An autonym is a name used by a group or individual to refer to themselves, often reflecting their cultural or linguistic identity. Understanding autonyms helps clarify self-identification versus external labels, reducing misrepresentation in communication. Discover how autonyms shape identity and influence social interactions by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
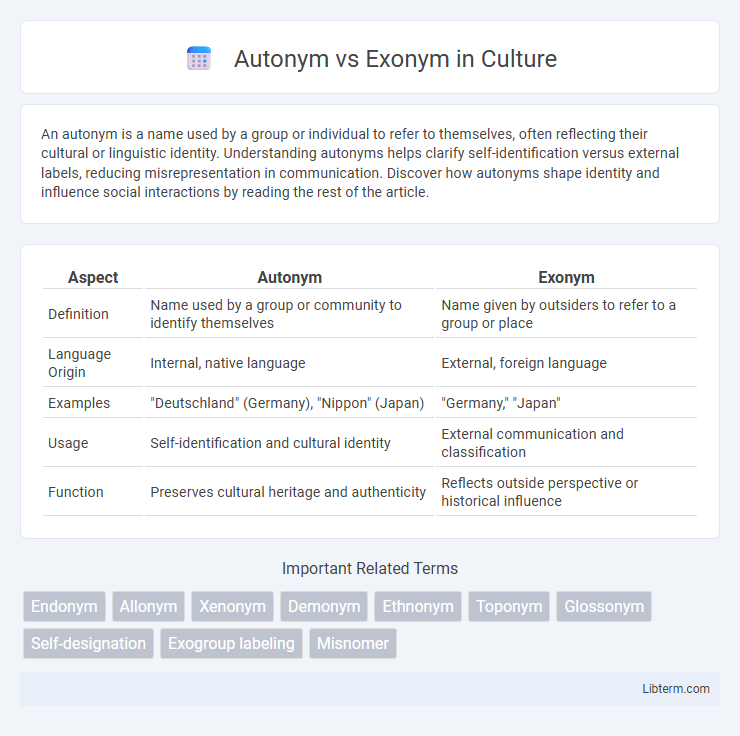
| Aspect | Autonym | Exonym |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Name used by a group or community to identify themselves | Name given by outsiders to refer to a group or place |
| Language Origin | Internal, native language | External, foreign language |
| Examples | "Deutschland" (Germany), "Nippon" (Japan) | "Germany," "Japan" |
| Usage | Self-identification and cultural identity | External communication and classification |
| Function | Preserves cultural heritage and authenticity | Reflects outside perspective or historical influence |
Introduction to Autonyms and Exonyms
Autonyms refer to the names that a group or place uses to identify itself, reflecting internal linguistic and cultural identity. Exonyms are the names given to that same group or place by outsiders, often differing significantly from the autonym due to language or historical reasons. Understanding the distinction between autonyms and exonyms is essential in fields like linguistics, geography, and ethnography to accurately represent cultural perspectives.
Defining Autonym: Meaning and Examples
An autonym is a name that a group of people use to refer to themselves or their language, reflecting their own cultural identity and self-perception. For example, "Deutsch" is the autonym Germans use for their language, while the English word "German" is an exonym. Autonyms provide insight into the internal perspective of a community, distinguishing their own terms from externally imposed names.
Understanding Exonym: Meaning and Examples
An exonym refers to the name for a geographical place, group, or language used by outsiders rather than the local population. Examples include "Germany" for the country known as "Deutschland" within its borders and "Florence" for the city called "Firenze" by Italians. Understanding exonyms helps in comprehending cultural perspectives and historical interactions between different linguistic communities.
Historical Origins of Autonyms and Exonyms
Autonyms and exonyms have roots in historical linguistic and cultural interactions, where autonyms emerged as self-designations used by communities to assert identity and sovereignty. Exonyms developed through external naming by neighboring groups, colonizers, or travelers, often reflecting phonetic adaptations or political perspectives. The study of these terms reveals patterns of power dynamics, migration, and cultural exchange in global history.
Linguistic Impact of Autonyms and Exonyms
Autonyms reflect a community's self-identity and cultural heritage, playing a crucial role in preserving linguistic diversity and local traditions. Exonyms, often shaped by historical, political, or colonial influences, can impact perceptions and sometimes contribute to the erasure or distortion of indigenous languages and identities. The interplay between autonyms and exonyms highlights the importance of respecting local nomenclature to support language revitalization and promote accurate cultural representation.
Cultural Significance in Naming Practices
Autonyms reflect a community's self-identity and cultural heritage by using names that originate within the group, preserving linguistic authenticity and historical continuity. Exonyms, assigned by outsiders, often reveal power dynamics and intercultural interactions, sometimes carrying colonial or ethnocentric connotations that impact cultural perception. The distinction between autonym and exonym is crucial for understanding respect in naming practices and the preservation of intangible cultural heritage.
Political Implications of Using Exonyms
The use of exonyms, or foreign place names, can carry significant political implications, often reflecting historical dominance or territorial disputes. Governments and communities may perceive exonyms as a form of cultural imperialism or disrespect towards their national identity and sovereignty. Choosing autonyms--the locally recognized names--strengthens national pride and supports diplomatic sensitivity in international relations.
Controversies and Sensitivities in Naming
Autonyms, or the names used by a community to identify themselves, often reflect cultural identity and heritage, while exonyms are external names assigned by others, sometimes sparking controversies due to perceived disrespect or historical misrepresentation. Sensitivities arise when exonyms perpetuate colonial legacies, ethnic discrimination, or political conflicts, prompting calls for the adoption of autonyms in official maps, documents, and discourse. The tension between global recognition and local identity underscores ongoing debates in geopolitics, linguistics, and cultural preservation.
Modern Shifts and Global Perspectives
The modern shift in linguistic usage highlights a growing preference for autonyms, as communities assert their cultural identity by using self-designated names rather than exonyms imposed by external groups. Global perspectives reveal that this trend supports respect for indigenous languages and fosters inclusivity in international discourse, challenging historical power dynamics embedded in place names. The increasing digital globalization facilitates real-time updates and widespread adoption of autonyms, reflecting evolving sociopolitical awareness and identity politics.
Conclusion: Balancing Autonym and Exonym Usage
Balancing autonym and exonym usage requires recognizing the importance of cultural respect and practical communication. Prioritizing autonyms preserves the identity and heritage of a place or people, while exonyms facilitate clarity and ease of understanding in global contexts. Effective naming strategies blend both, promoting inclusivity and mutual recognition in international discourse.
Autonym Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com