The geocentric model places Earth at the center of the universe, with all celestial bodies orbiting around it in perfect circles. This ancient concept shaped early astronomy and influenced scientific thought for centuries before the heliocentric model gained acceptance. Discover how the geocentric theory impacted our understanding of the cosmos in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
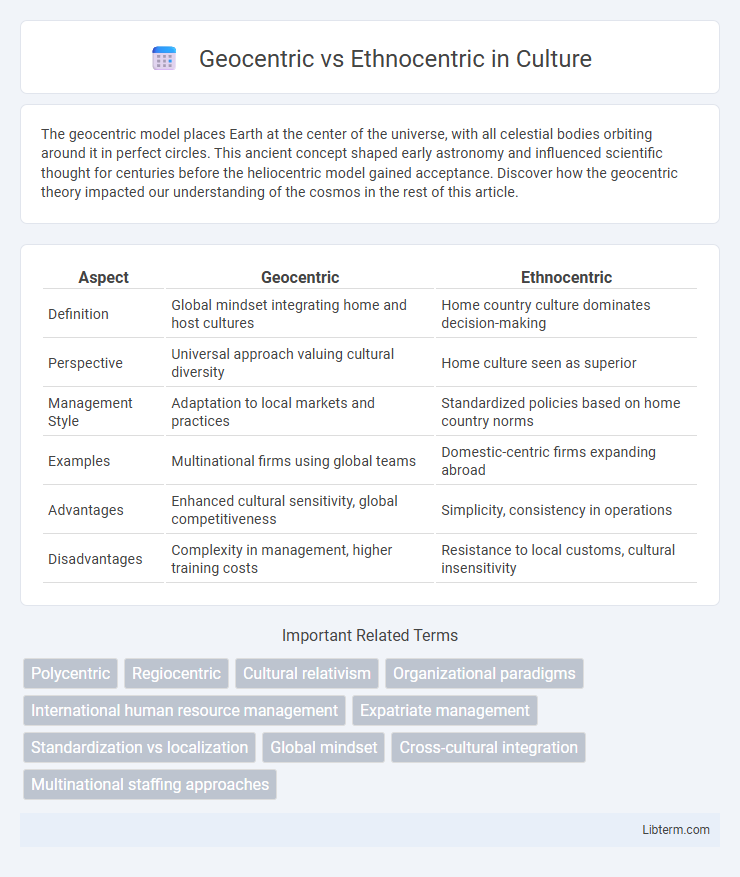
| Aspect | Geocentric | Ethnocentric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Global mindset integrating home and host cultures | Home country culture dominates decision-making |
| Perspective | Universal approach valuing cultural diversity | Home culture seen as superior |
| Management Style | Adaptation to local markets and practices | Standardized policies based on home country norms |
| Examples | Multinational firms using global teams | Domestic-centric firms expanding abroad |
| Advantages | Enhanced cultural sensitivity, global competitiveness | Simplicity, consistency in operations |
| Disadvantages | Complexity in management, higher training costs | Resistance to local customs, cultural insensitivity |
Introduction to Geocentric and Ethnocentric Perspectives
Geocentric and ethnocentric perspectives represent contrasting approaches in global management and cultural understanding. Geocentric perspective prioritizes a global outlook, integrating both local and international viewpoints to optimize business strategies and cultural interactions. Ethnocentric perspective centers on the home country's practices and values, often leading to a limited or biased understanding of other cultures.
Defining Geocentrism in Global Context
Geocentrism in a global business context refers to an orientation where companies integrate both global and local perspectives, treating the entire world as a potential market while valuing local practices and cultures. This approach balances global standardization with local adaptation, enabling multinational corporations to optimize operations, marketing strategies, and management practices across diverse cultures. Emphasizing geocentrism fosters global synergy and competitive advantage by leveraging the best talents and ideas regardless of geographic boundaries.
The Ethnocentric Approach Explained
The ethnocentric approach emphasizes management practices and business strategies based on the home country's culture and values, often leading organizations to apply domestic methods to international operations without significant adaptation. This strategy assumes the superiority of the home country's practices, resulting in employees from the parent country occupying key positions abroad. Companies using this approach may face challenges in local responsiveness and cultural sensitivity, potentially affecting global market success.
Key Differences Between Geocentric and Ethnocentric Views
Geocentric views prioritize a global perspective, integrating diverse cultural insights to create universal strategies, while ethnocentric views favor the home country's culture and practices as superior. Geocentric approaches promote inclusivity and adaptability in international business, contrasting with ethnocentric approaches that often lead to cultural bias and limited local responsiveness. The key difference lies in the geocentric emphasis on global integration versus the ethnocentric focus on domestic cultural dominance.
Advantages of a Geocentric Mindset
A geocentric mindset in global business fosters cultural integration by valuing diverse perspectives, enhancing innovation and collaboration across international teams. It enables organizations to leverage local expertise while maintaining a unified corporate strategy, improving decision-making and market responsiveness. This approach also reduces ethnocentric biases, promoting inclusivity and better adaptation to global markets.
Drawbacks of an Ethnocentric Approach
The drawbacks of an ethnocentric approach include limited cultural sensitivity, which can lead to miscommunication and poor relationships with international markets. This approach often results in a lack of local responsiveness, causing companies to overlook important cultural nuances and consumer preferences. Furthermore, ethnocentrism may hinder global expansion efforts by fostering resistance to diverse ideas and reducing the effectiveness of business strategies in foreign environments.
Impact on International Business Strategies
Geocentric strategies in international business promote a global mindset by integrating local responsiveness with global efficiency, leading to increased market adaptability and competitive advantage. Ethnocentric approaches prioritize home-country practices and standards, which can hinder cultural sensitivity and limit international market penetration. Companies adopting geocentric models often achieve better talent management and innovation through diverse perspectives, enhancing long-term global growth.
Cultural Implications of Geocentric vs Ethnocentric Policies
Geocentric policies promote cross-cultural integration by valuing global diversity and encouraging multinational collaboration, which fosters innovation and adaptability in diverse markets. Ethnocentric policies prioritize the home country's cultural norms and values, often leading to cultural biases and resistance in foreign subsidiaries, potentially causing miscommunication and reduced local employee engagement. Organizations adopting geocentric approaches typically achieve higher cultural sensitivity and improved global reputation compared to ethnocentric frameworks that risk cultural insensitivity and operational inefficiencies abroad.
Real-World Examples: Geocentric and Ethnocentric Models
Companies like McDonald's exemplify the geocentric model by blending global efficiency with local responsiveness, adapting menus to regional tastes while maintaining a consistent brand identity worldwide. In contrast, ethnocentric firms such as early Walmart operations impose home-country practices and management styles on foreign subsidiaries, often leading to cultural clashes and reduced local market effectiveness. The geocentric approach drives global integration and innovation, whereas ethnocentric models emphasize centralized control but risk overlooking important local consumer preferences.
Choosing the Right Perspective for Global Success
Choosing the right perspective between geocentric and ethnocentric approaches is crucial for global business success, as geocentric strategies foster integration by valuing diverse cultural insights, while ethnocentric approaches prioritize home-country practices that may limit local adaptation. Companies adopting a geocentric mindset benefit from enhanced cross-cultural collaboration and innovation, leading to sustainable international growth. Evaluating market demands, organizational goals, and cultural contexts helps in selecting a perspective that optimizes global competitiveness and operational efficiency.
Geocentric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com