Cultural lag occurs when changes in technology or society outpace the adaptation of cultural norms and values, leading to social conflicts or inefficiencies. This phenomenon highlights the delays in cultural adjustments that can affect laws, customs, and social behavior. Explore the rest of the article to understand how cultural lag impacts your community and societal development.
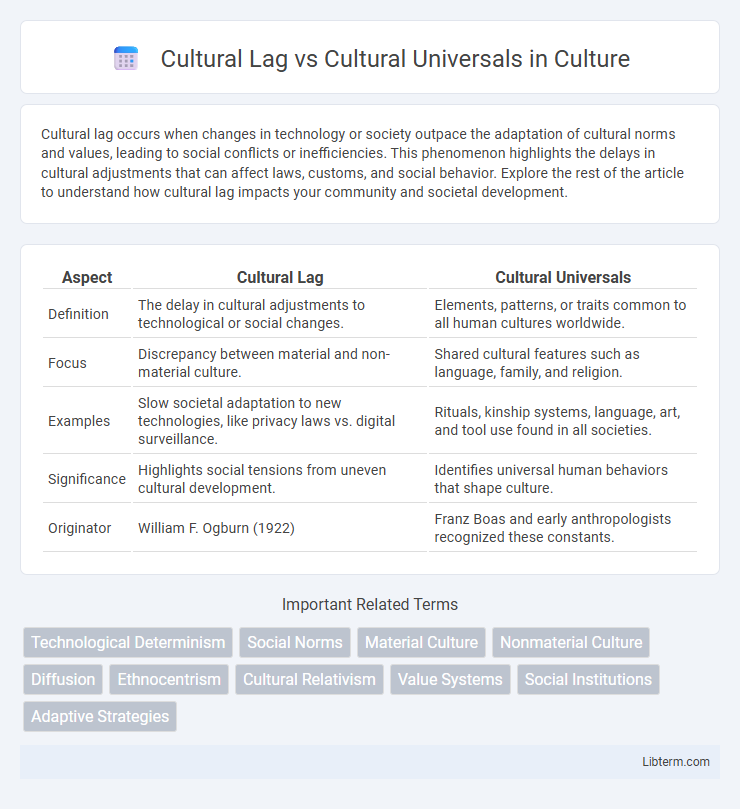
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Lag | Cultural Universals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The delay in cultural adjustments to technological or social changes. | Elements, patterns, or traits common to all human cultures worldwide. |
| Focus | Discrepancy between material and non-material culture. | Shared cultural features such as language, family, and religion. |
| Examples | Slow societal adaptation to new technologies, like privacy laws vs. digital surveillance. | Rituals, kinship systems, language, art, and tool use found in all societies. |
| Significance | Highlights social tensions from uneven cultural development. | Identifies universal human behaviors that shape culture. |
| Originator | William F. Ogburn (1922) | Franz Boas and early anthropologists recognized these constants. |
Understanding Cultural Lag: Definition and Origins
Cultural lag occurs when non-material culture, such as values and norms, struggles to keep pace with advancements in material culture like technology and infrastructure, creating a delay in societal adaptation. Originating from sociologist William F. Ogburn's theory, cultural lag highlights the tension between rapidly evolving innovations and slower-changing cultural beliefs, causing social conflicts or disorientation. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing social change dynamics and addressing challenges related to technological progress and cultural adjustment.
Exploring Cultural Universals: Meaning and Examples
Cultural universals refer to elements, patterns, traits, or institutions common to all human cultures worldwide, such as language, family structures, and religious beliefs, which arise from shared human experiences and social needs. Examples include marriage ceremonies, tool usage, and systems of education, highlighting how diverse societies independently develop similar solutions to comparable challenges. Understanding these universals provides insight into the fundamental aspects of human culture that transcend geographical and temporal boundaries.
The Relationship Between Material and Nonmaterial Culture
Cultural lag occurs when material culture, such as technological advancements, evolves faster than nonmaterial culture, including beliefs and values, leading to social adjustments and conflicts. Cultural universals, like language and family structures, exist across societies but can exhibit different expressions influenced by material conditions. The interplay between material and nonmaterial culture shapes how societies adapt, with material innovations often prompting gradual shifts in norms and cultural practices.
Causes and Consequences of Cultural Lag
Cultural lag occurs when material culture advances rapidly while non-material culture, such as beliefs and values, fails to keep pace, often due to resistance to change and established social norms. This lag causes social conflicts and inhibits the effective integration of new technologies, leading to disruptions in social institutions and roles. In contrast, cultural universals, like language and family systems, remain stable across societies, facilitating social cohesion despite cultural changes.
Examples of Cultural Universals Across Societies
Cultural universals such as language, family structures, and rituals appear across all societies, serving as fundamental elements that support social cohesion and identity. Every culture develops unique expressions of these universals, from storytelling traditions to systems of kinship and religious ceremonies, reflecting shared human experiences. These examples contrast with cultural lag, where technological or social innovations outpace cultural adaptations, creating temporary disparities in societal norms and behaviors.
Cultural Lag in the Era of Technological Advancement
Cultural lag occurs when nonmaterial culture, such as laws, values, and social norms, fails to keep pace with rapid technological advancements, resulting in social conflicts and ethical dilemmas. In the era of artificial intelligence and biotechnology, societies struggle to adapt legal frameworks and moral guidelines to emerging technologies like AI-driven decision-making and gene editing. This lag highlights the tension between technological innovation and the slow evolution of cultural responses, contrasting with cultural universals--elements shared across all human societies that provide a framework for addressing ethical and social challenges.
Bridging the Gap: Addressing Cultural Lag
Addressing cultural lag requires integrating technological advances with evolving social norms to minimize disparities between material culture and non-material culture. Strategies such as adaptive policy-making, inclusive education, and promoting cross-cultural dialogue help bridge this gap by aligning cultural values with innovations. Understanding cultural universals, like shared human behaviors and institutions, aids in creating frameworks that respect core similarities while accommodating cultural change.
How Cultural Universals Promote Social Cohesion
Cultural universals such as language, rituals, and family structures serve as foundational elements that promote social cohesion by creating shared experiences and collective identities across diverse societies. These universal cultural traits facilitate communication, cooperation, and mutual understanding, enabling groups to function cohesively despite differences in technology or ideology. In contrast, cultural lag occurs when material culture advances faster than non-material culture, causing temporary social disruptions, but cultural universals act as stabilizing agents that maintain societal continuity and harmony.
Cultural Lag vs Cultural Universals: Key Differences
Cultural lag refers to the time delay between changes in material culture and the slower adaptation of non-material culture, causing social conflicts or maladjustment. Cultural universals are elements, patterns, traits, or institutions that are common to all human cultures worldwide, such as language, family structures, and art. The key difference lies in cultural lag highlighting temporal discrepancies within a culture's adaptation process, whereas cultural universals emphasize shared characteristics that persist across diverse societies.
The Future of Culture: Adapting to Change and Preserving Universals
Cultural lag highlights the delay between technological advancements and societal adjustments, emphasizing the need for adaptive frameworks that integrate emerging innovations without losing core cultural values. Cultural universals--shared elements such as language, rituals, and social norms--serve as anchors that maintain identity amidst rapid change. The future of culture relies on balancing dynamic adaptation with the preservation of these universals, ensuring resilience and continuity in a globalized world.
Cultural Lag Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com