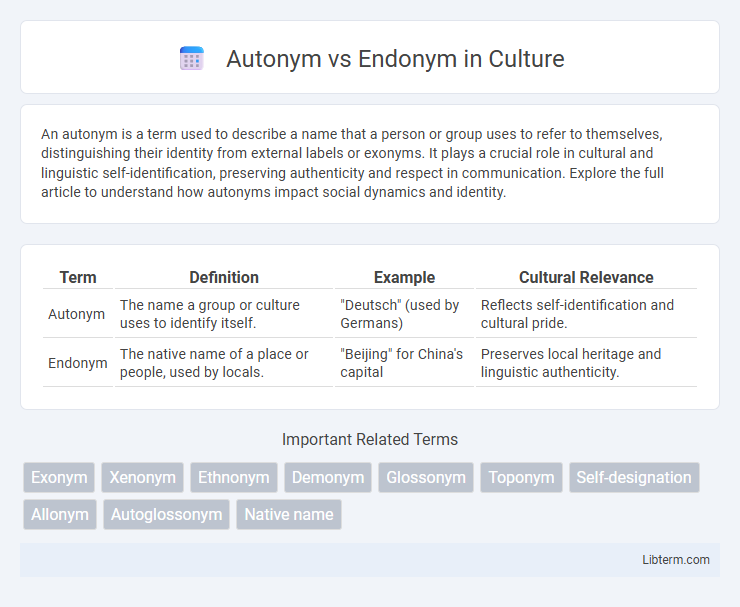
An autonym is a term used to describe a name that a person or group uses to refer to themselves, distinguishing their identity from external labels or exonyms. It plays a crucial role in cultural and linguistic self-identification, preserving authenticity and respect in communication. Explore the full article to understand how autonyms impact social dynamics and identity.
Table of Comparison
| Term | Definition | Example | Cultural Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autonym | The name a group or culture uses to identify itself. | "Deutsch" (used by Germans) | Reflects self-identification and cultural pride. |
| Endonym | The native name of a place or people, used by locals. | "Beijing" for China's capital | Preserves local heritage and linguistic authenticity. |
Introduction to Autonyms and Endonyms
Autonyms and endonyms are terms used in linguistics to describe names that groups use to identify themselves or their geographic locations. An autonym is a self-designation or the name a group or individual uses for themselves, reflecting internal identity and cultural significance. Endonyms are native or local names for places, used by the inhabitants, contrasting with exonyms, which are names given by outsiders.
Defining Autonym: Meaning and Usage
An autonym is a name used by a group or individual to refer to themselves, reflecting their own identity and linguistic preferences. Unlike exonyms or external names given by outsiders, autonyms preserve the authentic cultural and social significance embedded in self-identification. Understanding autonyms is crucial for accurate representation in ethnographic studies, cartography, and language documentation.
Understanding Endonym: Meaning and Application
An endonym is the name used by locals to identify a geographical place, reflecting the cultural and linguistic identity of its inhabitants. Unlike exonyms, which are names given by outsiders, endonyms provide authentic and intrinsic labels that preserve historical significance and community heritage. Understanding endonyms is essential for accurate geographical representation, fostering cultural respect, and enhancing communication in multilingual contexts.
Key Differences Between Autonym and Endonym
Autonym refers to the name a person or group uses to identify themselves, especially in linguistic or ethnographic contexts, whereas endonym is the native or local name used for a geographical place by its inhabitants. The key difference lies in scope: autonym applies primarily to people or languages, while endonym pertains to place names. Both terms contrast with exonyms, which are names given by outsiders.
Historical Context of Naming Cultures
Autonyms emerge from within a culture as self-designations reflecting internal identity and social cohesion, while endonyms specifically denote indigenous names used by native populations to identify places or peoples. Historical context reveals that autonyms often predate external contact, preserving original meanings and linguistic roots despite colonization or globalization pressures. Understanding endonyms in cultural history highlights resistance to imposed exonyms, as indigenous communities assert sovereignty and reclaim heritage through traditional nomenclature.
Examples of Autonyms Around the World
Autonyms are self-designations used by groups or individuals to identify themselves, such as "Deutsch" for Germans or "Francais" for the French, reflecting their own linguistic and cultural identity. Examples include "Nippon" or "Nihon" as the autonym for Japan, and "Magyar" for Hungarians, highlighting the differences from external exonyms like "Japan" or "Hungary." These autonyms provide insight into internal perspectives and are essential in understanding ethnic, national, and linguistic self-identification globally.
Examples of Endonyms Across Regions
Endonyms are the local names used by inhabitants to refer to their own geographic locations, such as "Deutschland" for Germany in German, "Espana" for Spain in Spanish, and "Zhong Guo " (Zhongguo) for China in Mandarin. These indigenous terms reflect the cultural identity and linguistic heritage of regions, unlike autonyms that may denote personal names or identifiers. Recognizing endonyms provides deeper insight into regional languages and the way communities view their own territories.
The Impact of Exonyms on Identity
Exonyms, as externally imposed place names, often shape perceptions and narratives that may conflict with a community's self-identified autonym or endonym, impacting cultural identity and heritage. The use of exonyms can reinforce colonial histories or political dominance, undermining local autonomy and the authenticity of indigenous languages. Recognition and restoration of endonyms contribute to the preservation of cultural integrity and promote respectful global understanding.
The Importance of Using Correct Names
Using correct names such as autonyms and endonyms is crucial for respecting cultural identity and fostering accurate communication. Autonyms, the names a group uses for itself, and endonyms, local place names used by inhabitants, preserve heritage and promote inclusivity in geopolitical contexts. Correct usage helps prevent misunderstandings and supports cultural recognition in international relations and academic research.
Autonym vs Endonym: Why It Matters Today
Autonym and endonym both refer to the names used by native speakers to identify themselves or their locations, with autonym specifically denoting a group's self-designation and endonym representing place names used within a local language. The distinction matters today in global communication, cultural preservation, and geopolitical recognition, as using correct autonyms and endonyms respects indigenous identity and counters colonial or external naming impositions. Emphasizing accurate autonyms and endonyms supports linguistic diversity and strengthens cultural heritage amid globalization and international diplomacy.
Autonym Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com