Mythos explores the rich tapestry of traditional stories that have shaped cultures and beliefs throughout history. Understanding these ancient narratives reveals the values and lessons embedded in human civilization's collective consciousness. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover how Mythos continues to influence your worldview today.
Table of Comparison
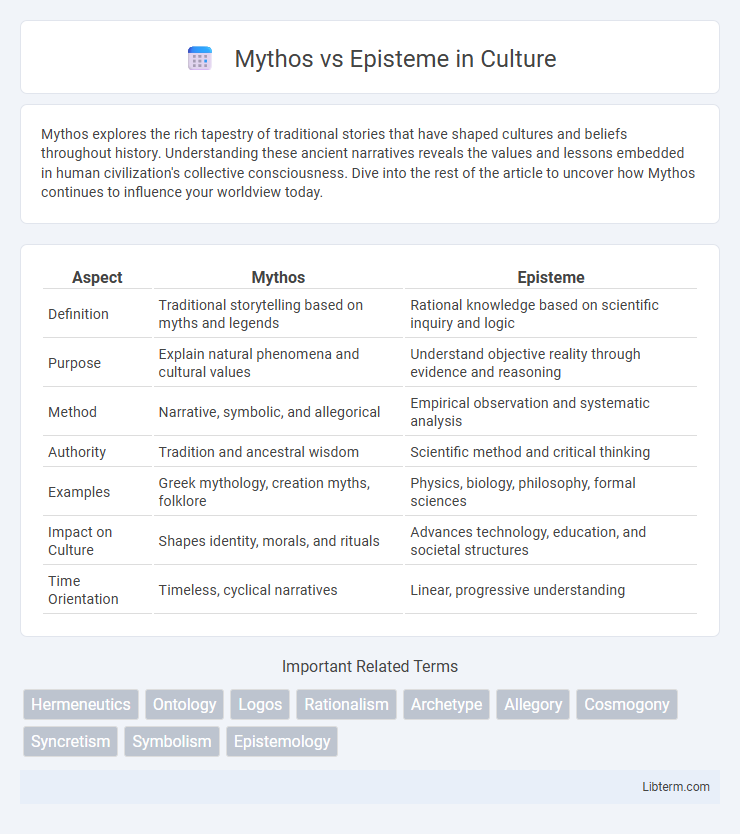
| Aspect | Mythos | Episteme |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional storytelling based on myths and legends | Rational knowledge based on scientific inquiry and logic |
| Purpose | Explain natural phenomena and cultural values | Understand objective reality through evidence and reasoning |
| Method | Narrative, symbolic, and allegorical | Empirical observation and systematic analysis |
| Authority | Tradition and ancestral wisdom | Scientific method and critical thinking |
| Examples | Greek mythology, creation myths, folklore | Physics, biology, philosophy, formal sciences |
| Impact on Culture | Shapes identity, morals, and rituals | Advances technology, education, and societal structures |
| Time Orientation | Timeless, cyclical narratives | Linear, progressive understanding |
Understanding Mythos and Episteme: Defining the Concepts
Mythos and episteme represent two fundamental modes of knowledge: mythos refers to narrative-based understanding rooted in cultural stories and symbolic meaning, while episteme denotes systematic, logical knowledge grounded in empirical evidence and rational analysis. In ancient philosophy, mythos conveyed collective truths through myths and religious traditions, shaping moral and existential perspectives. Episteme evolved with the rise of scientific inquiry, emphasizing verifiable facts and universal principles that form the basis of modern epistemology.
Historical Roots: Mythos and Episteme in Ancient Thought
Mythos and Episteme, foundational concepts in ancient Greek philosophy, delineate contrasting modes of understanding reality: Mythos embodies narrative-based knowledge grounded in tradition and mythology, while Episteme represents systematic, rational knowledge derived from logic and empirical observation. Ancient thinkers like Plato and Aristotle emphasized Episteme as a pursuit of universal truths through reason, contrasting it with the mythic explanations that characterized early oral cultures. This dichotomy reflects the historical roots of Western epistemology, where the transition from Mythos to Episteme marks the evolution from mythological interpretations to scientific inquiry.
