Intercultural competence enhances communication and collaboration across diverse cultural backgrounds, fostering mutual respect and understanding. Developing these skills is essential for thriving in globalized environments and overcoming cultural barriers. Explore the article to discover practical strategies for improving your intercultural interactions.
Table of Comparison
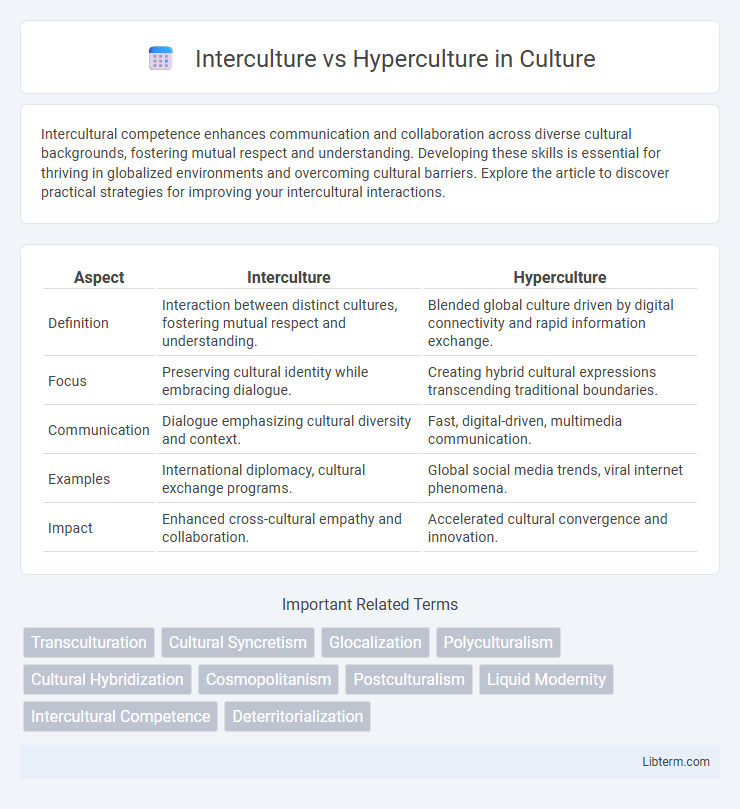
| Aspect | Interculture | Hyperculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interaction between distinct cultures, fostering mutual respect and understanding. | Blended global culture driven by digital connectivity and rapid information exchange. |
| Focus | Preserving cultural identity while embracing dialogue. | Creating hybrid cultural expressions transcending traditional boundaries. |
| Communication | Dialogue emphasizing cultural diversity and context. | Fast, digital-driven, multimedia communication. |
| Examples | International diplomacy, cultural exchange programs. | Global social media trends, viral internet phenomena. |
| Impact | Enhanced cross-cultural empathy and collaboration. | Accelerated cultural convergence and innovation. |
Defining Interculture and Hyperculture
Interculture refers to the interaction and blending of diverse cultural groups, emphasizing mutual understanding, communication, and respect among different traditions and values. Hyperculture, on the other hand, describes a globalized, digital-driven culture that transcends traditional cultural boundaries by integrating technology, shared virtual experiences, and rapid information exchange. Both concepts highlight evolving cultural dynamics but differ in their focus on localized cultural exchange versus a pervasive, technology-based cultural environment.
Historical Context of Intercultural Relations
Intercultural relations have historically evolved through trade routes, colonization, and migration, fostering exchanges between distinct cultural groups and shaping shared practices and beliefs. Interculture emphasizes interpersonal communication and understanding between diverse cultural identities, often rooted in specific historical encounters. Hyperculture, emerging in the digital age, transcends traditional boundaries by integrating multiple cultural elements into a fluid, globalized network influenced by technological advancements and mass media.
The Rise of Hyperculture in a Globalized World
Hyperculture emerges as a dominant force in the globalized world by transcending traditional intercultural exchanges and blending diverse cultural elements into a unified, dynamic identity. Driven by digital communication technologies, multinational corporations, and cross-border collaborations, hyperculture accelerates cultural convergence and creates shared values, languages, and practices across continents. This phenomenon reshapes social interactions and business strategies by prioritizing adaptability, innovation, and inclusivity in a globally interconnected environment.
Key Differences Between Interculture and Hyperculture
Interculture emphasizes authentic exchange between distinct cultural groups, focusing on mutual understanding, respect, and identity preservation, whereas Hyperculture represents a globalized blend where cultural boundaries blur, leading to hybrid identities. Interculture values cultural specificity and dialogue, while Hyperculture prioritizes fluidity and integration across diverse cultural elements. The key difference lies in Interculture's commitment to maintaining cultural uniqueness versus Hyperculture's tendency toward cultural convergence and amalgamation.
Impact on Language and Communication
Interculture emphasizes the preservation of distinct cultural identities, influencing language use through the maintenance of native languages and culturally specific communication styles, which fosters deeper understanding and respect in multilingual interactions. Hyperculture promotes the blending and merging of languages and communication norms, leading to hybrid linguistic forms and more fluid, adaptive communication patterns in global contexts. Both frameworks shape how individuals navigate cultural differences, with interculture reinforcing diversity and hyperculture encouraging linguistic convergence and innovation.
Cultural Identity: Preservation vs. Fusion
Interculture emphasizes the preservation of distinct cultural identities by encouraging dialogue and mutual respect between diverse groups, fostering a sense of belonging rooted in heritage and tradition. Hyperculture promotes cultural fusion, blending elements from multiple cultures to create new, hybrid identities that transcend traditional boundaries and encourage innovation. This dynamic shift from preservation to fusion highlights the evolving nature of cultural identity in a globalized world.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Hyperculture
Technology accelerates the development of hyperculture by enabling instantaneous global communication and information exchange, breaking down traditional cultural boundaries. Digital platforms, social media, and virtual environments create shared experiences that transcend local customs, fostering a collective identity shaped by technological innovation. This continuous connectivity strengthens hyperculture's dynamic nature, contrasting with interculture's focus on interaction between distinct, localized cultures.
Social Dynamics in Intercultural vs. Hypercultural Settings
Intercultural social dynamics involve interactions between distinct cultural groups, emphasizing communication, adaptation, and negotiation of diverse cultural norms and values. Hypercultural settings transcend traditional cultural boundaries through digital connectivity, fostering a fluid, hybrid identity where social interactions are less constrained by geographic or ethnic origins. This shift results in faster social innovations and more inclusive communities but challenges conventional cultural coherence and identity stability.
Challenges and Opportunities in a Hypercultural Society
Interculture involves navigating diverse cultural identities within distinct social groups, presenting challenges such as communication barriers and cultural misunderstandings, while offering opportunities for enhanced empathy and global collaboration. Hyperculture refers to a globalized, media-driven cultural fusion that challenges traditional norms through rapid information exchange and cultural blending, enabling innovation and cross-cultural creativity but also risking cultural homogenization and identity loss. In hypercultural societies, managing these dynamics requires adaptive intercultural competence and strategic policies to foster inclusion, preserve cultural diversity, and leverage technological connectivity for societal advancement.
Future Perspectives: Balancing Interculture and Hyperculture
Future perspectives on balancing interculture and hyperculture emphasize the integration of diverse cultural identities with global digital connectivity. Strategies involve fostering intercultural dialogue through technology while preserving unique cultural heritages in hyperconnected environments. Advancements in AI and virtual reality create immersive platforms that promote mutual understanding and cultural exchange, supporting sustainable cultural coexistence.
Interculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com