Polycentric approaches prioritize multiple centers of decision-making power, promoting diversity and adaptability within organizations or urban planning. This model fosters collaboration among various independent units, enhancing innovation and local responsiveness. Discover how embracing polycentric strategies can transform Your systems by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
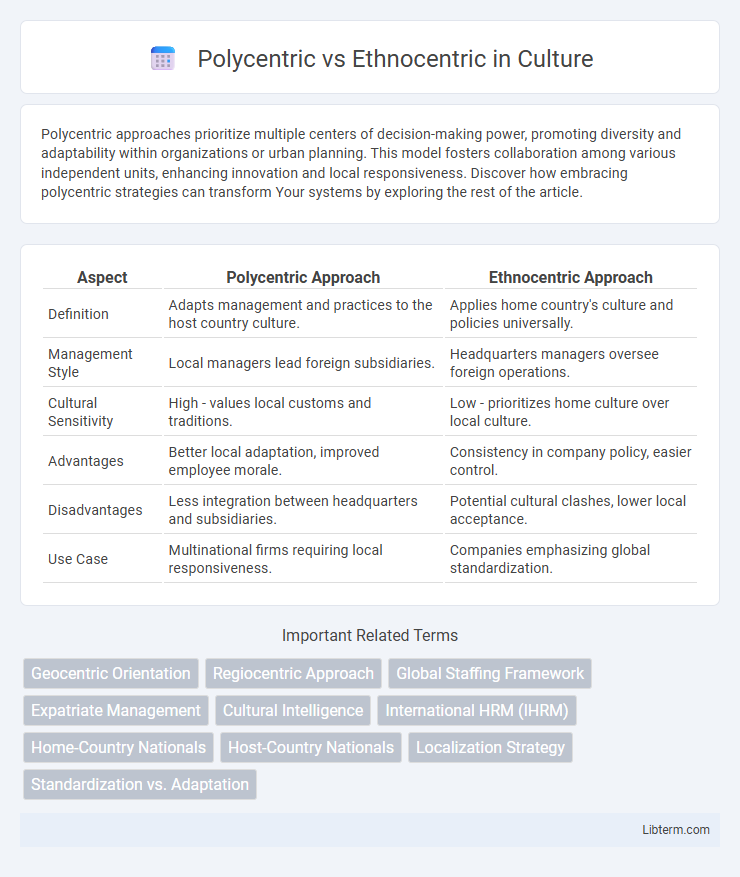
| Aspect | Polycentric Approach | Ethnocentric Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapts management and practices to the host country culture. | Applies home country's culture and policies universally. |
| Management Style | Local managers lead foreign subsidiaries. | Headquarters managers oversee foreign operations. |
| Cultural Sensitivity | High - values local customs and traditions. | Low - prioritizes home culture over local culture. |
| Advantages | Better local adaptation, improved employee morale. | Consistency in company policy, easier control. |
| Disadvantages | Less integration between headquarters and subsidiaries. | Potential cultural clashes, lower local acceptance. |
| Use Case | Multinational firms requiring local responsiveness. | Companies emphasizing global standardization. |
Introduction to Polycentric and Ethnocentric Approaches
The polycentric approach to international management emphasizes adapting business strategies to local markets by employing host country nationals in key positions, fostering cultural sensitivity and local responsiveness. In contrast, the ethnocentric approach centers on transferring home country practices and personnel to foreign subsidiaries, ensuring consistency and centralized control across international operations. Understanding these approaches is crucial for multinational companies aiming to balance global integration with local adaptation.
Defining Polycentric Orientation
Polycentric orientation defines a management approach where multinational companies tailor strategies and operations to fit the cultural norms and consumer behaviors of each host country. This approach prioritizes local responsiveness by employing local managers who understand the unique market conditions and regulatory environments. Polycentric orientation contrasts with ethnocentric orientation, which emphasizes home-country practices and centralized decision-making.
Understanding Ethnocentric Perspective
The ethnocentric perspective centers on evaluating other cultures based on the standards of one's own culture, often leading to biased decision-making in global business. This approach can hinder effective cross-cultural communication and limit the ability to adapt marketing strategies to local markets. Understanding ethnocentrism is crucial for multinational corporations aiming to balance home-country interests with diverse cultural contexts.
Key Differences Between Polycentric and Ethnocentric Strategies
Polycentric strategy prioritizes local responsiveness by hiring and promoting employees from the host country, while ethnocentric strategy emphasizes a home-country orientation with key positions occupied by parent-country nationals. Decision-making in polycentric approaches is decentralized, allowing subsidiaries greater autonomy, whereas ethnocentric approaches maintain centralized control from headquarters. Cultural adaptation and market-specific strategies characterize polycentric models, contrasted by the standardization and uniformity seen in ethnocentric frameworks.
Advantages of Polycentric Approach in Global Business
The polycentric approach enables multinational companies to tailor business strategies to local markets, enhancing cultural sensitivity and customer satisfaction. It promotes better compliance with local laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues and fostering goodwill within host countries. Employing local managers through this approach improves communication, decision-making, and employee motivation, leading to increased operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
Drawbacks of Ethnocentric Approach in Multinational Firms
The ethnocentric approach in multinational firms often leads to cultural insensitivity, causing miscommunication and reduced employee morale in host countries. This approach limits local talent development by prioritizing parent country nationals, which can hinder effective adaptation to regional markets. Moreover, it risks alienating local customers and partners due to a lack of understanding of diverse cultural and business practices.
Impact on Human Resource Management
Polycentric staffing strategies prioritize hiring local employees in foreign subsidiaries, enhancing cultural integration and reducing expatriate costs, which improves employee retention and local responsiveness. Ethnocentric approaches deploy home-country nationals to key positions abroad, ensuring aligned corporate values and tighter control but often result in higher relocation expenses and potential cultural clashes. Effective human resource management balances these models to optimize global talent deployment, leadership development, and organizational cohesion across diverse markets.
Case Studies: Polycentric vs Ethnocentric Companies
Polycentric companies adapt their management strategies to suit the cultural contexts of host countries, as demonstrated by McDonald's localization approach in India, where menu customization improved market acceptance. Ethnocentric companies, like Walmart's initial entry into Germany, imposed home-country practices that often clashed with local consumer preferences and regulatory environments, leading to operational failures. Case studies reveal polycentric firms achieve higher local engagement and flexibility, while ethnocentric firms struggle with cultural misalignment and reduced market responsiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach for Market Expansion
Choosing the right approach for market expansion involves evaluating polycentric and ethnocentric strategies based on the target market's cultural, economic, and regulatory environments. A polycentric approach emphasizes adapting marketing, management, and product strategies to local preferences, enhancing customer relevance and competitive advantage in diverse regions. Ethnocentric strategies centralize decision-making and use home-country practices, which can ensure consistency and control but may risk misalignment with local market needs.
Future Trends in International Business Strategies
Future trends in international business strategies show a shift toward polycentric approaches, emphasizing local responsiveness and adaptation to diverse markets. Advances in digital communication technologies facilitate decentralized decision-making, enabling subsidiaries to tailor strategies to regional consumer preferences and regulatory environments. Corporations increasingly balance ethnocentric control with polycentric flexibility to optimize global integration while fostering innovation and cultural sensitivity.
Polycentric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com