Transculturalism promotes the blending and interaction of diverse cultures, fostering mutual understanding and enriched global perspectives. It challenges rigid cultural boundaries by encouraging individuals to embrace multiple cultural identities in everyday life. Explore the rest of the article to discover how transculturalism can transform your worldview and relationships.
Table of Comparison
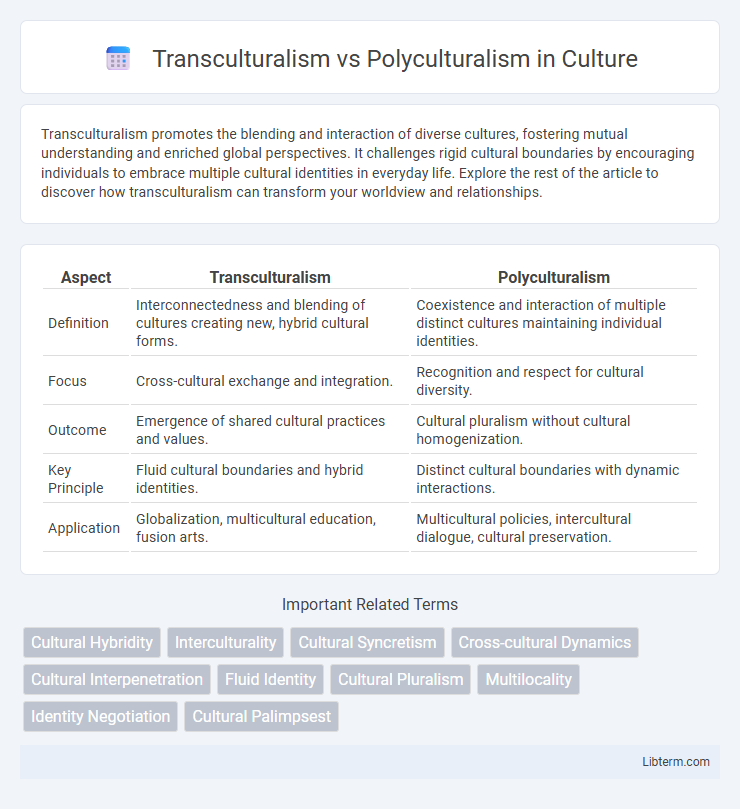
| Aspect | Transculturalism | Polyculturalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interconnectedness and blending of cultures creating new, hybrid cultural forms. | Coexistence and interaction of multiple distinct cultures maintaining individual identities. |
| Focus | Cross-cultural exchange and integration. | Recognition and respect for cultural diversity. |
| Outcome | Emergence of shared cultural practices and values. | Cultural pluralism without cultural homogenization. |
| Key Principle | Fluid cultural boundaries and hybrid identities. | Distinct cultural boundaries with dynamic interactions. |
| Application | Globalization, multicultural education, fusion arts. | Multicultural policies, intercultural dialogue, cultural preservation. |
Defining Transculturalism
Transculturalism defines the dynamic process where individuals and cultures interact, blend, and evolve beyond fixed cultural boundaries, fostering mutual understanding and shared experiences. It emphasizes the fluid exchange and transformation of cultural identities rather than maintaining isolated or hierarchical relationships. This concept contrasts with polyculturalism, which highlights the coexistence of multiple distinct cultures within a shared space while recognizing their interconnections.
Understanding Polyculturalism
Polyculturalism emphasizes dynamic interactions and continuous exchanges among diverse cultural groups, highlighting interconnected histories and shared influences rather than fixed identities. It promotes recognizing cultural hybridity and reciprocal relationships, fostering social cohesion through mutual respect and collaborative growth. Understanding polyculturalism involves appreciating how cultures evolve together, shaping collective identities beyond rigid boundaries.
Historical Evolution of Both Concepts
Transculturalism and polyculturalism emerged as responses to globalization and multicultural societies, with transculturalism tracing its roots to early 20th-century anthropology emphasizing fluid cultural boundaries. Polyculturalism developed later, gaining prominence in the late 20th century, highlighting the interconnectedness and interaction of multiple cultures within social and historical contexts. Both concepts evolved through scholarly debates on cultural identity, hybridity, and the dynamics of cultural exchange in postcolonial and migration studies.
Core Principles: Differences and Similarities
Transculturalism emphasizes the blending and merging of cultures into a new, shared cultural experience, focusing on dialogue, interaction, and the creation of hybrid identities. Polyculturalism highlights the coexistence and interrelation of multiple distinct cultures within a society, recognizing their interconnected histories without erasing individual cultural boundaries. Both frameworks promote cultural exchange and relational understanding, but transculturalism centers on synthesis, while polyculturalism values multiplicity and ongoing cultural connections.
Impact on Identity and Community
Transculturalism fosters fluid identities by encouraging the blending and interaction of diverse cultural elements, promoting inclusive communities where individuals share cross-cultural experiences. Polyculturalism emphasizes multiple coexisting cultures within communities, highlighting interconnected histories and hybridity, which strengthens group identities while recognizing diversity. Both frameworks impact social cohesion by reshaping how individuals relate to cultural boundaries and collective belonging.
Influence on Global Communication
Transculturalism promotes the blending of cultural elements to create a shared global identity, enhancing mutual understanding and reducing cultural barriers in international communication. Polyculturalism emphasizes the coexistence and interaction of diverse cultures while maintaining their distinctiveness, fostering intercultural dialogue and respect in global exchanges. Both frameworks influence global communication by shaping how cultural differences are negotiated and integrated within multinational organizations and digital platforms.
Transculturalism in Education
Transculturalism in education emphasizes the integration of diverse cultural perspectives to create a holistic learning environment that transcends traditional cultural boundaries. This approach fosters critical thinking, empathy, and global awareness by encouraging students to engage with multiple cultural narratives and experiences simultaneously. Unlike polyculturalism, which highlights the coexistence of distinct cultures, transculturalism seeks to blend and synthesize cultural elements, promoting interconnectedness and dynamic cultural exchange in educational settings.
Polyculturalism in Social Dynamics
Polyculturalism in social dynamics emphasizes the interconnectedness and constant interaction among diverse cultural groups, promoting shared experiences and mutual influence rather than fixed cultural boundaries. This approach fosters social cohesion by recognizing the fluidity of identities and encouraging collaboration across cultural lines, which contrasts with transculturalism's focus on blending cultures into a unified whole. Polyculturalism supports dynamic social environments where cultural exchange shapes community development and collective identity in diverse societies.
Challenges and Criticisms
Transculturalism faces challenges related to the loss of distinct cultural identities as it emphasizes blending cultures, which critics argue can lead to cultural homogenization and the dilution of heritage. Polyculturalism is criticized for potentially oversimplifying complex cultural interactions by focusing on interconnections without adequately addressing power imbalances and historical inequalities among cultures. Both paradigms struggle with practical implementation in diverse societies, as they must reconcile the tension between promoting unity and respecting distinct cultural narratives.
Future Perspectives and Societal Implications
Transculturalism promotes the blending and integration of multiple cultures to create new, hybrid identities that foster mutual understanding and innovation, supporting future societies toward greater cohesion and adaptability. Polyculturalism emphasizes the coexistence and interaction of diverse cultures while preserving distinct traditions, encouraging societal frameworks that value pluralism and dynamic cultural exchange. Both perspectives influence future policies on multicultural education, social inclusivity, and global collaboration, shaping increasingly interconnected communities resilient to cultural conflicts.
Transculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com