Digital anthropology explores the impact of digital technologies on human behavior, culture, and social interactions, providing insights into how online environments shape identity and community. This field examines virtual worlds, social media, and emerging digital practices to understand evolving communication patterns and cultural dynamics. Discover how digital anthropology reveals the profound ways technology influences your everyday life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
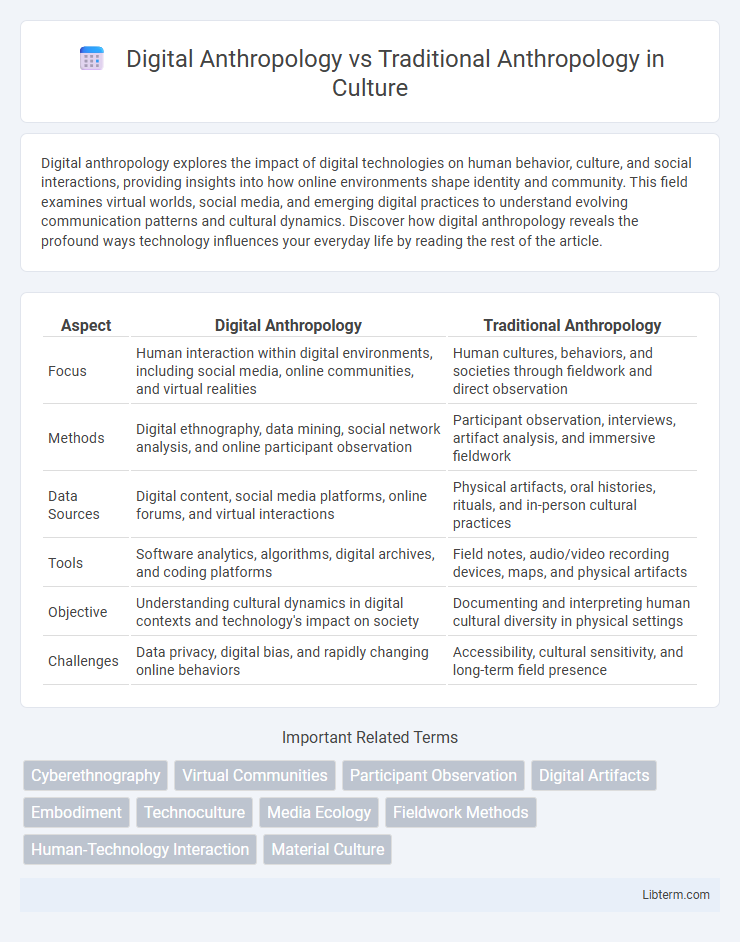
| Aspect | Digital Anthropology | Traditional Anthropology |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Human interaction within digital environments, including social media, online communities, and virtual realities | Human cultures, behaviors, and societies through fieldwork and direct observation |
| Methods | Digital ethnography, data mining, social network analysis, and online participant observation | Participant observation, interviews, artifact analysis, and immersive fieldwork |
| Data Sources | Digital content, social media platforms, online forums, and virtual interactions | Physical artifacts, oral histories, rituals, and in-person cultural practices |
| Tools | Software analytics, algorithms, digital archives, and coding platforms | Field notes, audio/video recording devices, maps, and physical artifacts |
| Objective | Understanding cultural dynamics in digital contexts and technology's impact on society | Documenting and interpreting human cultural diversity in physical settings |
| Challenges | Data privacy, digital bias, and rapidly changing online behaviors | Accessibility, cultural sensitivity, and long-term field presence |
Defining Digital Anthropology
Digital Anthropology examines human behavior and cultural patterns through the lens of digital technologies, including social media, online communities, and virtual environments. It integrates ethnographic methods with digital tools to analyze how technology shapes identity, communication, and social interaction. This field contrasts with Traditional Anthropology by focusing specifically on digital contexts rather than physical or historical settings.
