Language maintenance plays a crucial role in preserving a community's cultural identity and ensuring intergenerational communication. It involves active efforts such as education, media use, and family practices to keep a language vibrant despite external influences. Discover how you can contribute to sustaining linguistic heritage by exploring effective language maintenance strategies in the rest of this article.
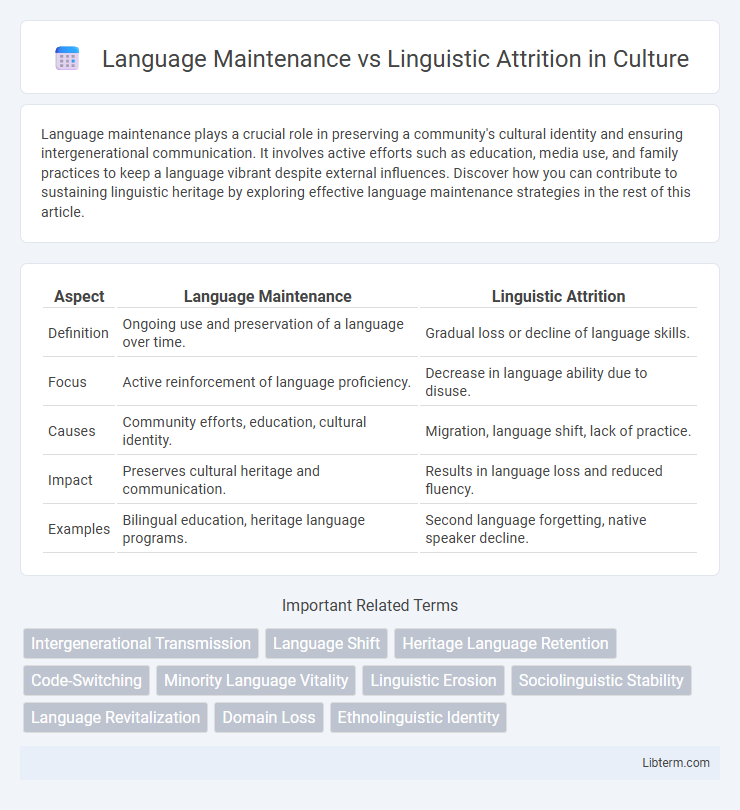
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Language Maintenance | Linguistic Attrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing use and preservation of a language over time. | Gradual loss or decline of language skills. |
| Focus | Active reinforcement of language proficiency. | Decrease in language ability due to disuse. |
| Causes | Community efforts, education, cultural identity. | Migration, language shift, lack of practice. |
| Impact | Preserves cultural heritage and communication. | Results in language loss and reduced fluency. |
| Examples | Bilingual education, heritage language programs. | Second language forgetting, native speaker decline. |
Introduction: Defining Language Maintenance and Linguistic Attrition
Language maintenance refers to the continued use and preservation of a language within a community or individual over time, despite external pressures or dominant language influences. Linguistic attrition describes the gradual loss or decline of a language skill in individuals or groups, often due to reduced exposure or use. These concepts are central to understanding how languages persist or diminish across generations and sociolinguistic environments.
Factors Influencing Language Maintenance
Language maintenance is strongly influenced by factors such as community support, frequency of language use, and access to cultural resources. Family language policies and educational opportunities also play critical roles in preserving linguistic skills across generations. Social identity and attitudes toward the heritage language directly impact the motivation to maintain or shift language use.
Causes and Processes of Linguistic Attrition
Linguistic attrition occurs when a speaker gradually loses proficiency in a language due to reduced use, often caused by immersion in a dominant language environment or lack of practice. Cognitive processes such as memory decay and interference from the dominant language accelerate attrition, impacting vocabulary retention, grammatical accuracy, and pronunciation. Social factors, including shifting identity and decreased motivation, further contribute to the decline in language performance over time.
The Role of Community and Social Networks
Community engagement and social networks are crucial in language maintenance, providing daily interactions that reinforce linguistic skills and cultural identity. Strong social bonds within a community promote consistent language use, preventing linguistic attrition by creating a supportive environment for language transmission across generations. Conversely, weakened community ties and limited social interaction often accelerate language loss, as speakers shift toward dominant languages to integrate socially and economically.
Family Influence in Language Retention
Family influence plays a crucial role in language maintenance by providing a consistent environment for using the heritage language, promoting intergenerational transmission and reinforcing cultural identity. In contrast, linguistic attrition often occurs when family members shift toward dominant languages, reducing opportunities for active use and leading to gradual loss of proficiency. Strong familial support, including regular communication and cultural practices, significantly enhances language retention across generations.
Education and Institutional Support
Education systems play a crucial role in language maintenance by providing formal instruction and creating literacy opportunities that reinforce minority languages, thereby preventing linguistic attrition. Institutional support such as bilingual education programs, government policies promoting mother tongue instruction, and community language resources steadily sustain language proficiency across generations. Conversely, the absence of such educational frameworks often accelerates linguistic attrition as speakers shift toward dominant languages for academic and socioeconomic advancement.
Individual Attitudes Towards Language Use
Individual attitudes towards language use significantly influence language maintenance and linguistic attrition. Positive attitudes and strong emotional ties to a language enhance motivation to preserve language skills, reducing attrition rates. Conversely, negative perceptions or lack of community support often accelerate linguistic attrition and hinder active language maintenance.
Case Studies: Success and Failure in Language Maintenance
Case studies in language maintenance reveal diverse outcomes influenced by community engagement, educational programs, and intergenerational transmission. Successful cases, such as the revival of Welsh through immersive schooling and media promotion, demonstrate how institutional support and cultural pride sustain minority languages. Conversely, failure often stems from lack of resources, dominant language pressure, and insufficient policy backing, as seen in many Indigenous languages facing rapid linguistic attrition.
Strategies to Combat Linguistic Attrition
Effective strategies to combat linguistic attrition include immersive language exposure, consistent practice through speaking and writing, and engagement with native speakers to reinforce fluency. Structured language courses and the use of multimedia resources such as films, podcasts, and literature in the target language help maintain vocabulary and grammar proficiency. Regular participation in language communities, both online and offline, supports sustained language use and cultural connection, crucial for language maintenance.
Future Directions in Language Preservation
Future directions in language preservation emphasize integrating advanced AI technologies and community-driven digital platforms to counteract linguistic attrition effectively. Research prioritizes developing adaptive tools that support language maintenance by facilitating immersive learning experiences and real-time language use tracking. Emphasizing interdisciplinary collaboration among linguists, technologists, and native speakers enhances sustainable strategies for preserving endangered languages globally.
Language Maintenance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com