Emerging cultures blend traditional values with innovative practices, shaping new social norms and creative expressions. They influence various aspects of life, from technology and fashion to communication and community-building. Discover how emerging culture can impact your worldview and daily experiences in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
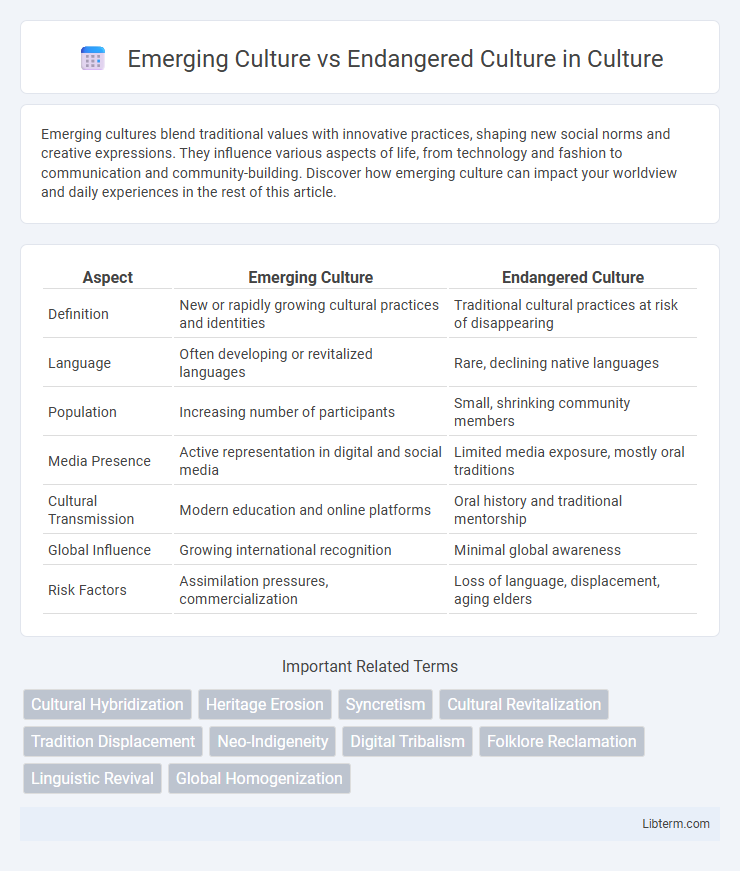
| Aspect | Emerging Culture | Endangered Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | New or rapidly growing cultural practices and identities | Traditional cultural practices at risk of disappearing |
| Language | Often developing or revitalized languages | Rare, declining native languages |
| Population | Increasing number of participants | Small, shrinking community members |
| Media Presence | Active representation in digital and social media | Limited media exposure, mostly oral traditions |
| Cultural Transmission | Modern education and online platforms | Oral history and traditional mentorship |
| Global Influence | Growing international recognition | Minimal global awareness |
| Risk Factors | Assimilation pressures, commercialization | Loss of language, displacement, aging elders |
Understanding Emerging Cultures
Emerging cultures are characterized by evolving social norms, innovative traditions, and adaptive practices driven by globalization and technological advancements. Understanding emerging cultures requires analyzing shifts in language, art, technology adoption, and hybrid identities that reflect both local heritage and global influences. This insight helps in preserving cultural diversity while fostering inclusive development in rapidly changing societies.
Defining Endangered Cultures
Endangered cultures are communities whose languages, traditions, and customs face a significant risk of disappearing due to factors like globalization, urbanization, and cultural assimilation. These cultures often experience declining numbers of native speakers and erosion of traditional knowledge passed down through generations. Preservation efforts emphasize documentation, revitalization of native languages, and support for cultural practices to protect these vulnerable cultural identities.
Drivers Behind Cultural Emergence
Cultural emergence is driven by factors such as globalization, technological innovation, and youth demographic shifts that foster new social practices and values. Economic development and media influence catalyze the creation and spread of emerging cultures by enabling cross-cultural interactions and hybrid identities. In contrast, endangered cultures often face pressures from political marginalization, environmental changes, and loss of linguistic diversity, which erode traditional knowledge and cultural expressions.
Causes of Cultural Endangerment
Rapid globalization and technological advancement often accelerate cultural homogenization, causing unique traditions to fade as dominant cultures prevail. Environmental changes, such as climate disasters and habitat loss, displace indigenous communities, disrupting cultural transmission and practices. Political oppression and forced assimilation policies also systematically diminish endangered cultures, eroding linguistic diversity and traditional knowledge.
The Role of Globalization
Globalization accelerates the spread of emerging cultures by facilitating cross-cultural exchanges and digital connectivity, promoting new cultural trends and innovations worldwide. Conversely, it poses threats to endangered cultures by imposing dominant cultural norms and economic pressures that erode traditional practices and languages. The dynamic interplay between global influence and local identity shapes cultural evolution, often challenging the survival of vulnerable cultural heritages.
Technology’s Impact on Culture
Technology accelerates the evolution of emerging cultures by enabling fast communication, digital creativity, and global connectivity, leading to new cultural expressions and lifestyles. Endangered cultures face significant risks as traditional practices and languages struggle to survive amid digital homogenization and widespread adoption of dominant technological platforms. Preservation efforts increasingly rely on technology for documentation, virtual reality experiences, and digital archiving to sustain cultural heritage in the face of rapid modernization.
Preserving Cultural Identity
Preserving cultural identity involves safeguarding endangered cultures by documenting traditions, languages, and rituals at risk of extinction. Emerging cultures contribute to global diversity by evolving new customs that blend historical roots with contemporary influences. Effective preservation strategies balance supporting endangered cultural practices while fostering the organic growth of emerging cultural expressions.
Cultural Fusion and Exchange
Emerging cultures thrive on the dynamic fusion of diverse traditions, languages, and practices, creating innovative expressions and identities that reflect global interconnectedness. Endangered cultures face challenges preserving their unique customs and languages amid dominant global influences, risking loss of heritage and historical knowledge. Cultural exchange acts as a vital mechanism for blending emerging and endangered cultures, fostering mutual understanding while promoting the survival and evolution of cultural diversity.
Challenges in Safeguarding Heritage
Emerging cultures face the challenge of integrating modern influences while preserving their distinct heritage, often contending with rapid globalization and digital transformation. Endangered cultures confront threats such as language extinction, loss of traditional practices, and diminishing community engagement due to urbanization and assimilation pressures. Safeguarding heritage requires targeted documentation, community-led initiatives, and sustainable cultural policies to ensure the transmission of knowledge and identity across generations.
The Future of Cultural Diversity
Emerging cultures thrive through technological innovation and globalization, reshaping cultural identities and fostering new expressions of creativity worldwide. Endangered cultures face threats from assimilation, loss of language, and diminishing traditional practices, risking the disappearance of unique worldviews and knowledge systems. Preserving cultural diversity requires proactive measures such as revitalization programs, inclusive policies, and global collaboration to ensure the coexistence and evolution of both emerging and endangered cultures for future generations.
Emerging Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com