Understanding Traditional Anthropology
Traditional Anthropology centers on studying human cultures, societies, and behaviors through fieldwork, participant observation, and ethnographic methods. It emphasizes in-depth, qualitative data collection within natural settings to understand social norms, rituals, and cultural evolution. This classical approach provides foundational insights into human diversity, laying the groundwork for comparative analyses in emerging fields like Digital Anthropology.
Core Methods in Digital Anthropology
Digital Anthropology employs ethnographic methods adapted for virtual environments, utilizing digital tools such as social media analysis, online participant observation, and data mining to study human behavior in digital contexts. Unlike Traditional Anthropology, which relies heavily on in-person fieldwork, interviews, and physical artifacts, Digital Anthropology emphasizes the analysis of digital footprints, algorithmic interactions, and networked communication patterns. Core methods include virtual ethnography, digital content analysis, and computational social science techniques, enabling the examination of cultural dynamics within online communities and digital ecosystems.
Research Techniques in Traditional Anthropology
Traditional anthropology mainly employs ethnographic methods such as participant observation, in-depth interviews, and fieldwork to gather qualitative data on human cultures. Researchers immerse themselves in communities for extended periods, using direct interaction to understand social behaviors and cultural practices. These hands-on techniques provide rich, contextual insights that contrast with the more data-driven, digital analysis used in digital anthropology.
Comparing Data Collection Approaches
Digital Anthropology employs advanced technologies such as social media analytics, big data mining, and virtual ethnography to collect vast amounts of real-time, user-generated data. Traditional Anthropology relies on ethnographic methods like participant observation, interviews, and field notes, emphasizing immersive, qualitative data collection within physical communities. The digital approach offers scalability and rapid data access, whereas traditional methods provide deep contextual understanding through direct human interaction.
Key Areas of Study: Digital vs Traditional
Digital anthropology examines human behavior through the lens of digital technology, focusing on online identities, virtual communities, and the impact of social media on culture. Traditional anthropology studies human societies by analyzing physical artifacts, rituals, language, and social structures in real-world environments. The key areas of study differ as digital anthropology prioritizes virtual interactions and technological mediation, while traditional anthropology emphasizes ethnographic fieldwork and material culture.
Challenges in Digital Anthropology
Digital Anthropology faces challenges such as navigating ethical concerns related to privacy and consent in online environments, managing vast and diverse digital datasets, and addressing the rapidly evolving nature of technology that complicates longitudinal studies. Researchers must also contend with the digital divide and cultural biases embedded in digital platforms, which can skew data representation and interpretation. Unlike Traditional Anthropology, which relies on in-person ethnographic methods, Digital Anthropology requires new methodologies to analyze virtual interactions and digital cultures accurately.
Ethical Considerations in Both Fields
Ethical considerations in digital anthropology emphasize data privacy, informed consent, and the responsible handling of online identities, given the pervasive use of digital platforms and the potential for surveillance. Traditional anthropology faces ethical challenges related to cultural sensitivity, community consent, and the impact of ethnographic research on indigenous populations. Both fields require rigorous ethical frameworks to navigate issues of representation, power dynamics, and the protection of vulnerable subjects in rapidly evolving contexts.
Impact of Technology on Anthropological Research
Digital anthropology revolutionizes traditional anthropology by integrating advanced technologies such as big data analytics, virtual reality, and social media platforms into ethnographic research, enabling more dynamic, real-time data collection and analysis. Traditional anthropology relies predominantly on face-to-face fieldwork and manual observation, limiting the scale and speed of data gathering compared to digital methods. The impact of technology enhances anthropological research by expanding access to diverse cultural insights globally, improving data accuracy, and facilitating cross-disciplinary collaboration.
Future Trends in Digital and Traditional Anthropology
Future trends in digital anthropology emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and virtual reality to analyze human behavior and cultural patterns in online environments. Traditional anthropology is evolving by incorporating digital tools for ethnographic research while maintaining its foundational methods of fieldwork and participant observation. The convergence of digital technologies and classical methodologies promises a hybrid approach that enhances cultural insights and broadens the scope of anthropological studies.
Digital Anthropology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com