The Role of Mythos in Shaping Cultural Narratives
Mythos plays a crucial role in shaping cultural narratives by embodying collective values, beliefs, and traditions through symbolic stories that transcend empirical knowledge. It influences social cohesion and identity formation by providing a shared framework for understanding human experience and natural phenomena. These narratives often serve as foundational myths that guide moral codes and communal practices across diverse cultures.
Episteme and the Pursuit of Rational Knowledge
Episteme represents systematic, rational knowledge grounded in empirical evidence and logical reasoning, forming the foundation of scientific inquiry and critical thinking. It emphasizes objective understanding through verified facts and consistent methodologies, distinguishing itself from mythos, which relies on narrative and traditional beliefs. Pursuing episteme involves rigorous validation processes, fostering advancements in technology, medicine, and philosophy by prioritizing reason over intuition or myth.
Mythos vs Episteme: Divergent Paths to Truth
Mythos and Episteme represent divergent approaches to understanding truth, with Mythos rooted in narrative, tradition, and symbolic meaning, while Episteme emphasizes rationality, empirical evidence, and scientific inquiry. Mythos conveys cultural values and existential insights through myths and stories, shaping collective identity and moral frameworks. Episteme seeks objective knowledge through systematic investigation, prioritizing verifiable facts and logical reasoning to explain natural phenomena and human behavior.
Intersections: When Mythos and Episteme Converge
Mythos and Episteme converge in the shared pursuit of understanding reality through narrative frameworks and structured knowledge. Mythos imparts cultural values and existential meanings, while Episteme offers empirical investigation and rational analysis, creating a dynamic interplay where mythological stories inform scientific paradigms and scientific discoveries reshape cultural myths. This intersection highlights how human cognition integrates symbolic interpretation with logical reasoning to construct comprehensive worldviews.
Modern Society: Balancing Mythological and Scientific Perspectives
Modern society navigates the tension between Mythos and Episteme by integrating mythological narratives with empirical scientific knowledge to address complex social and existential questions. Mythos provides cultural identity, ethical values, and meaning-making frameworks, while Episteme drives technological innovation, rational inquiry, and evidence-based decision-making. This balance fosters a holistic worldview that respects traditional wisdom and cultural heritage alongside scientific progress and critical thinking.
Case Studies: Mythos and Episteme in Literature and Science
Case studies in literature reveal Mythos as narrative-driven, embodying cultural myths and collective human experiences, while Episteme represents systematic knowledge grounded in rational analysis and empirical evidence. In science, Mythos often appears in the form of foundational myths or paradigms influencing research directions, whereas Episteme manifests through methodological rigor and verifiable data underpinning scientific theories. Examining works like Homeric epics alongside scientific revolutions highlights how Mythos and Episteme interact to shape human understanding across disciplines.
The Enduring Relevance of Mythos and Episteme Today
Mythos and episteme represent two foundational modes of understanding: mythos through narrative and symbolic meaning, and episteme through empirical knowledge and rational inquiry. The enduring relevance of mythos lies in its ability to convey cultural values and existential truths that shape identity and moral frameworks. Episteme remains crucial for advancing scientific progress and technological innovation, while mythos continues to influence human psychology and social cohesion.
Rethinking the Dichotomy: Toward a Unified Understanding
Mythos and episteme have traditionally represented contrasting ways of understanding the world, with mythos rooted in narrative and symbolic meaning, and episteme grounded in empirical knowledge and rationality. Recent scholarship advocates rethinking this dichotomy as a false binary, emphasizing their interconnectedness in shaping human cognition and culture. Integrating mythos and episteme fosters a unified epistemology that acknowledges both the symbolic depth of myths and the rigor of scientific inquiry in constructing knowledge.
Mythos Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com