogic logic developed through philosophical advancements in ancient Greece, emphasizing patterns and relationships to draw parallels between different concepts and phenomena. The evolution of these logic types reflects a shift from experiential, time-bound reasoning to more abstract, pattern-based thought, foundational for modern analytical disciplines.
Core Differences Between Narrative and Analogic Logic
Narrative logic organizes information sequentially, emphasizing cause-and-effect relationships and chronological progression to construct coherent stories. In contrast, analogic logic relies on similarity and resemblance between concepts, using metaphor and analogy to connect ideas beyond linear order. The core difference lies in narrative logic's dependence on temporal and causal structure, while analogic logic prioritizes pattern recognition and relational meaning.
Applications in Communication and Decision Making
Narrative logic excels in communication by structuring information through stories, enabling audiences to connect emotionally and comprehend complex situations via cause-and-effect sequences. Analogic logic, based on similarity and metaphor, enhances decision making by allowing individuals to draw parallels between known and new scenarios, facilitating intuitive problem-solving and innovation. Both logics complement each other in organizational strategy, where narrative logic aids persuasive messaging, and analogic logic supports creative thinking and adaptive responses.
Cognitive Processes: How the Brain Utilizes Each Logic
Narrative logic engages the brain's temporal sequencing and memory centers to construct meaning through causal, story-based frameworks, facilitating understanding via events linked in time. Analogic logic activates pattern recognition and relational mapping processes, enabling the brain to identify similarities and draw conclusions based on abstract correspondences and analogies. These cognitive processes operate complementarily, with narrative logic enhancing sequential comprehension and analogic logic supporting inferential reasoning and problem-solving.
Strengths and Limitations of Narrative Logic
Narrative logic excels in making complex information relatable and memorable by organizing data into coherent stories, which enhances understanding and emotional engagement. Its strength lies in contextualizing events and human experiences, allowing for intuitive meaning construction, but this approach can be limited by its subjective bias and potential for oversimplification or distortion of facts. Narrative logic struggles when precision, systematic analysis, or reproducibility are required, making it less effective for scientific or technical disciplines compared to analogic logic.
Strengths and Limitations of Analogic Logic
Analogic logic excels in processing complex, ambiguous information through pattern recognition and holistic thinking, enabling intuitive problem-solving and creative insights. Its strength lies in visual and experiential reasoning, which facilitates understanding without relying solely on explicit, sequential steps typical of narrative logic. However, analogic logic struggles with precision and clarity, making it less effective for structured arguments or detailed, linear explanations required in formal reasoning or analytic tasks.
Integrating Narrative and Analogic Logic for Enhanced Reasoning
Integrating narrative and analogic logic enhances reasoning by combining the strengths of story-based causal sequences with pattern recognition and relational comparisons. Narrative logic organizes information through temporal and causal connections, facilitating understanding of events and motivations, while analogic logic identifies similarities and analogies across contexts to generate novel insights. This integration supports comprehensive decision-making and problem-solving by aligning structured storytelling with dynamic analogical mapping.
Narrative Logic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com