Adaptation is a crucial process that enables organisms to survive and thrive in changing environments by developing traits suited to new conditions. This biological mechanism supports evolution and species diversity, ensuring long-term survival through natural selection. Discover how adaptation shapes life and impacts ecosystems by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
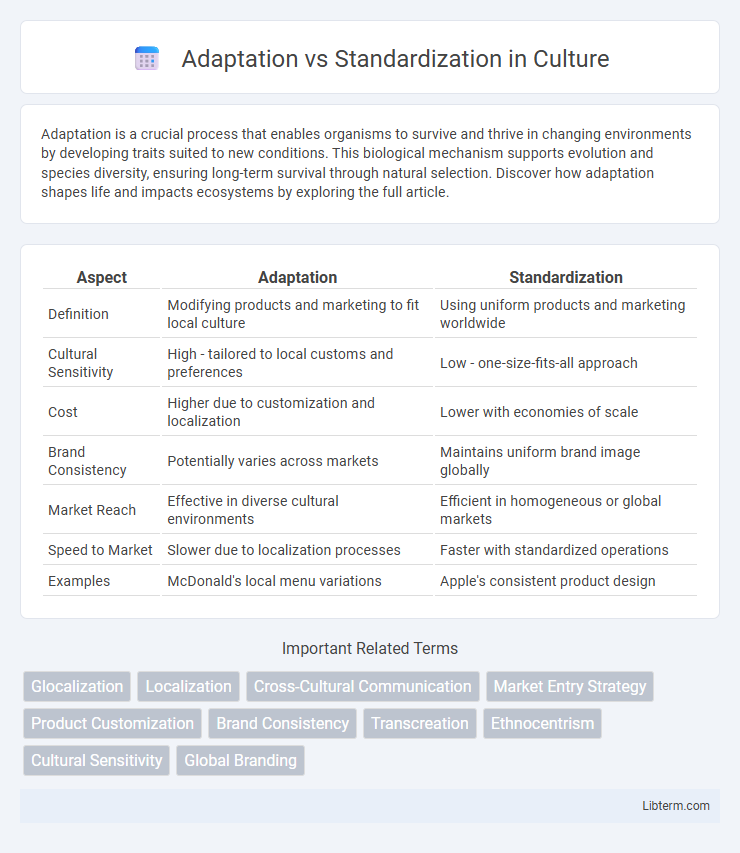
| Aspect | Adaptation | Standardization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modifying products and marketing to fit local culture | Using uniform products and marketing worldwide |
| Cultural Sensitivity | High - tailored to local customs and preferences | Low - one-size-fits-all approach |
| Cost | Higher due to customization and localization | Lower with economies of scale |
| Brand Consistency | Potentially varies across markets | Maintains uniform brand image globally |
| Market Reach | Effective in diverse cultural environments | Efficient in homogeneous or global markets |
| Speed to Market | Slower due to localization processes | Faster with standardized operations |
| Examples | McDonald's local menu variations | Apple's consistent product design |
Understanding Adaptation and Standardization
Adaptation involves modifying marketing strategies to align with local cultures, preferences, and market conditions, enhancing consumer relevance and acceptance. Standardization emphasizes using uniform marketing approaches across different regions to achieve consistency, cost efficiency, and a cohesive brand image. Effective global marketing balances adaptation and standardization to optimize market penetration and maintain brand integrity.
Key Differences Between Adaptation and Standardization
Adaptation involves customizing marketing strategies and products to meet the specific cultural, legal, and consumer preferences of each international market, whereas standardization uses uniform marketing approaches and products across all markets to achieve consistency and efficiency. Key differences include the level of localization, with adaptation requiring extensive market research and product modifications, while standardization emphasizes economies of scale and brand uniformity. Adaptation tends to increase costs but improves customer relevance, whereas standardization reduces expenses but may sacrifice local appeal.
The Importance of Adaptation in Global Markets
Adaptation is crucial in global markets because it allows brands to tailor products, marketing strategies, and communication to local cultures, consumer behaviors, and regulatory environments, enhancing relevance and customer engagement. Companies that prioritize adaptation can respond effectively to diverse market demands, improve competitive advantage, and increase market penetration by respecting regional preferences and sensitivities. This localized approach drives better customer satisfaction and boosts long-term profitability in diverse international markets.
Benefits and Challenges of Standardization
Standardization offers benefits such as consistent brand messaging, reduced marketing costs, and streamlined global operations, which enhance efficiency across international markets. Challenges include limited cultural relevance, potential consumer disconnect, and decreased flexibility to address local preferences, risking reduced market penetration and customer engagement. Balancing standardization requires addressing these issues while maintaining global brand coherence.
Factors Influencing the Choice: Adaptation or Standardization
Factors influencing the choice between adaptation and standardization include cultural differences, market conditions, and consumer behavior, which drive companies to tailor products and marketing strategies to local preferences for higher relevance and acceptance. Economic environment, regulatory requirements, and competitive landscape further shape the decision by impacting cost structures and operational feasibility. Technological infrastructure and brand positioning also play critical roles in determining whether a uniform or customized approach will maximize global business performance and customer engagement.
Industry Examples of Adaptation Strategies
In the fast-food industry, McDonald's adaptation strategy involves localizing menus to suit regional tastes, such as offering the McSpicy Paneer in India and Teriyaki Burgers in Japan. The automotive sector showcases adaptation with Toyota customizing vehicle features to comply with different countries' regulations and consumer preferences. Consumer electronics brands like Samsung adjust marketing campaigns and product functionalities to align with cultural differences and technological infrastructure in various global markets.
Case Studies: Successful Standardization Approaches
Global brands such as Coca-Cola and Apple demonstrate successful standardization by maintaining consistent branding, product design, and marketing campaigns across diverse international markets, ensuring a unified global identity. Starbucks standardizes its core menu and store experience worldwide, balancing local preferences with a strong global brand presence, resulting in widespread customer loyalty. Samsung utilizes standardized technology and product features globally while customizing only minor elements, achieving efficiency in production and marketing while satisfying consumer expectations.
Impact on Branding and Consumer Perception
Adaptation in marketing allows brands to tailor messages and products to local cultures, enhancing relevance and consumer connection, which can strengthen brand loyalty and positive perception. Standardization ensures a consistent global brand image, fostering recognition and trust across diverse markets but may risk alienating consumers if cultural differences are ignored. Balancing adaptation and standardization is crucial for maintaining brand equity while meeting local consumer expectations effectively.
Balancing Adaptation and Standardization for Global Success
Balancing adaptation and standardization involves customizing marketing strategies to fit local cultural, legal, and consumer preferences while maintaining a unified brand identity and consistent quality across global markets. Effective global companies analyze market data and use segment-specific approaches to optimize product offerings, pricing, and promotional tactics, ensuring relevance and customer loyalty. Striking this balance enhances competitive advantage by leveraging global efficiencies and local responsiveness simultaneously.
Future Trends in Global Marketing Strategies
Future trends in global marketing strategies emphasize increased personalization through advanced AI-driven data analytics, enabling tailored adaptation to diverse cultural preferences and consumer behaviors. Standardization will evolve with the integration of global digital platforms, promoting consistent brand messaging while allowing localized content adjustments to enhance relevance. Emerging technologies like augmented reality and blockchain will further support dynamic adaptation and secure global consumer engagement, blending uniformity with customization.
Adaptation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com