Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, fostering mutual respect and understanding among different groups. It enriches communities by encouraging the exchange of traditions, languages, and perspectives, which enhances social cohesion and innovation. Explore the rest of this article to discover how multiculturalism can positively impact your community and daily life.
Table of Comparison
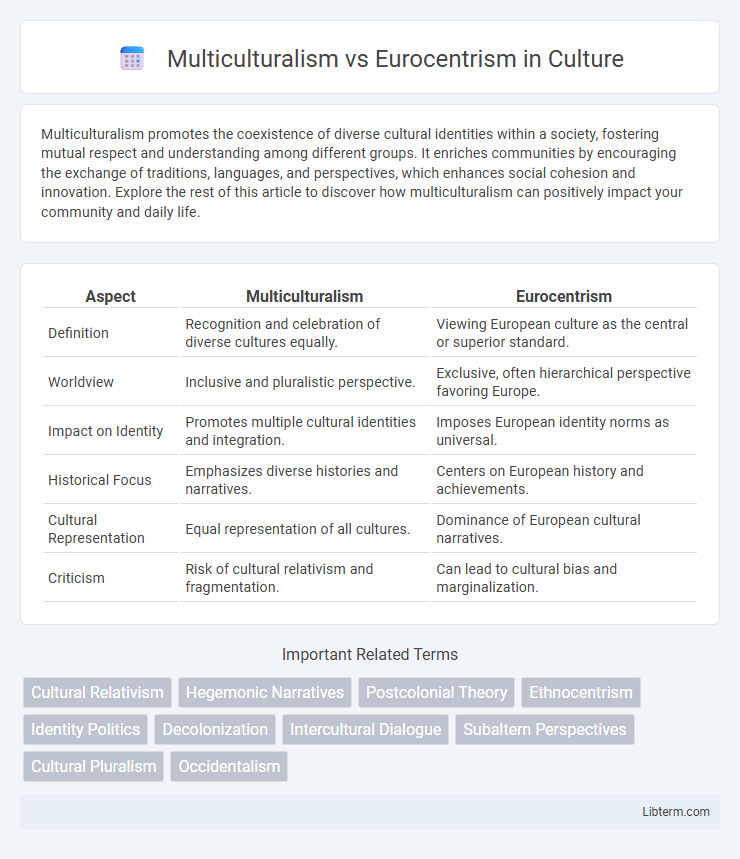
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Eurocentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recognition and celebration of diverse cultures equally. | Viewing European culture as the central or superior standard. |
| Worldview | Inclusive and pluralistic perspective. | Exclusive, often hierarchical perspective favoring Europe. |
| Impact on Identity | Promotes multiple cultural identities and integration. | Imposes European identity norms as universal. |
| Historical Focus | Emphasizes diverse histories and narratives. | Centers on European history and achievements. |
| Cultural Representation | Equal representation of all cultures. | Dominance of European cultural narratives. |
| Criticism | Risk of cultural relativism and fragmentation. | Can lead to cultural bias and marginalization. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: A Global Perspective
Multiculturalism promotes the recognition and celebration of diverse cultural identities, emphasizing inclusivity and equal representation across ethnic, linguistic, and religious groups worldwide. It challenges Eurocentrism by critiquing the dominance of European cultural norms as universal standards, advocating for a more pluralistic and equitable global narrative. This global perspective fosters cross-cultural dialogue, enabling societies to appreciate varied worldviews and diminish systemic biases rooted in colonial histories.
Defining Eurocentrism: Historical Roots and Influence
Eurocentrism originated during the European Renaissance and Age of Exploration, positioning European culture and history as the universal standard for global narratives. This worldview emphasizes European values, achievements, and perspectives while marginalizing non-European cultures and histories. The influence of Eurocentrism persists in education, media, and politics, shaping global perceptions and reinforcing cultural hierarchies that challenge multicultural approaches.
Key Differences Between Multiculturalism and Eurocentrism
Multiculturalism promotes the inclusion and equal representation of diverse cultures, emphasizing cultural pluralism and respect for multiple worldviews. Eurocentrism centers on European cultural norms and values, often marginalizing non-European perspectives and imposing Western standards as universal. The key differences lie in multiculturalism's embrace of cultural diversity versus Eurocentrism's dominance of European-centric narratives and historical interpretations.
The Impact of Eurocentrism on Education and Knowledge
Eurocentrism in education often prioritizes Western perspectives, marginalizing diverse cultural viewpoints and knowledge systems. This bias can limit critical thinking by presenting Eurocentric history, literature, and sciences as universal truths, thereby inhibiting a broader understanding of global diversity. Challenging Eurocentric curricula by incorporating multicultural content fosters inclusivity and enhances students' cultural competence and empathy.
Multiculturalism in Modern Societies: Benefits and Challenges
Multiculturalism in modern societies fosters cultural diversity, promotes social inclusion, and enhances mutual respect among different ethnic groups, contributing to social cohesion and economic innovation. It encourages the preservation of cultural identities while enabling individuals to participate fully in civic life, leading to enriched educational environments and diverse workplaces. Challenges include managing cultural conflicts, addressing systemic inequalities, and overcoming resistance from Eurocentric perspectives that often prioritize Western values and histories.
Representation in Media: Multiculturalism vs. Eurocentrism
Representation in media shaped by multiculturalism embraces diverse cultural narratives, promoting inclusivity and reflecting global societies more accurately. Eurocentrism in media, however, often prioritizes Western perspectives, marginalizing or stereotyping non-European cultures and limiting cross-cultural understanding. This contrast influences public perception by either enriching cultural awareness or reinforcing narrow, dominant viewpoints.
Policy Approaches: Embracing Diversity or Upholding Eurocentric Norms
Policy approaches to multiculturalism emphasize inclusive frameworks that recognize and celebrate diverse cultural identities, promoting equitable representation and social cohesion. In contrast, Eurocentric policies often prioritize Western cultural norms and values, marginalizing non-European perspectives and limiting cultural pluralism. Effective diversity policies integrate multicultural perspectives in education, governance, and media, challenging the dominance of Eurocentric paradigms to foster genuine intercultural understanding.
The Role of Multiculturalism in Social Integration
Multiculturalism fosters social integration by promoting mutual respect and understanding among diverse ethnic groups, enabling inclusive participation in societal institutions. It actively challenges Eurocentric narratives that often marginalize non-Western cultures, thereby creating a more equitable social framework. Policies centered on multiculturalism support cultural pluralism, which strengthens community cohesion and reduces social fragmentation.
Critiques and Controversies Surrounding Eurocentrism
Eurocentrism faces critiques for marginalizing non-European histories and perspectives, fostering a biased worldview that elevates Western norms as universal standards. Critics argue this perspective perpetuates cultural dominance and undermines the plurality of global experiences, often neglecting contributions from African, Asian, and Indigenous civilizations. Controversies highlight how Eurocentric frameworks influence education, media, and policy, prompting calls for more inclusive, multicultural approaches that recognize diverse epistemologies and cultural identities.
Future Directions: Moving Beyond Eurocentrism to Inclusive Multiculturalism
Future directions emphasize shifting from Eurocentrism to inclusive multiculturalism by integrating diverse cultural perspectives into education, policy, and media representation. Embracing multiculturalism fosters global understanding, equity, and innovation through recognition of non-Western histories and knowledge systems. This paradigm shift challenges dominant narratives and promotes intercultural dialogue essential for sustainable social cohesion in an increasingly interconnected world.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com