Tradition shapes cultural identity by preserving customs and values passed down through generations, fostering a strong sense of community and continuity. It influences social behaviors, celebrations, and rituals that connect individuals to their heritage. Discover how tradition impacts your life and society in the rest of this article.
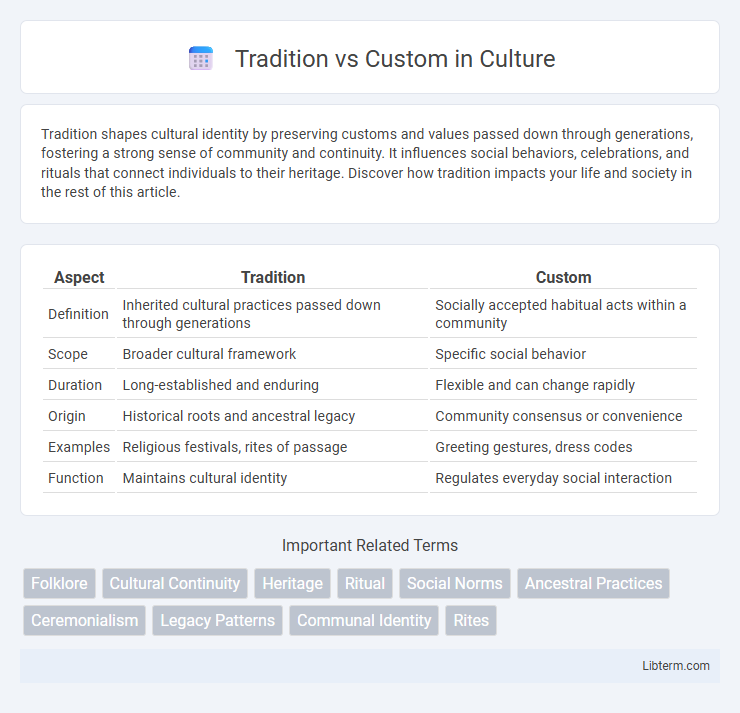
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tradition | Custom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inherited cultural practices passed down through generations | Socially accepted habitual acts within a community |
| Scope | Broader cultural framework | Specific social behavior |
| Duration | Long-established and enduring | Flexible and can change rapidly |
| Origin | Historical roots and ancestral legacy | Community consensus or convenience |
| Examples | Religious festivals, rites of passage | Greeting gestures, dress codes |
| Function | Maintains cultural identity | Regulates everyday social interaction |
Defining Tradition and Custom
Tradition refers to long-established beliefs, practices, and rituals passed down through generations, often holding cultural or religious significance. Custom involves habitual practices and behaviors regularly observed by a community or group, reflecting social norms and conventions. While traditions are deeply rooted and symbolic, customs can be more flexible and shaped by current societal contexts.
Historical Origins of Traditions and Customs
Traditions originate from historical events and cultural heritage passed down through generations, often embodying collective values and shared identities within a community. Customs, rooted in habitual practices and social norms, develop over time as adaptations to local environments and societal needs. Understanding the historical origins of traditions and customs reveals their role in shaping cultural continuity and social cohesion.
Key Differences Between Traditions and Customs
Traditions are long-established practices or beliefs passed down through generations, often carrying symbolic meanings within a culture, whereas customs are specific habitual actions or behaviors commonly practiced by a group at a particular time or event. Traditions tend to be broader, encompassing values and collective identity, while customs are more specific and situational, reflecting everyday social practices. Key differences include the scope, rigidity, and the underlying purpose, with traditions often shaping cultural continuity and customs facilitating social interaction.
Cultural Significance of Traditions
Traditions are culturally significant practices passed down through generations, embodying the collective identity and values of a community. They offer continuity and stability by preserving rituals, festivals, and ceremonies that reinforce social bonds and shared heritage. Customs, while often shaped by traditions, are more flexible behaviors adapted to changing social contexts but rooted in the same cultural foundation.
The Role of Customs in Daily Life
Customs shape daily routines by influencing social behaviors, rituals, and community interactions, promoting a sense of identity and continuity. They guide everyday practices such as greetings, dress codes, and meal preparations, reinforcing cultural cohesion. The persistent observance of customs sustains communal harmony and transmits values across generations.
How Traditions Shape Community Identity
Traditions serve as foundational elements that preserve cultural heritage and reinforce a community's collective identity by passing down values, beliefs, and practices through generations. They create a shared sense of belonging and continuity, distinguishing one community from another while fostering social cohesion. Customs, often more adaptable and localized, complement traditions by allowing communities to respond to changing environments without losing their core identity.
The Evolution of Customs Over Time
Traditions often originate from long-established cultural practices, while customs evolve more fluidly in response to societal changes, reflecting shifts in values and technology. Over time, customs adapt by integrating new influences, such as globalization and digital communication, which reshape communal behaviors and rituals. This dynamic evolution illustrates how living societies balance heritage preservation with contemporary innovation.
Tradition vs Custom in Modern Society
Tradition in modern society serves as a steadfast link to cultural heritage, preserving rituals and values passed down through generations, while custom reflects adaptive behaviors shaped by current social environments and practical needs. The coexistence of tradition and custom allows communities to maintain identity and continuity, yet embrace change and innovation to address contemporary challenges. This dynamic interplay influences social norms, where tradition offers stability and custom provides flexibility in evolving societal contexts.
Preserving Traditions and Customs
Preserving traditions and customs involves maintaining cultural practices, rituals, and values that define community identity and continuity. Traditions are long-established beliefs or behaviors passed down through generations, while customs are habitual practices specific to a group or region. Effective preservation requires documentation, active participation, and intergenerational transmission to ensure cultural heritage remains vibrant and relevant in evolving societies.
The Impact of Globalization on Local Practices
Globalization significantly influences local traditions and customs by introducing diverse cultural elements that blend or sometimes replace indigenous practices. The widespread exchange of ideas, goods, and technologies leads to the hybridization of customs, often diluting original meanings but also fostering cultural innovation. Local communities adapt by preserving core traditional values while integrating global trends, which reshapes cultural identities in a rapidly interconnected world.
Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com